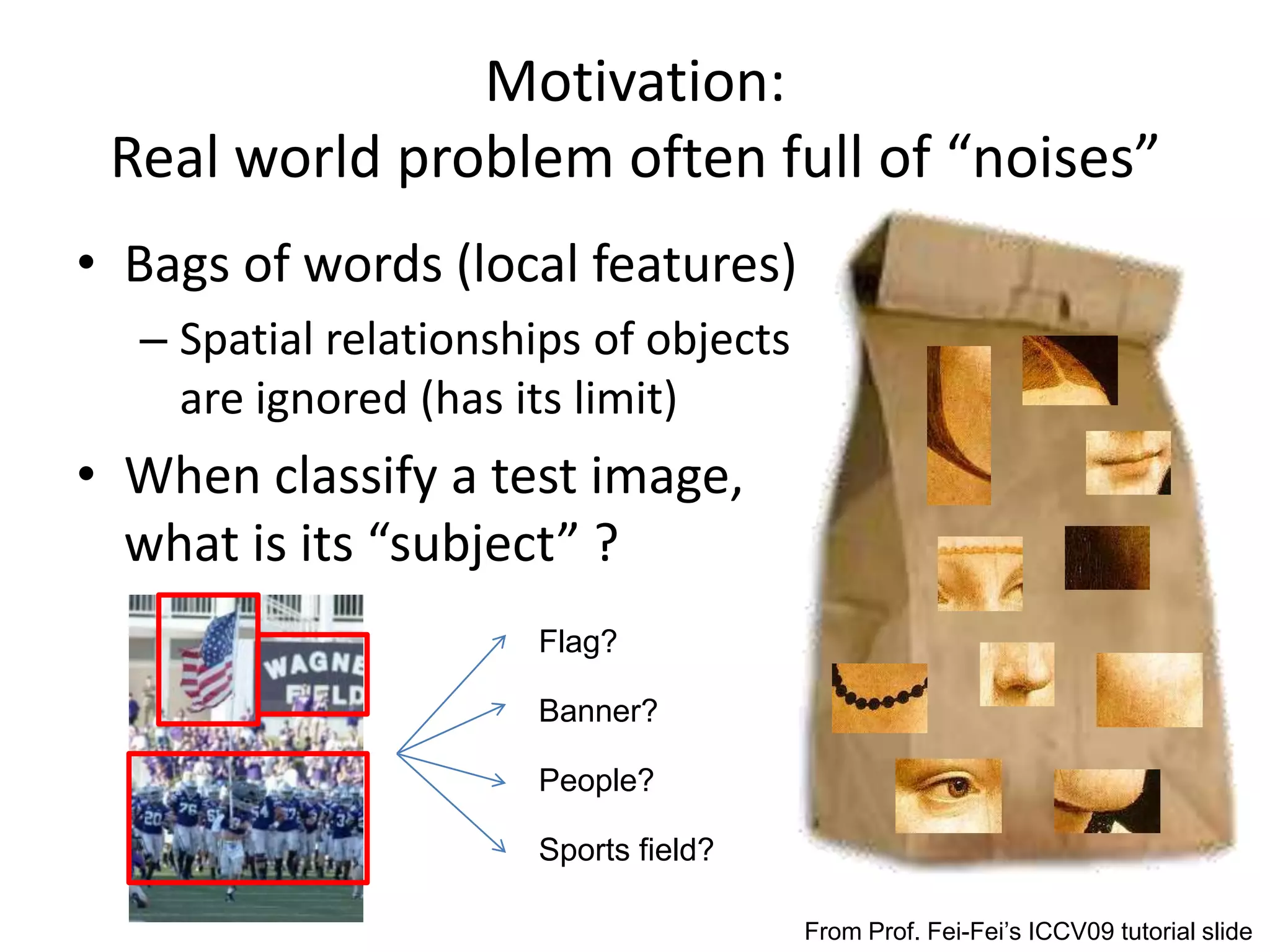
