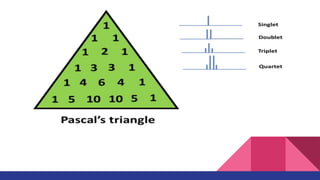
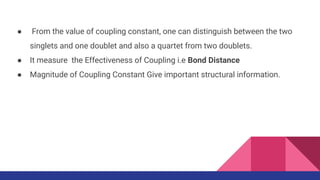
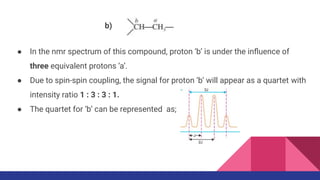
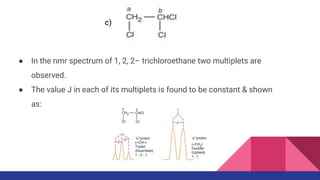
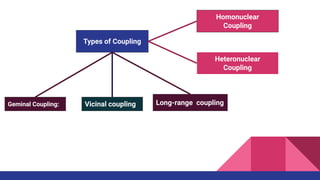
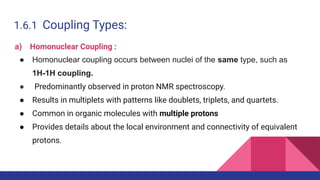
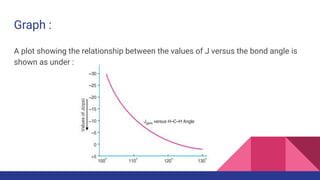
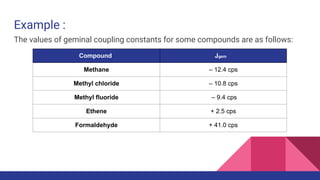
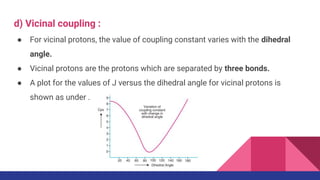
This document discusses spin-spin coupling in NMR spectroscopy. It describes how the magnetic moments of adjacent nuclei interact, resulting in the splitting of NMR signals into multiplets such as doublets and triplets. The number of peaks in a multiplet, known as the multiplicity, reflects the number of neighboring nuclei. The distance between peaks, called the coupling constant J, provides important structural information. Different types of coupling are discussed, including homonuclear, heteronuclear, geminal, vicinal, and long-range coupling. Examples and diagrams are provided to illustrate these concepts.