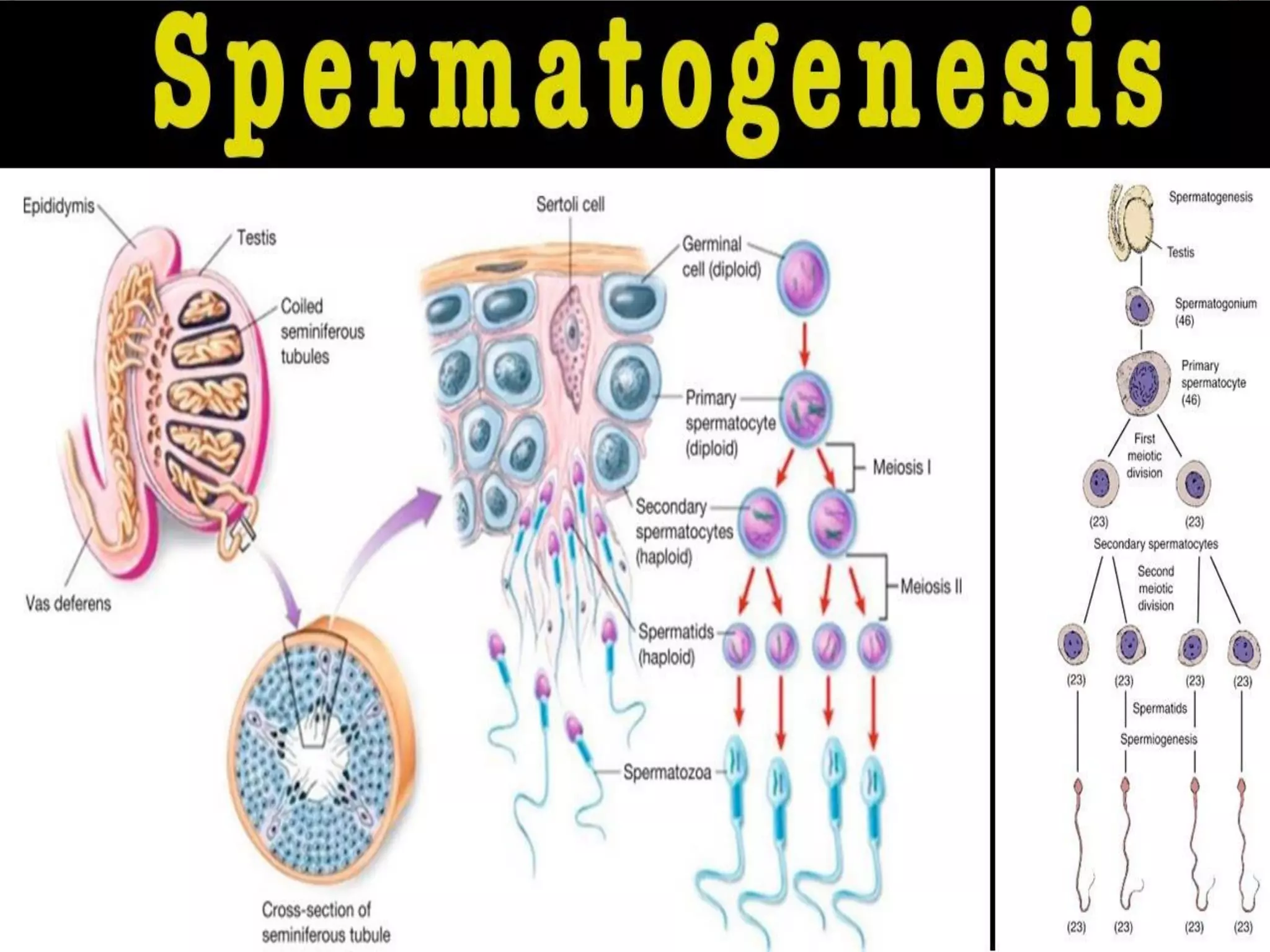
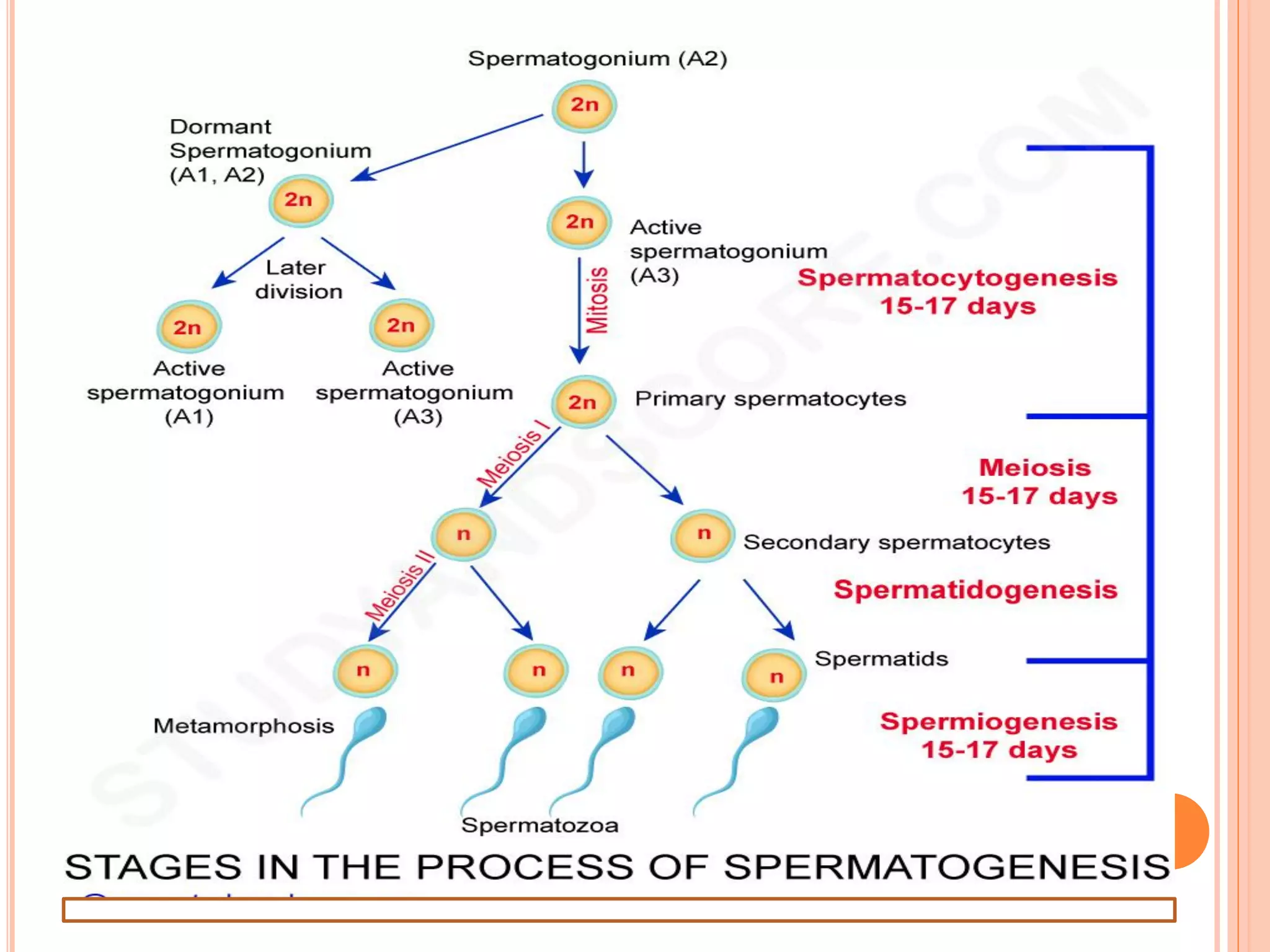
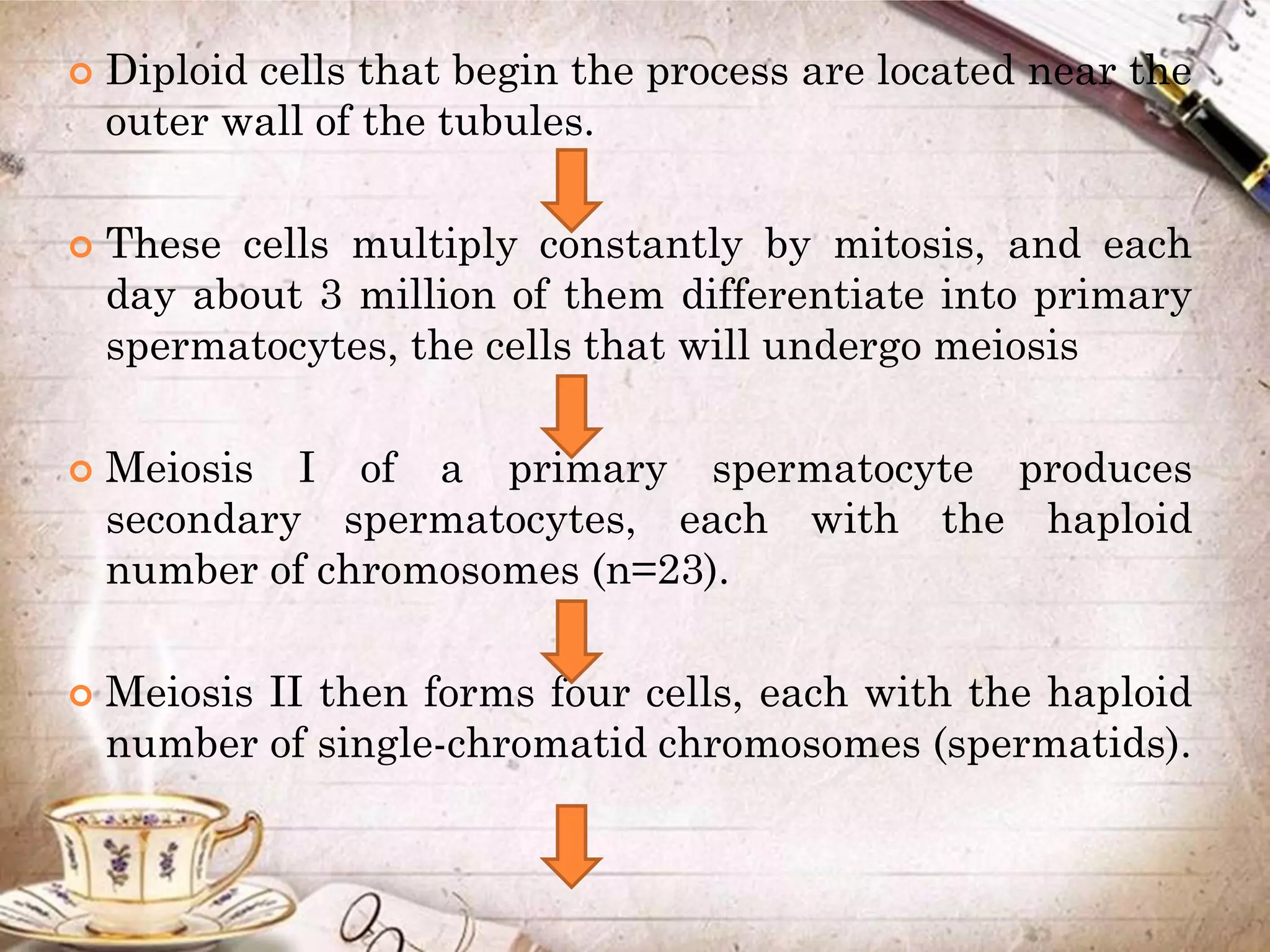