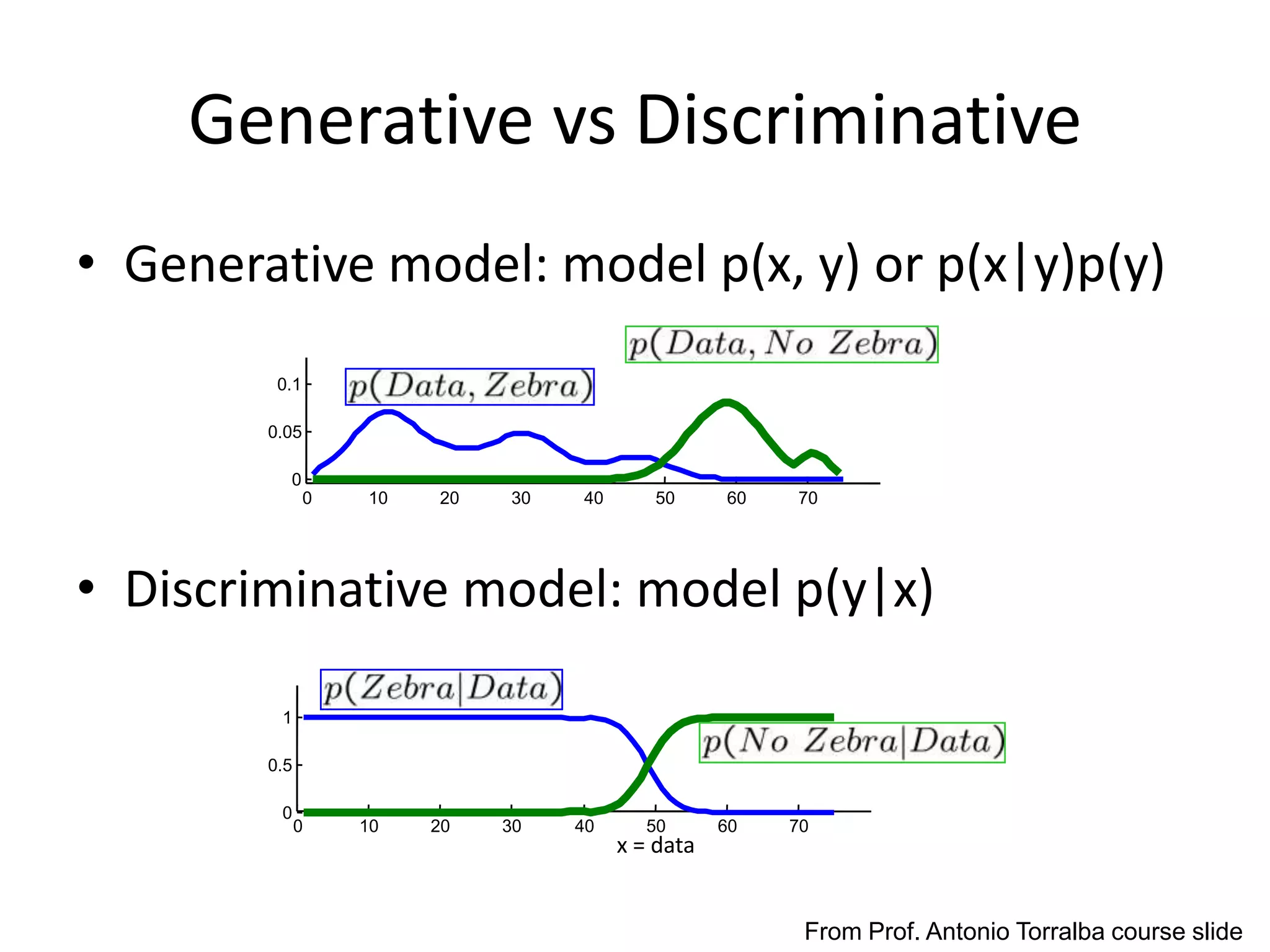
