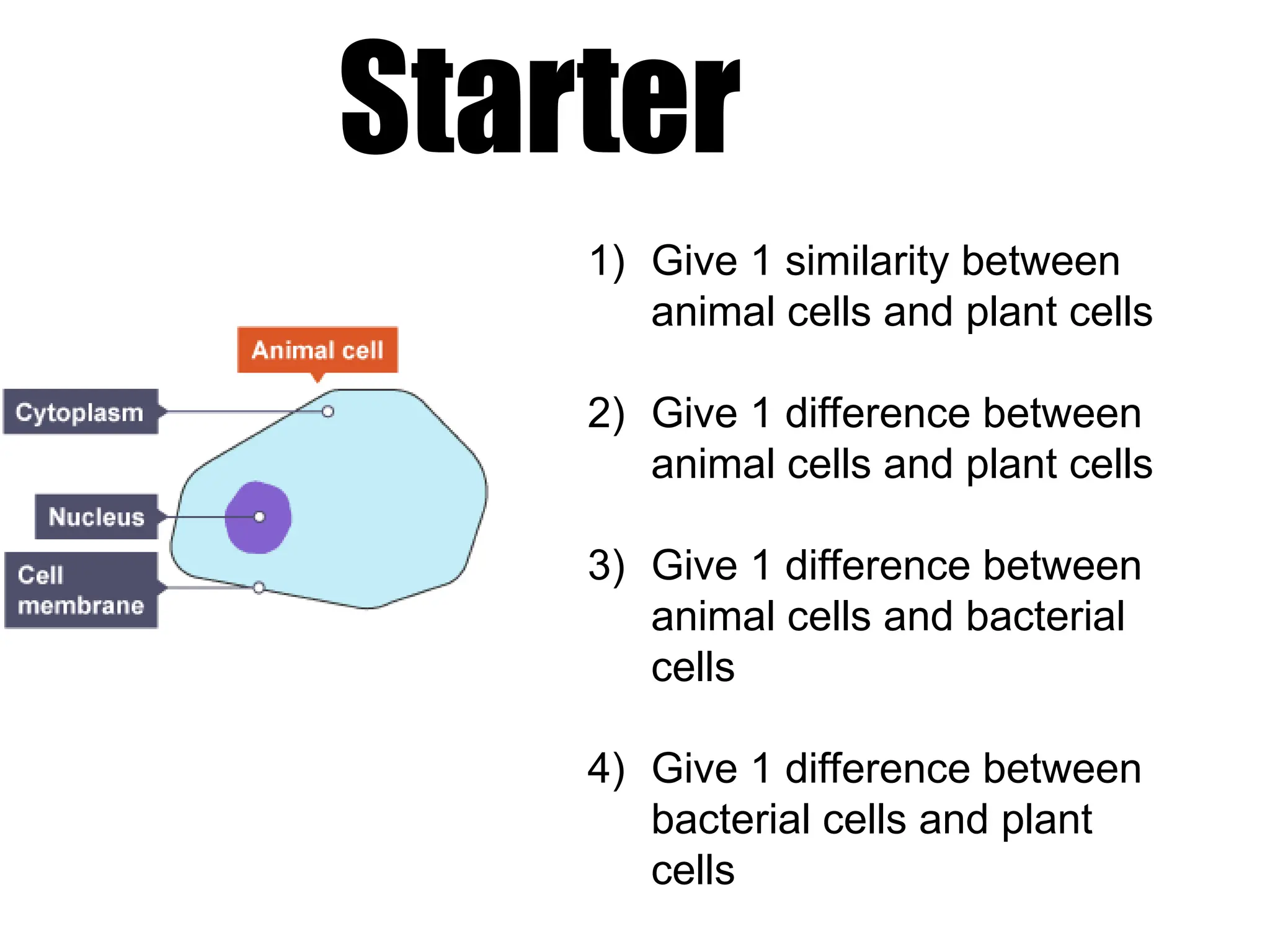
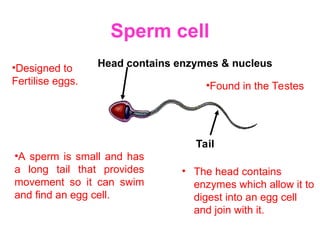
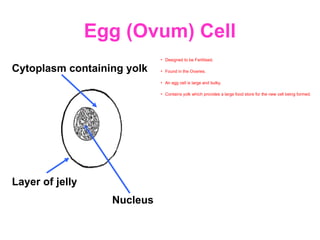
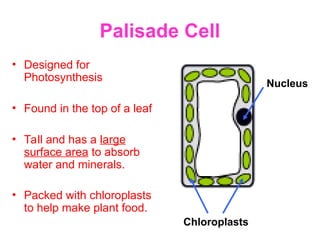
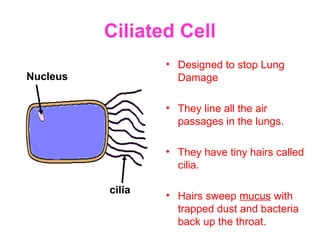
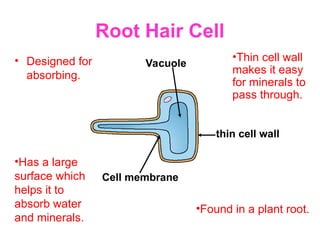
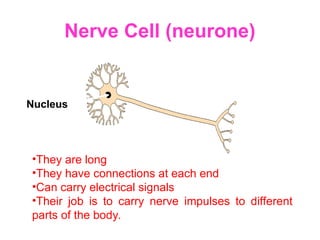
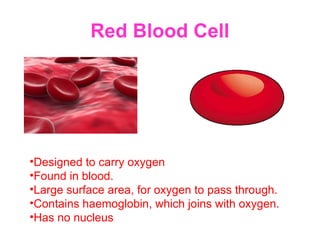
The document discusses the similarities and differences between animal, plant, and bacterial cells, emphasizing cell specialization and various cell types for specific functions. It outlines examples of specialized cells like sperm, egg, palisade, ciliated, root hair, nerve, and red blood cells, detailing their unique features and roles. Additionally, it includes questions to enhance understanding of the material presented.