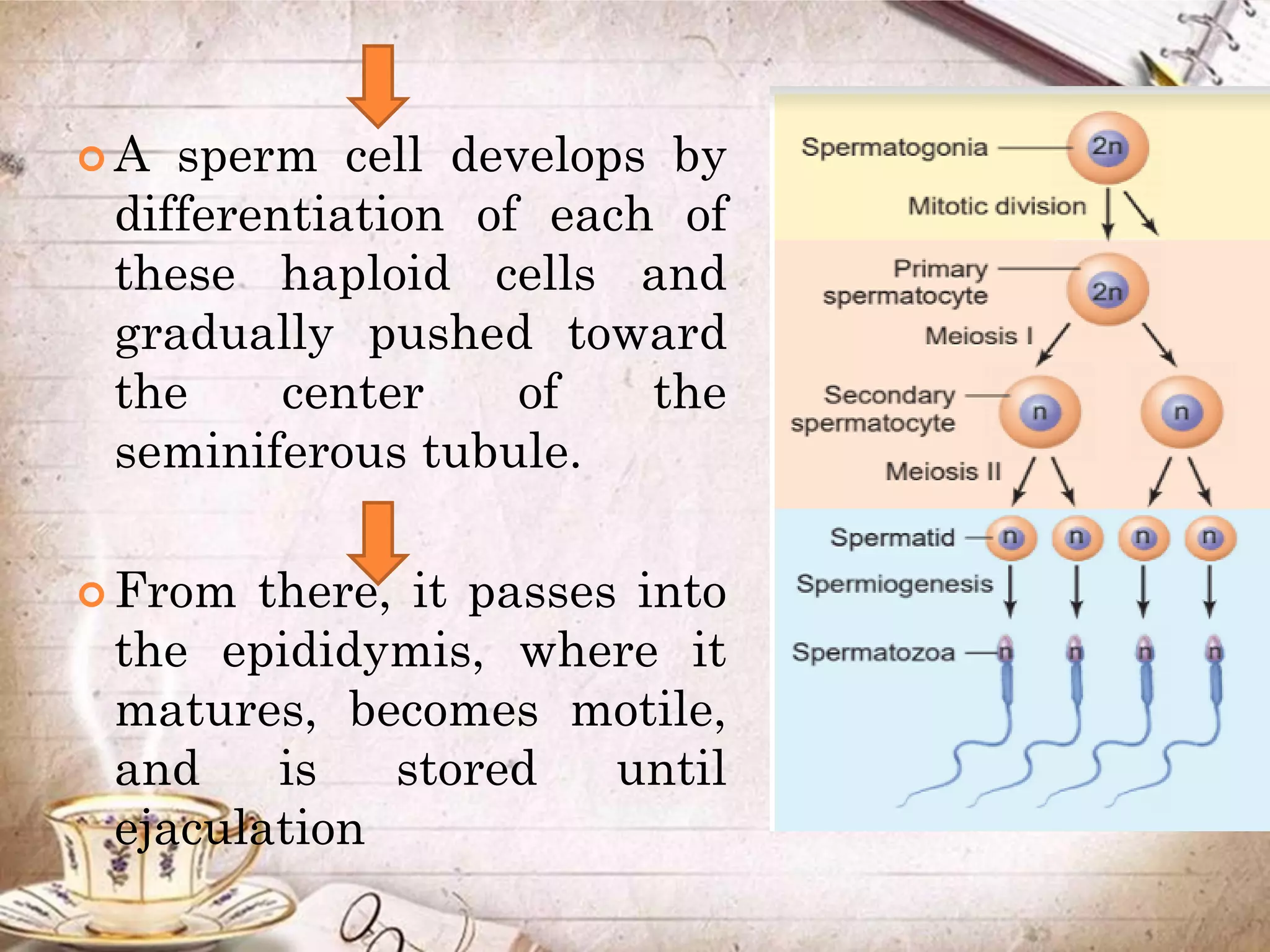
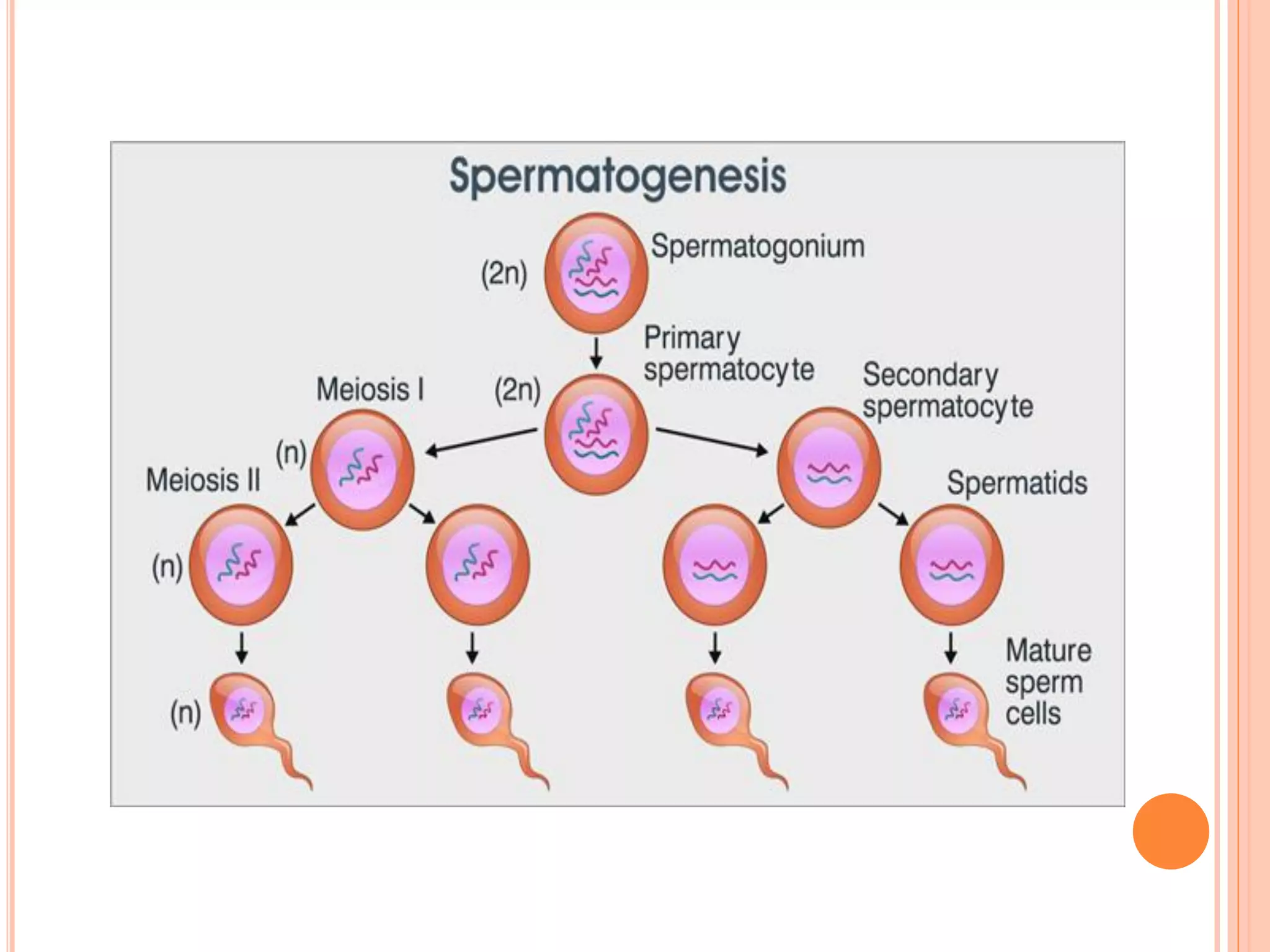
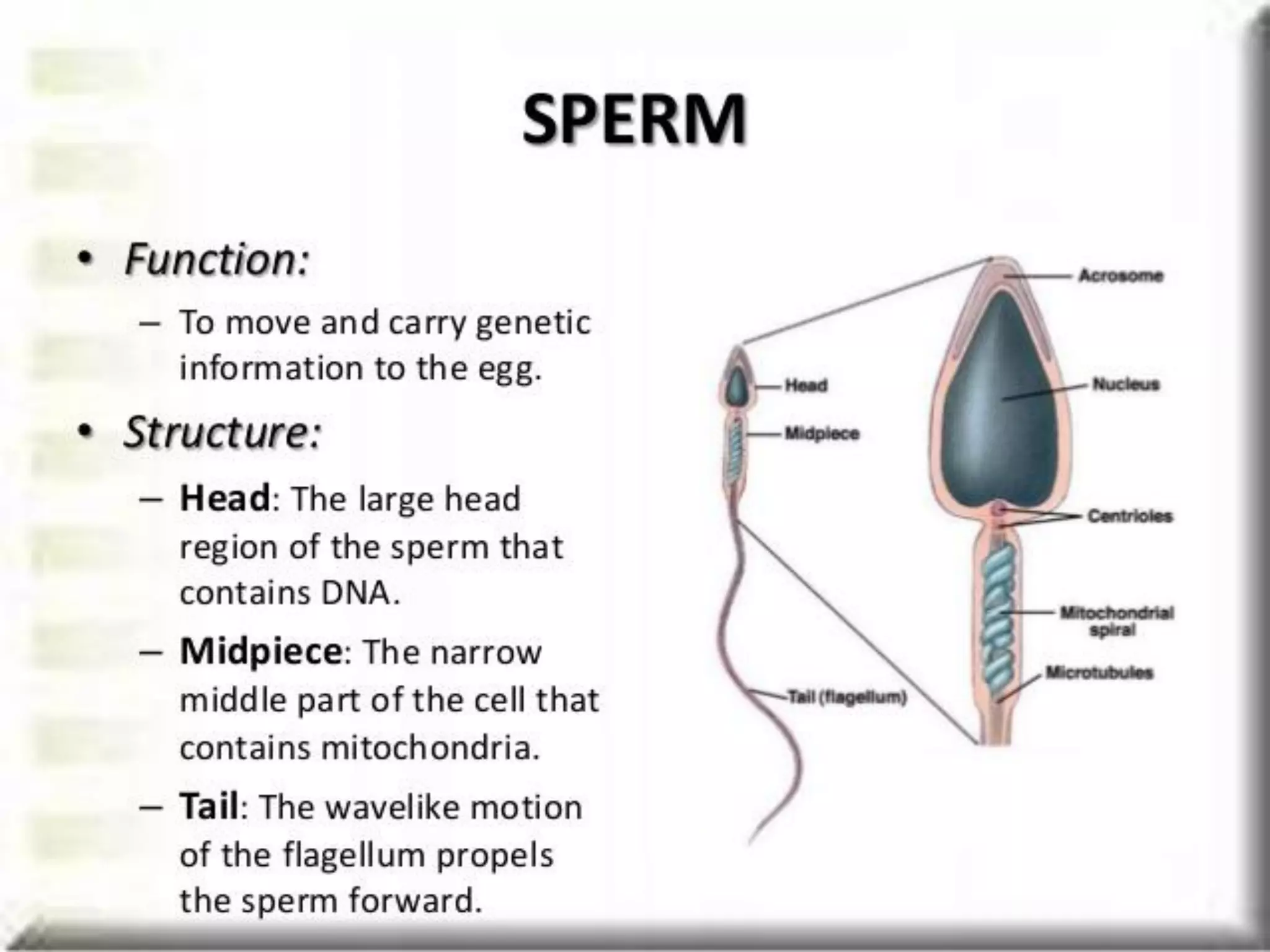
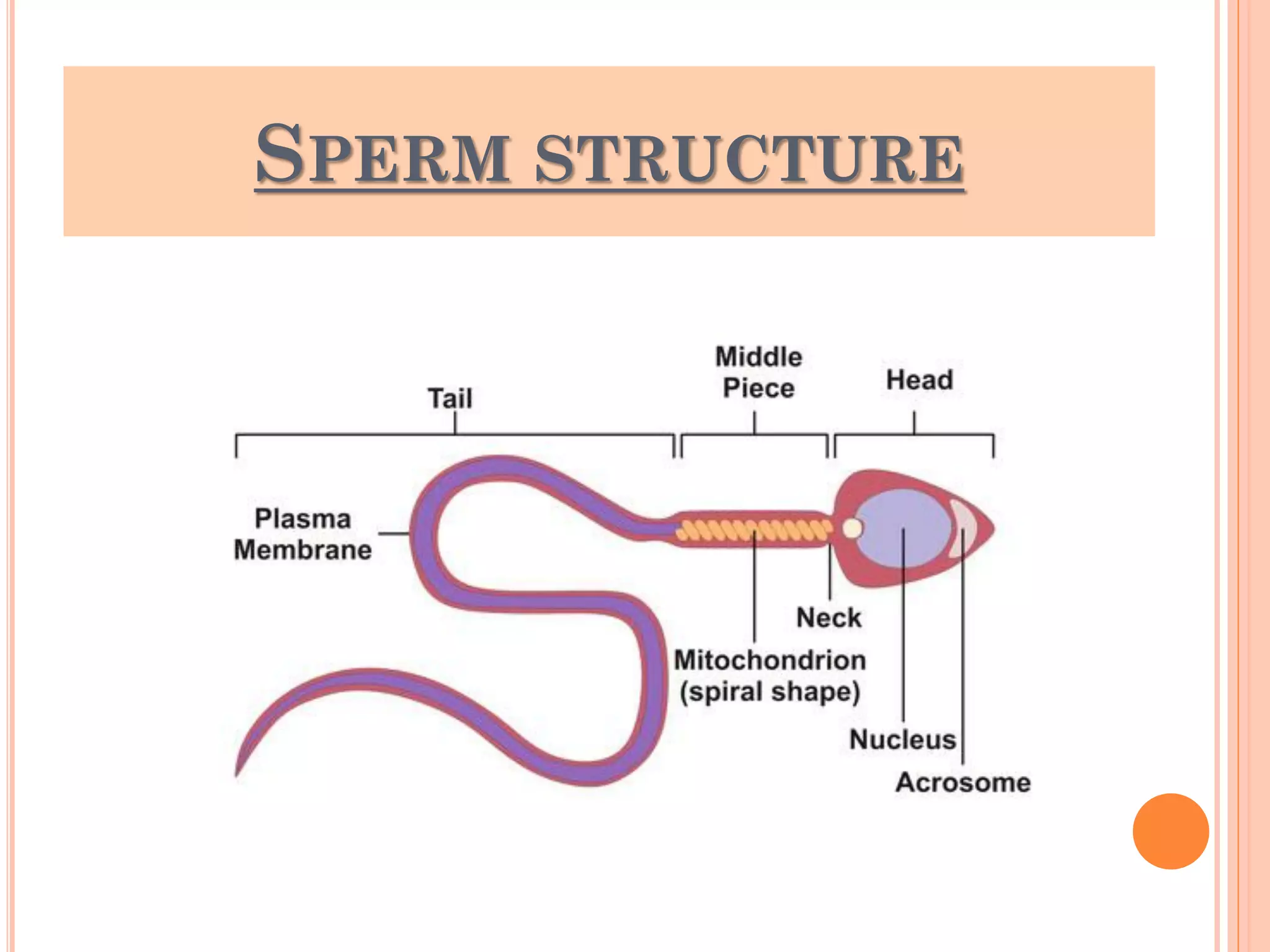