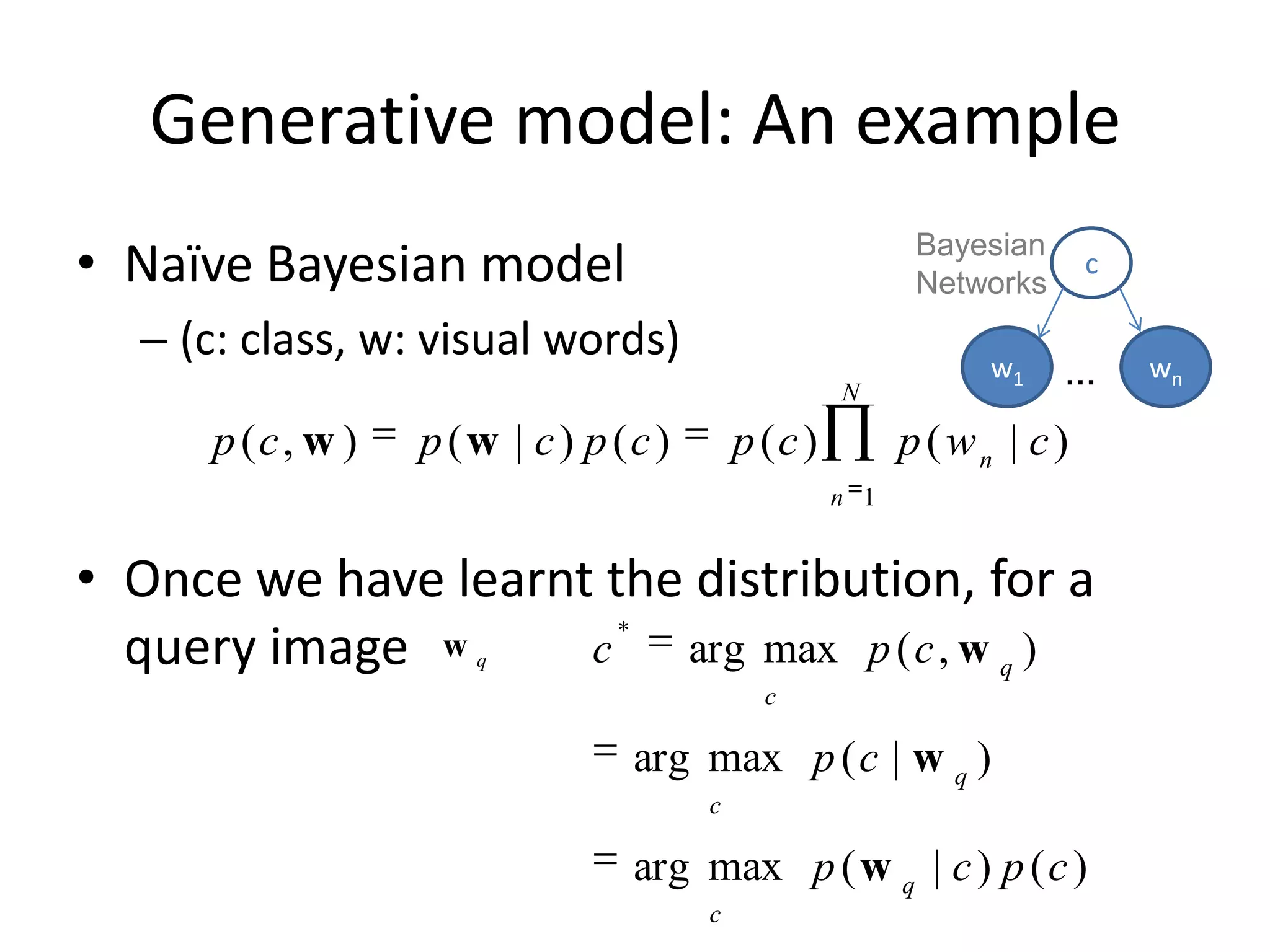