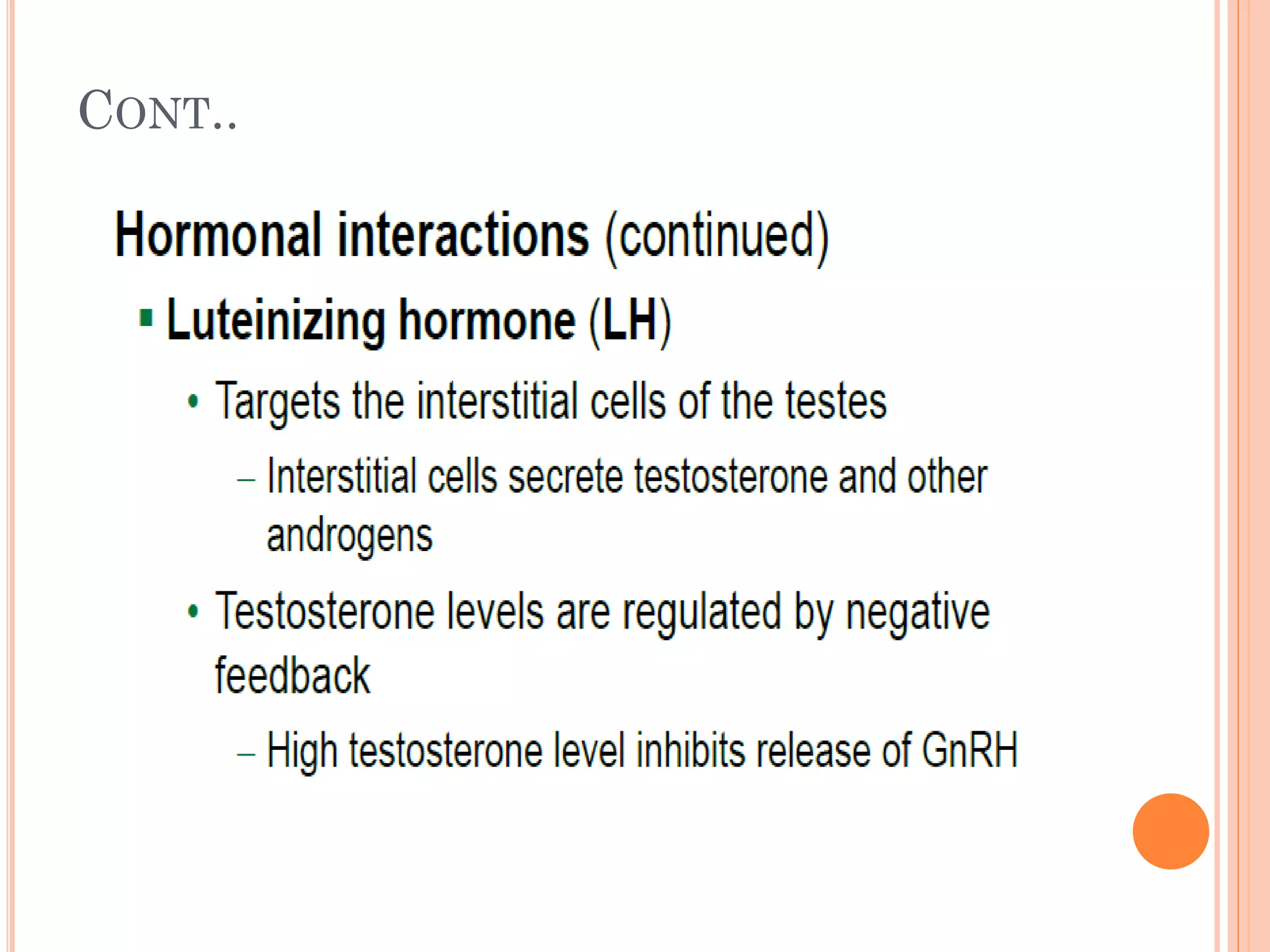
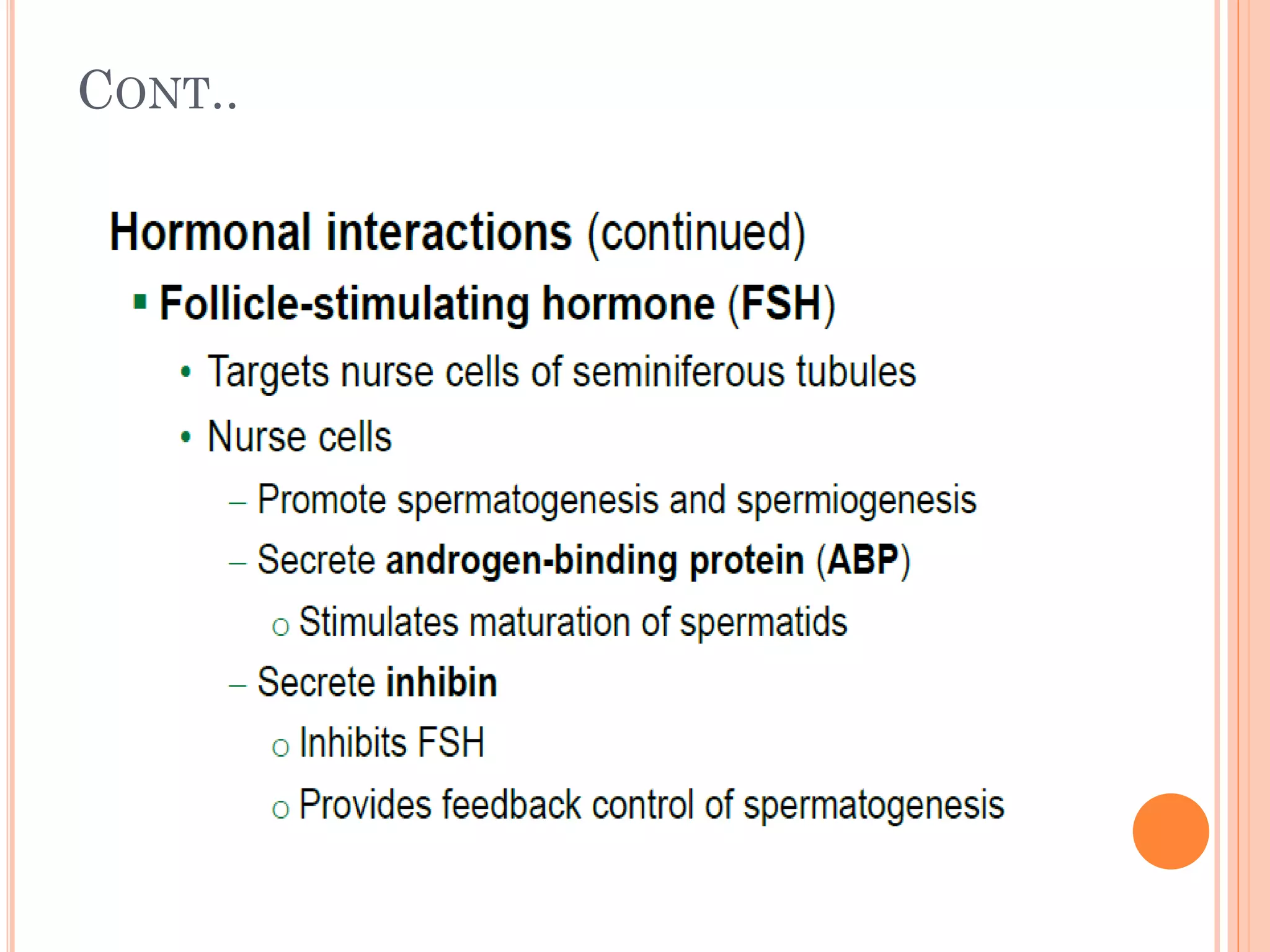
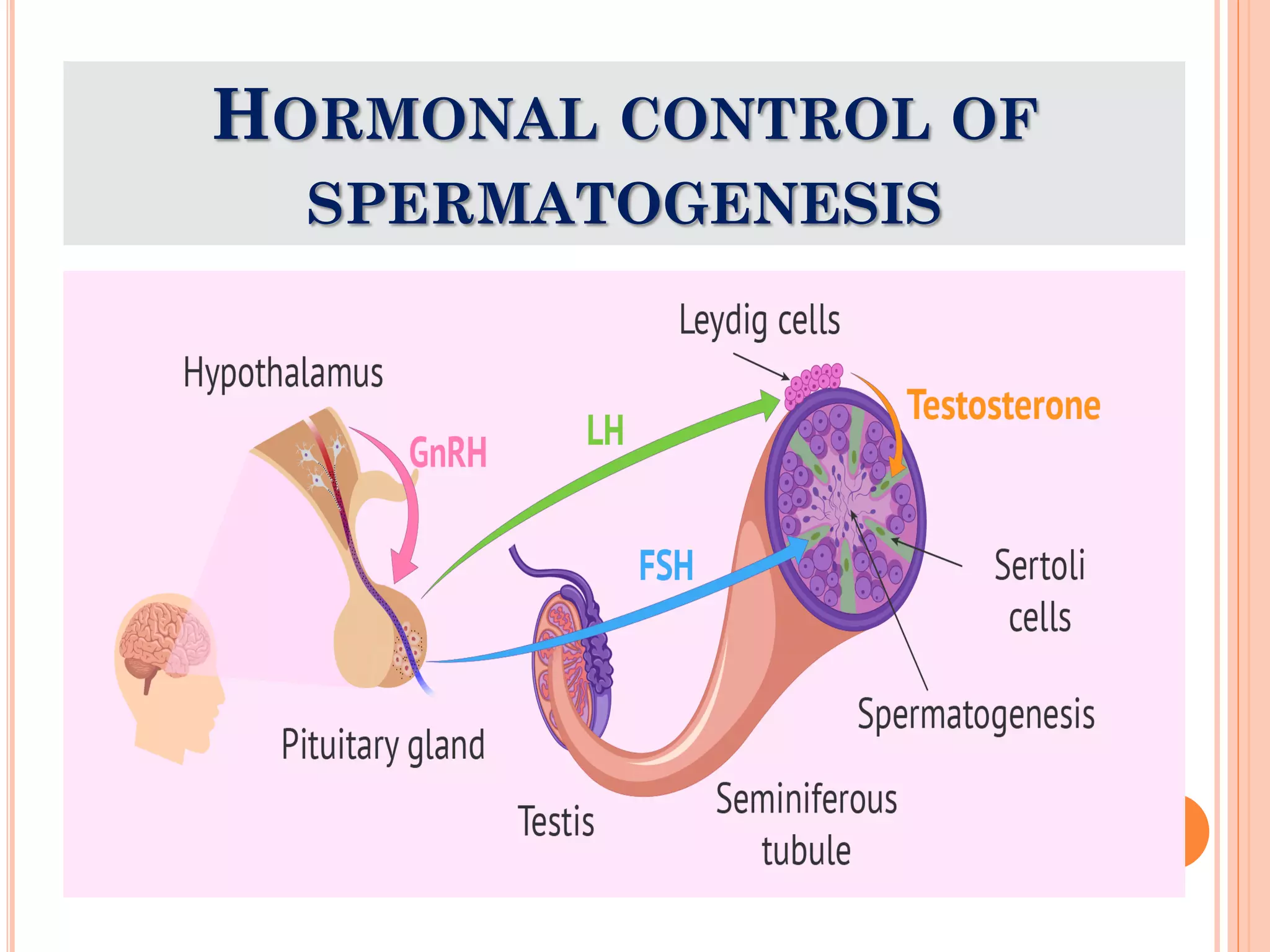