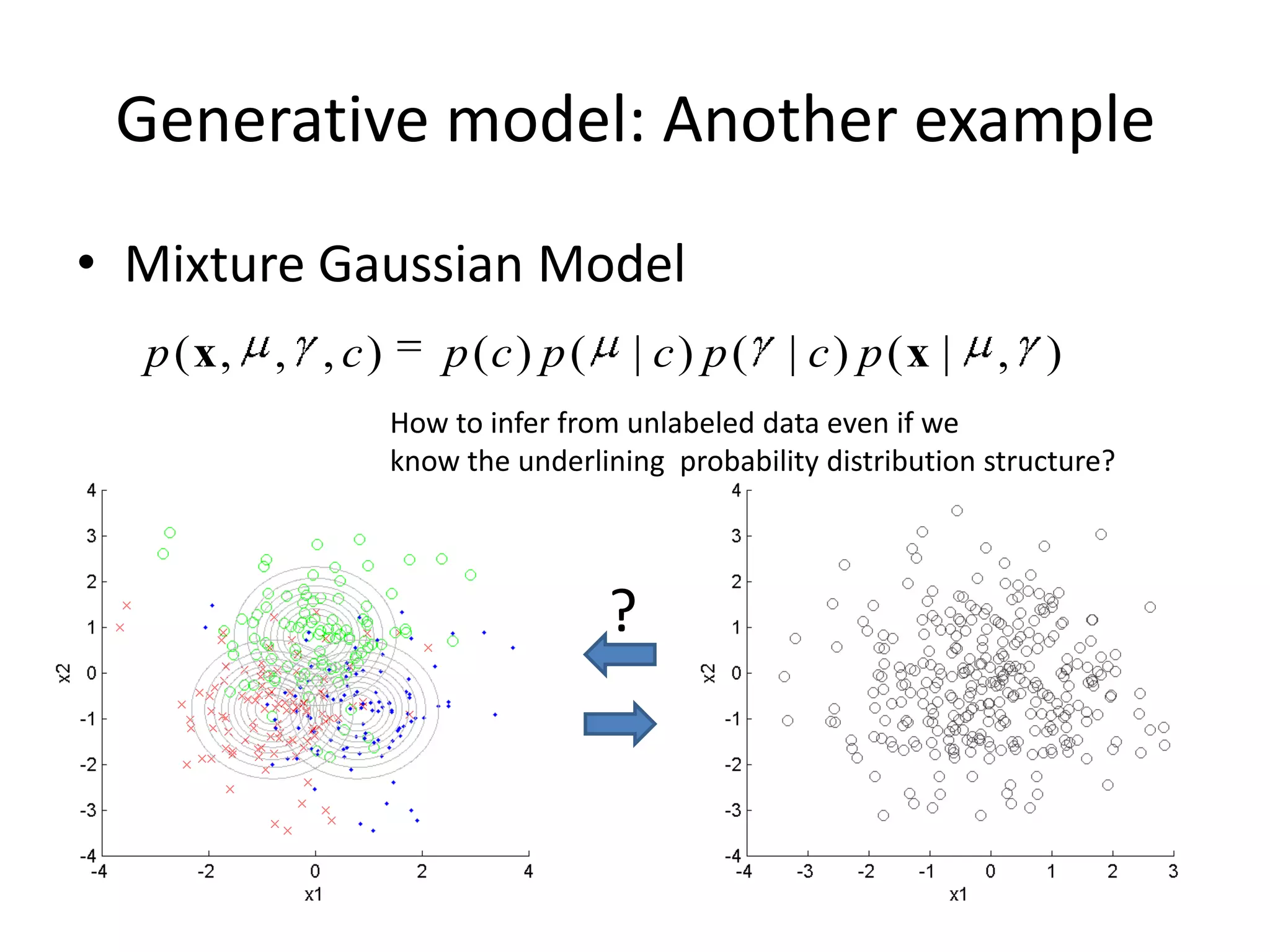