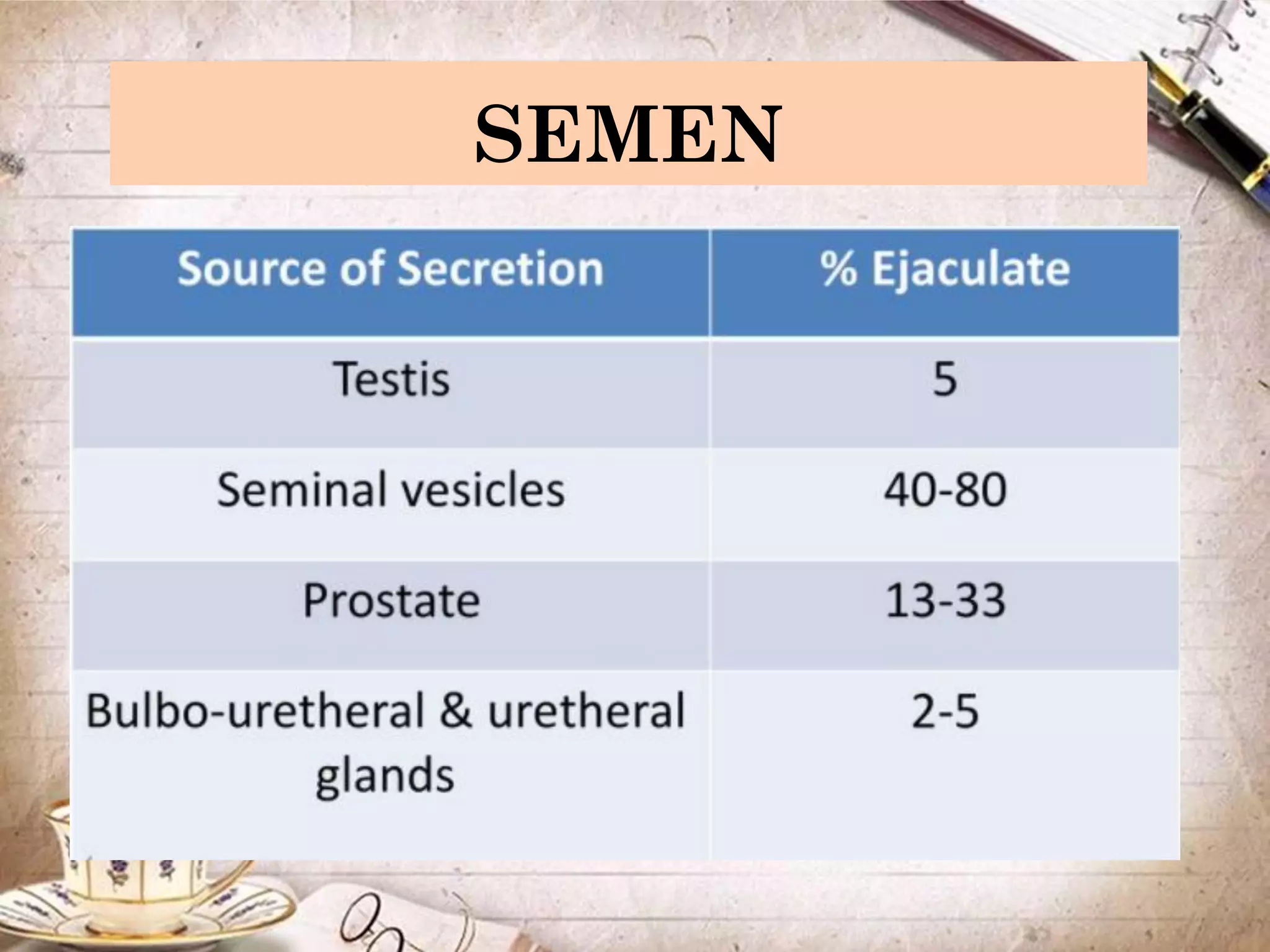
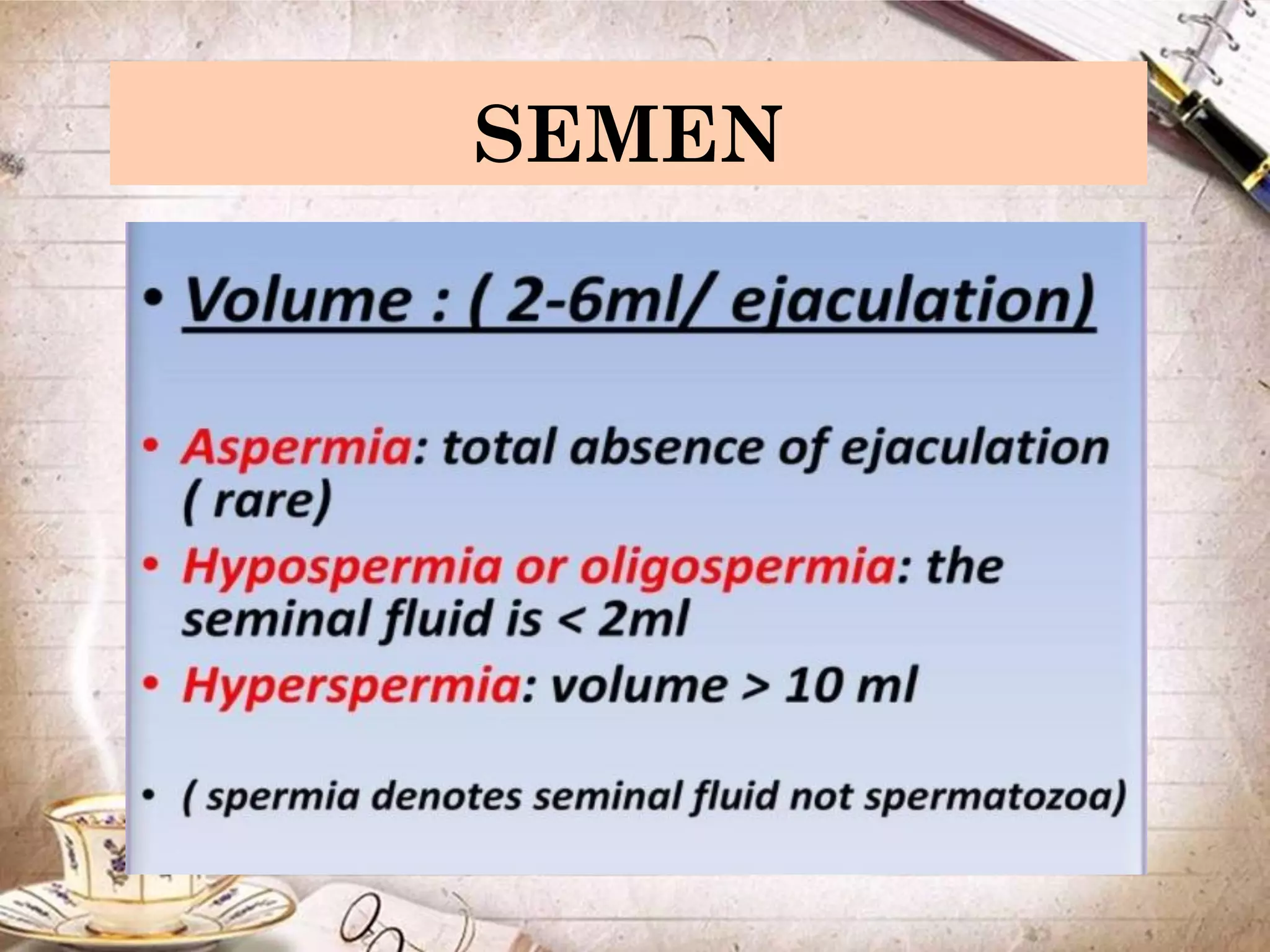
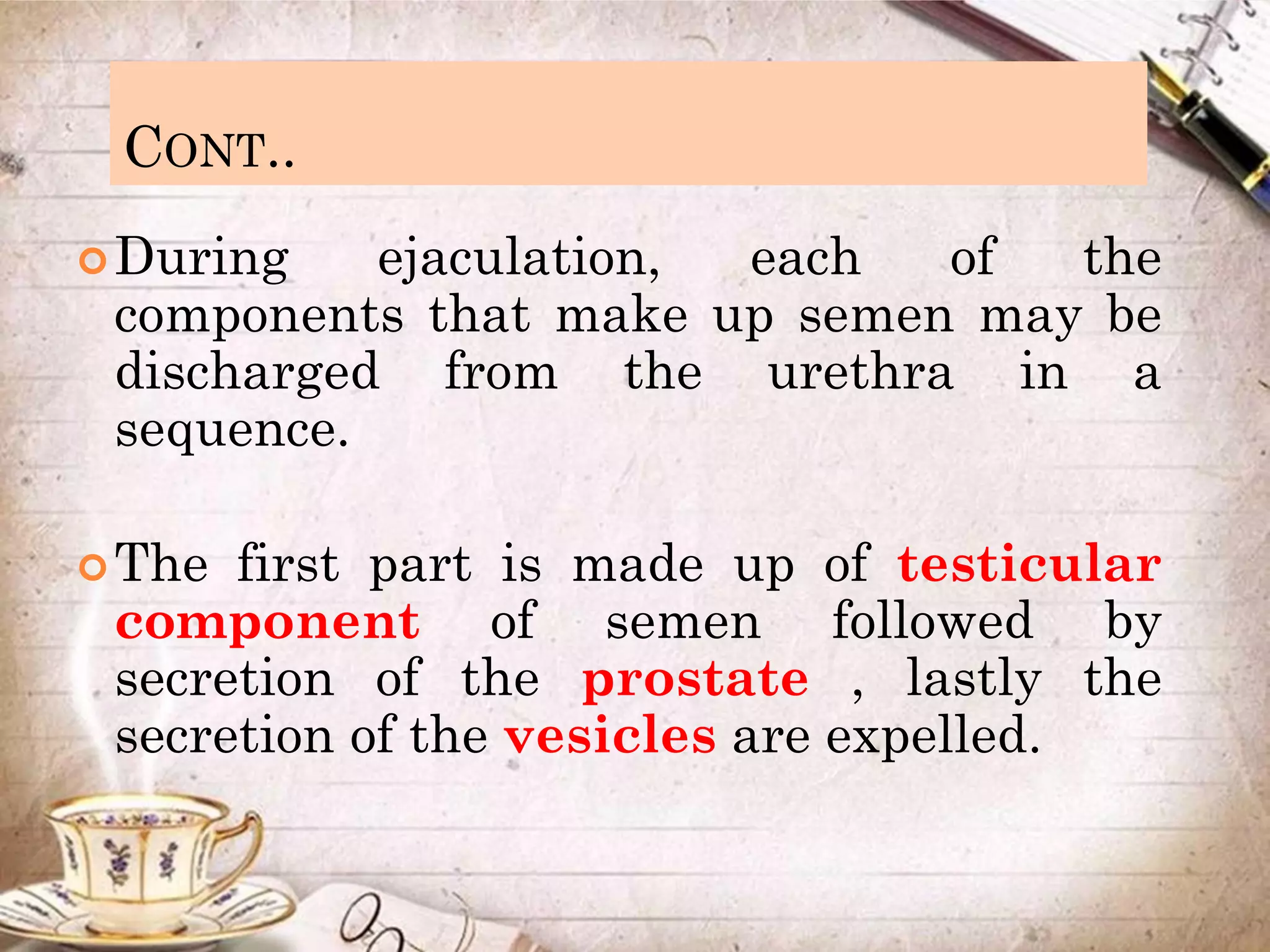
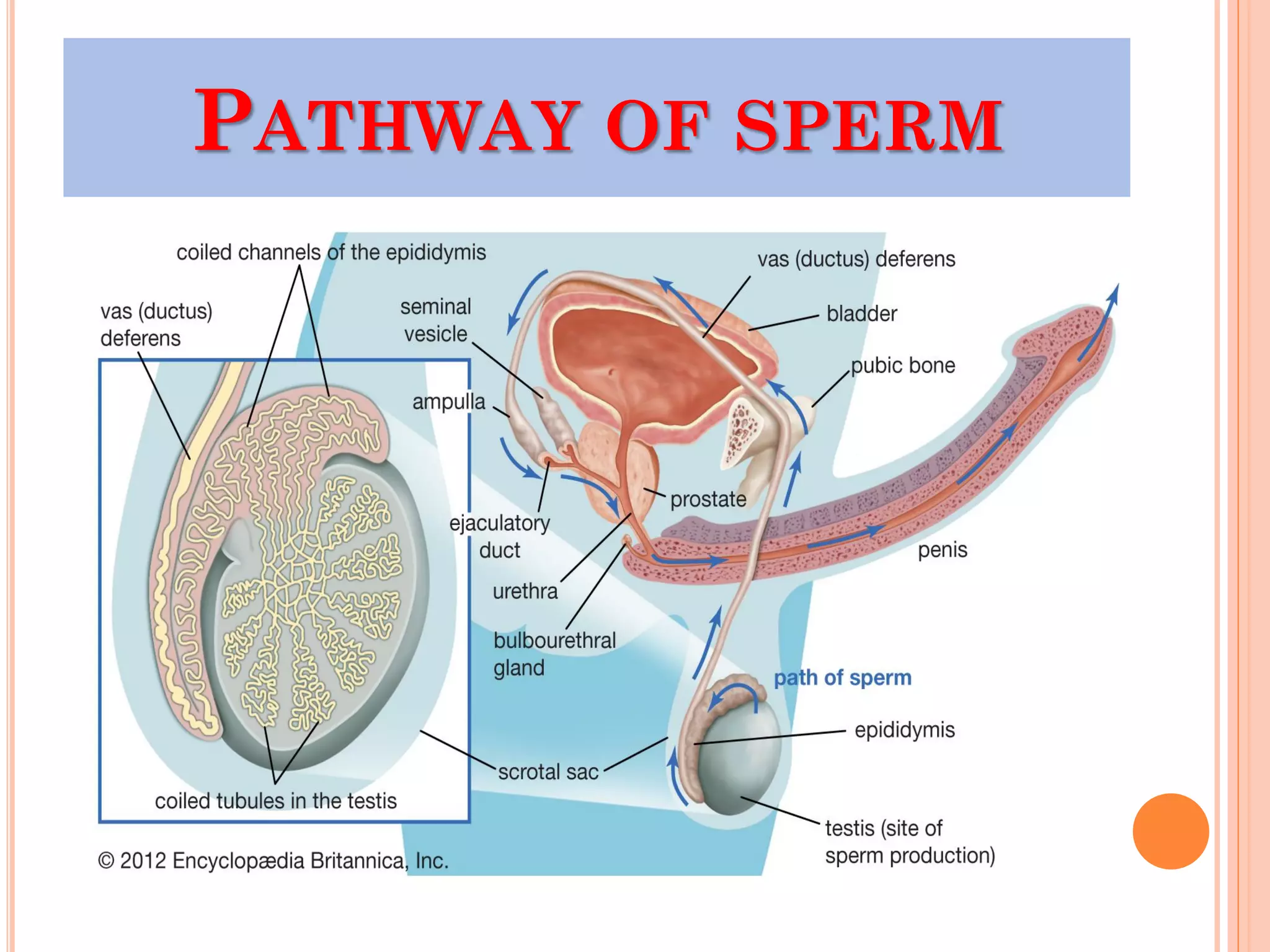