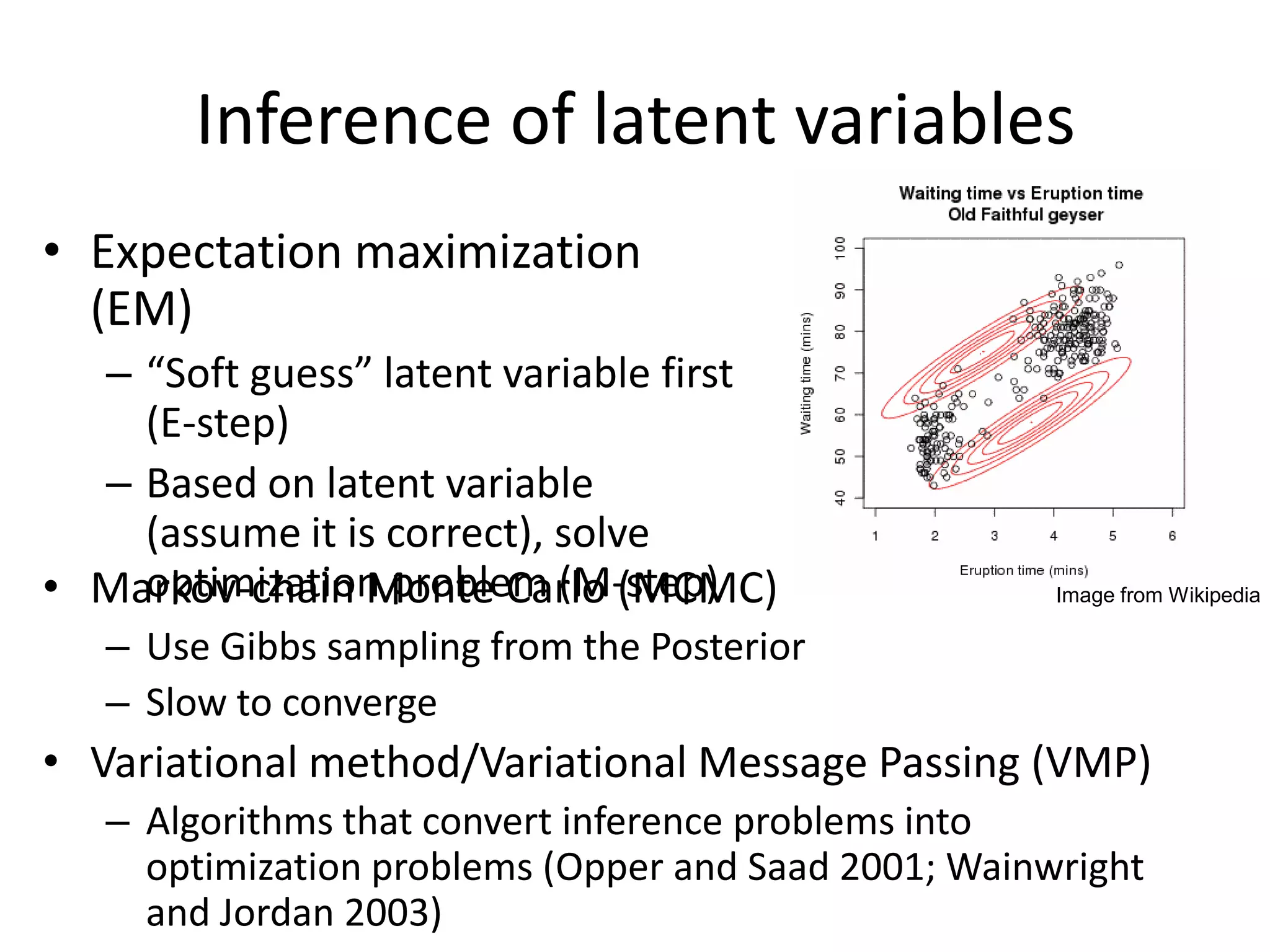
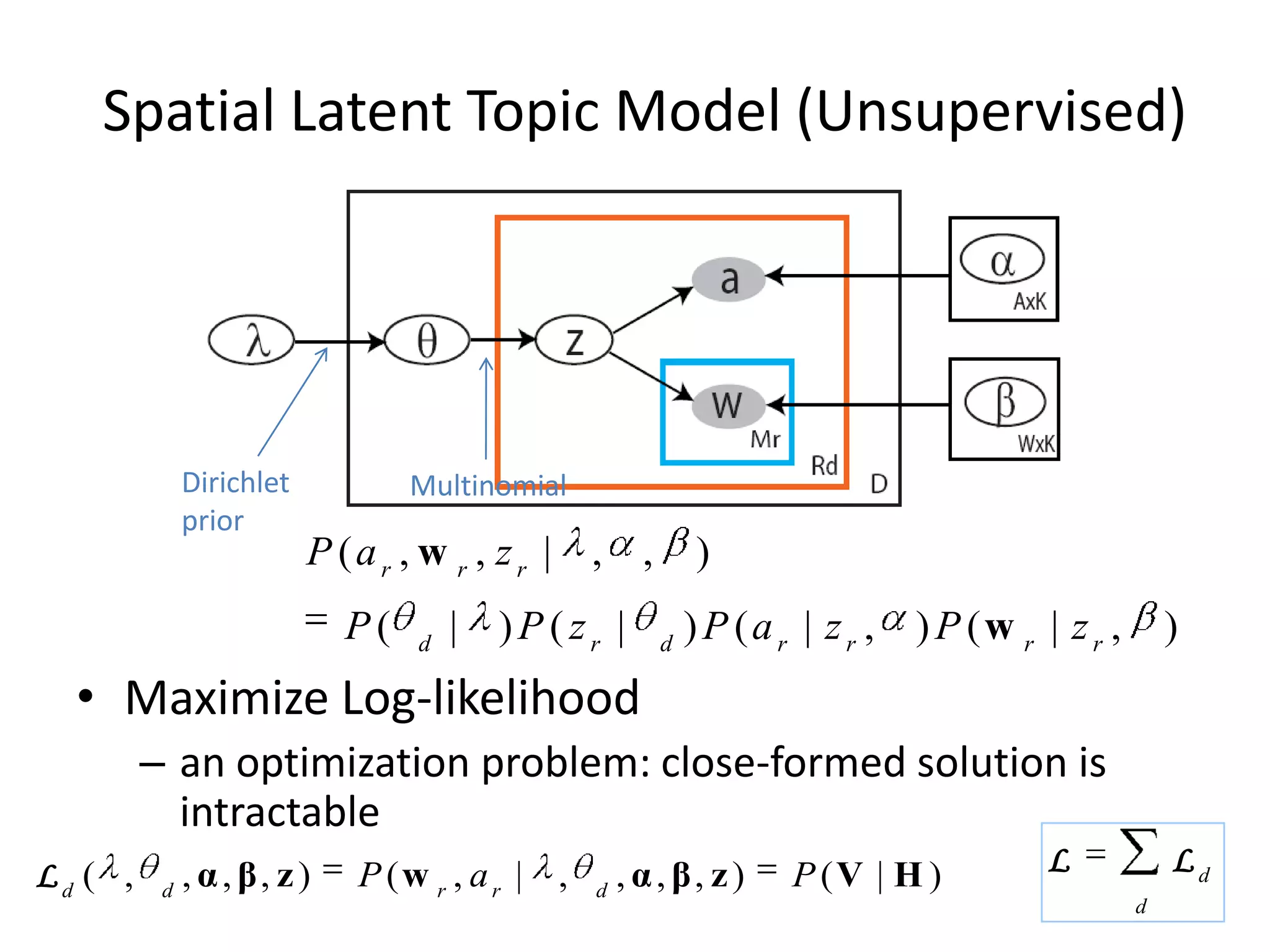
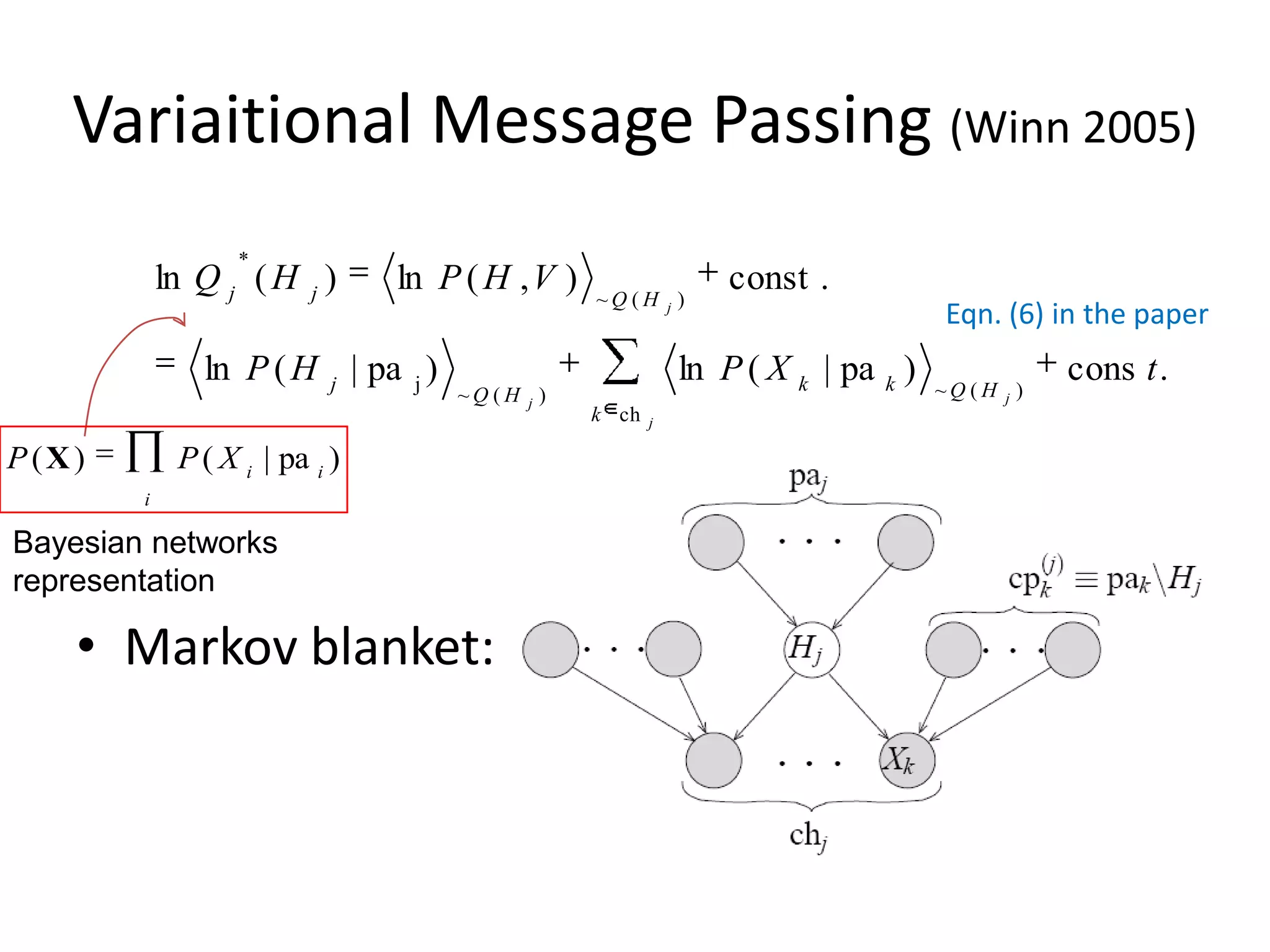