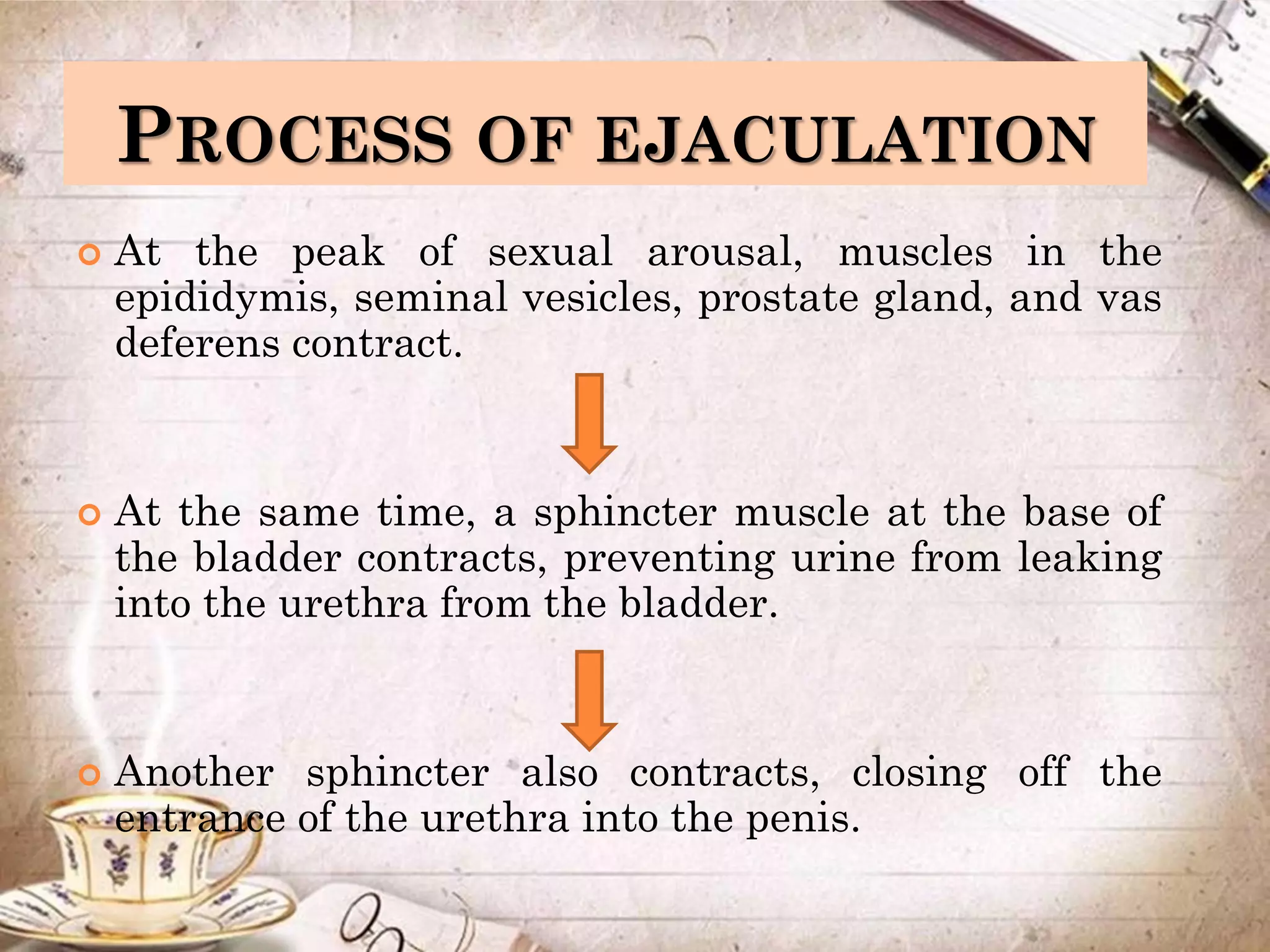
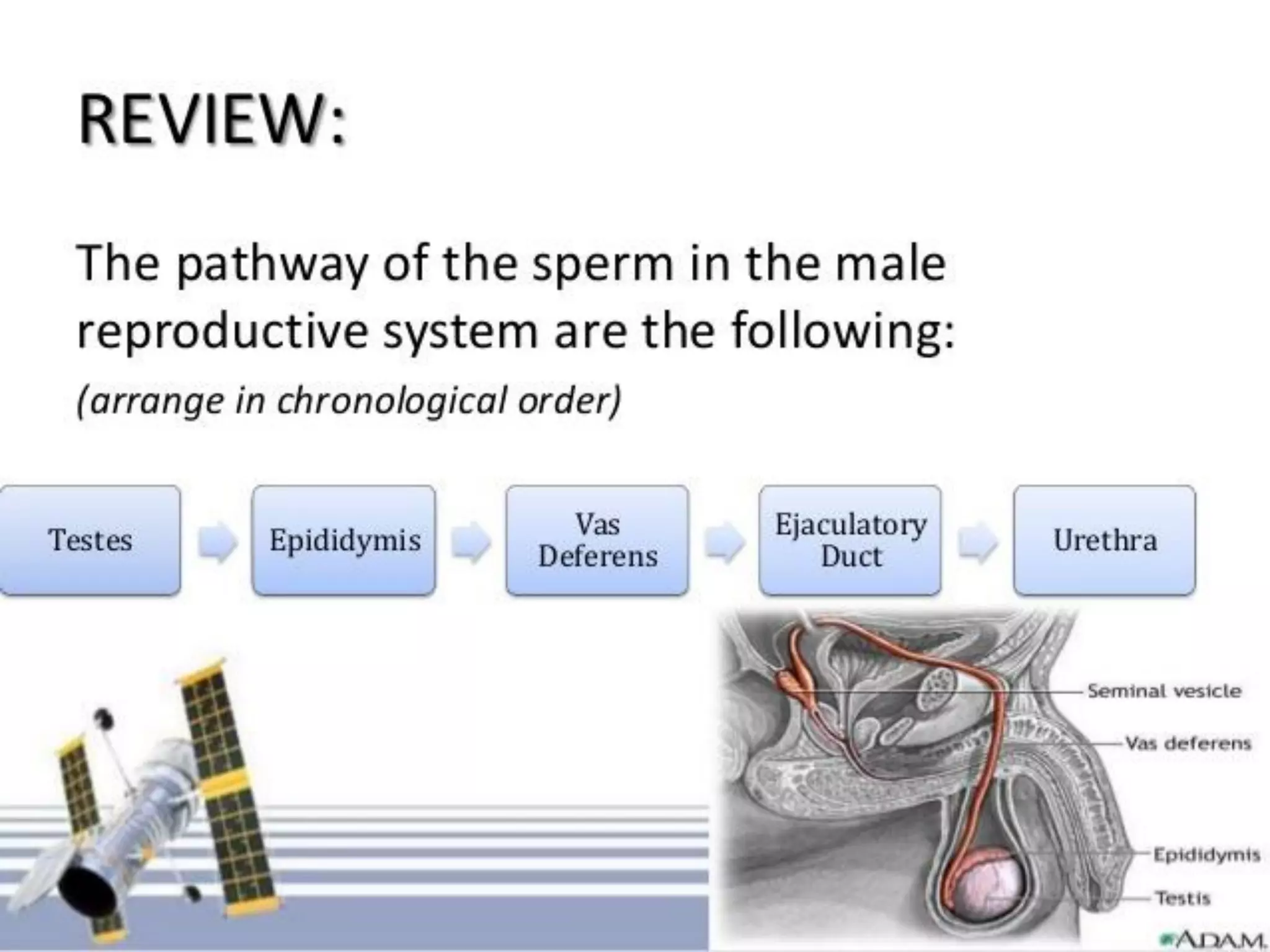
Spermatogenesis is the process by which sperm cells are formed in the seminiferous tubules of the testes. It begins with diploid cells near the tubule wall multiplying through mitosis. These cells then undergo meiosis to form haploid secondary spermatocytes and eventually haploid spermatids. Each spermatid then develops into a mature sperm cell which is gradually pushed toward the center of the tubule and stored in the epididymis until ejaculation.