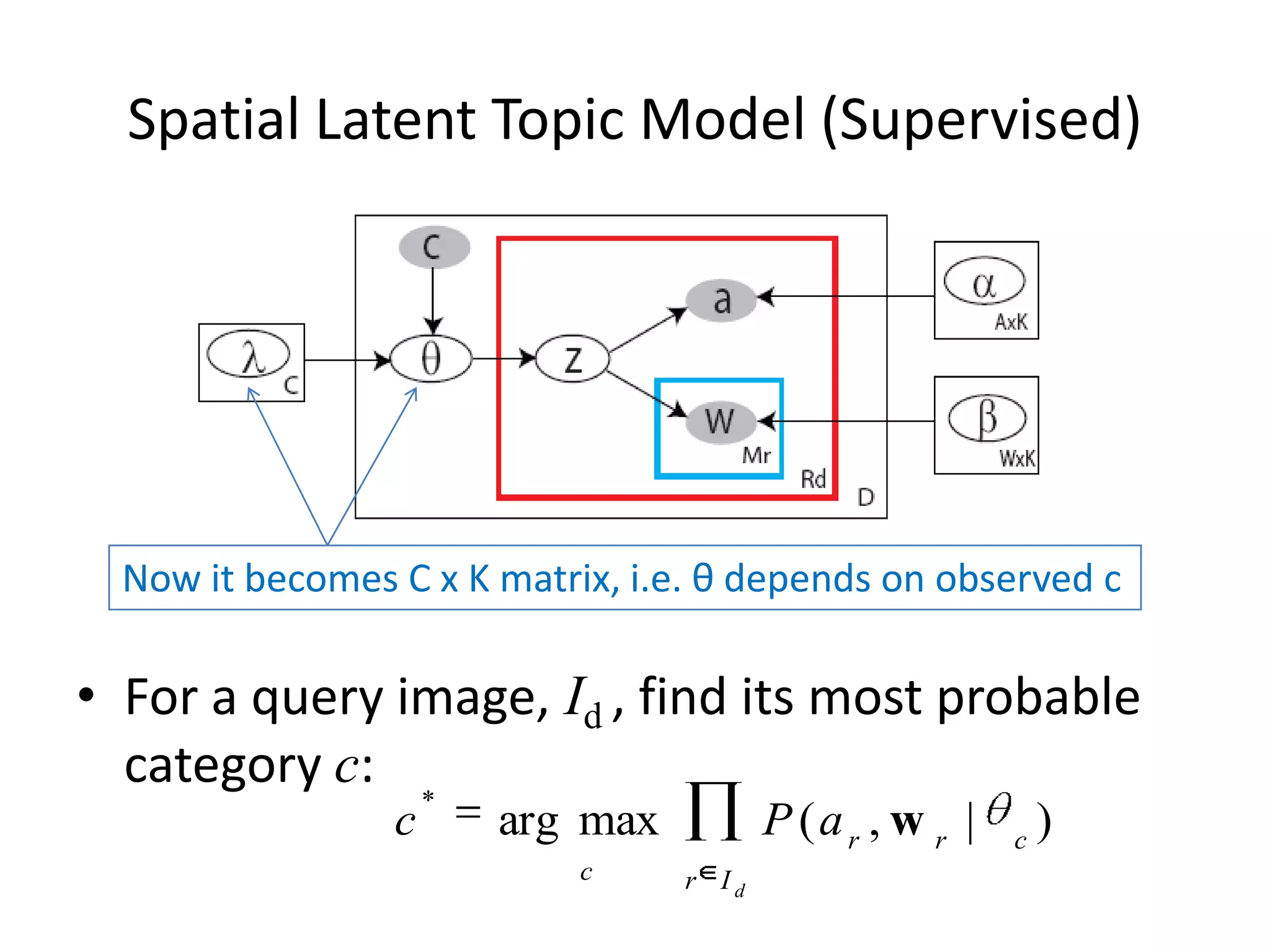
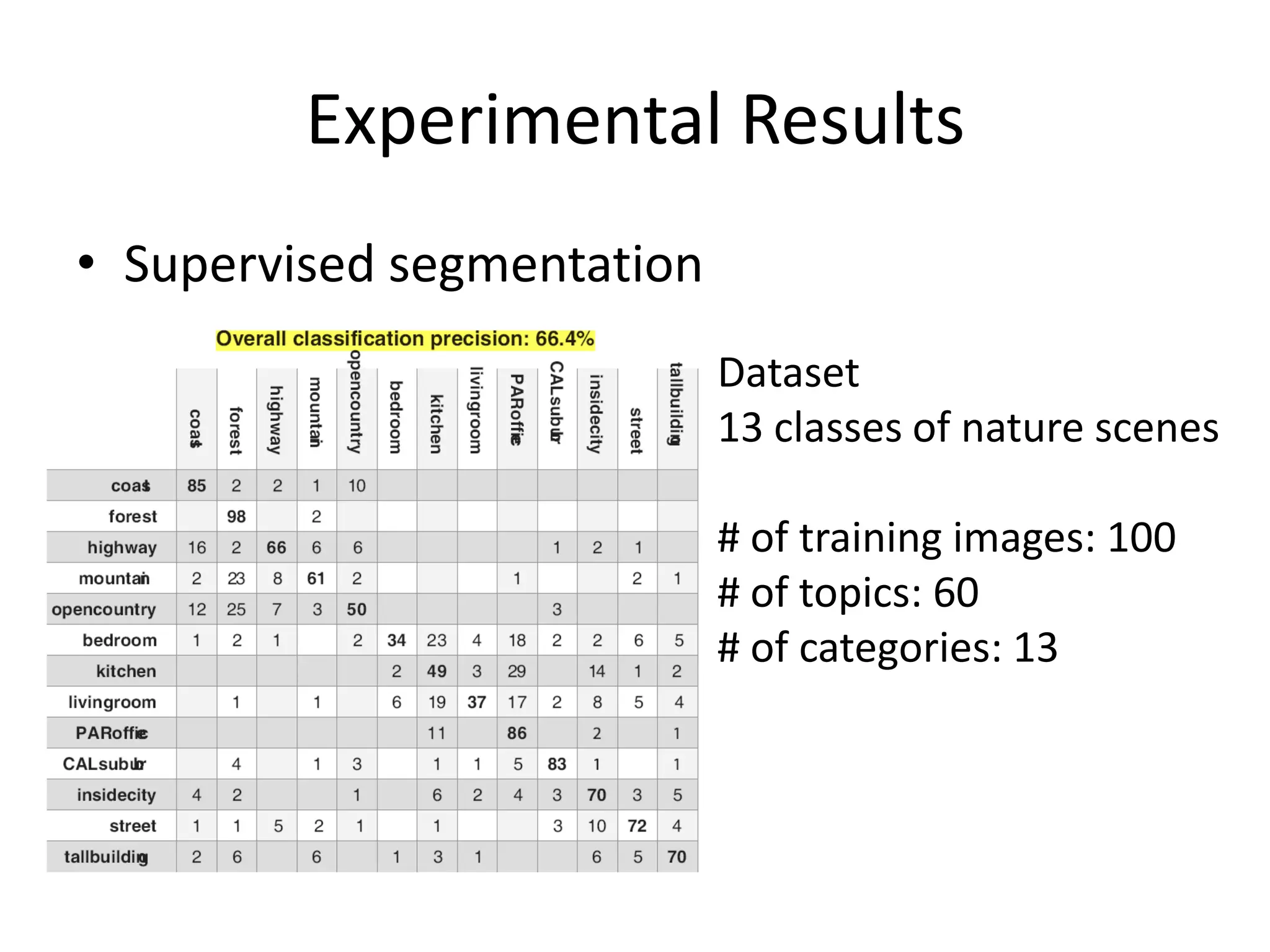
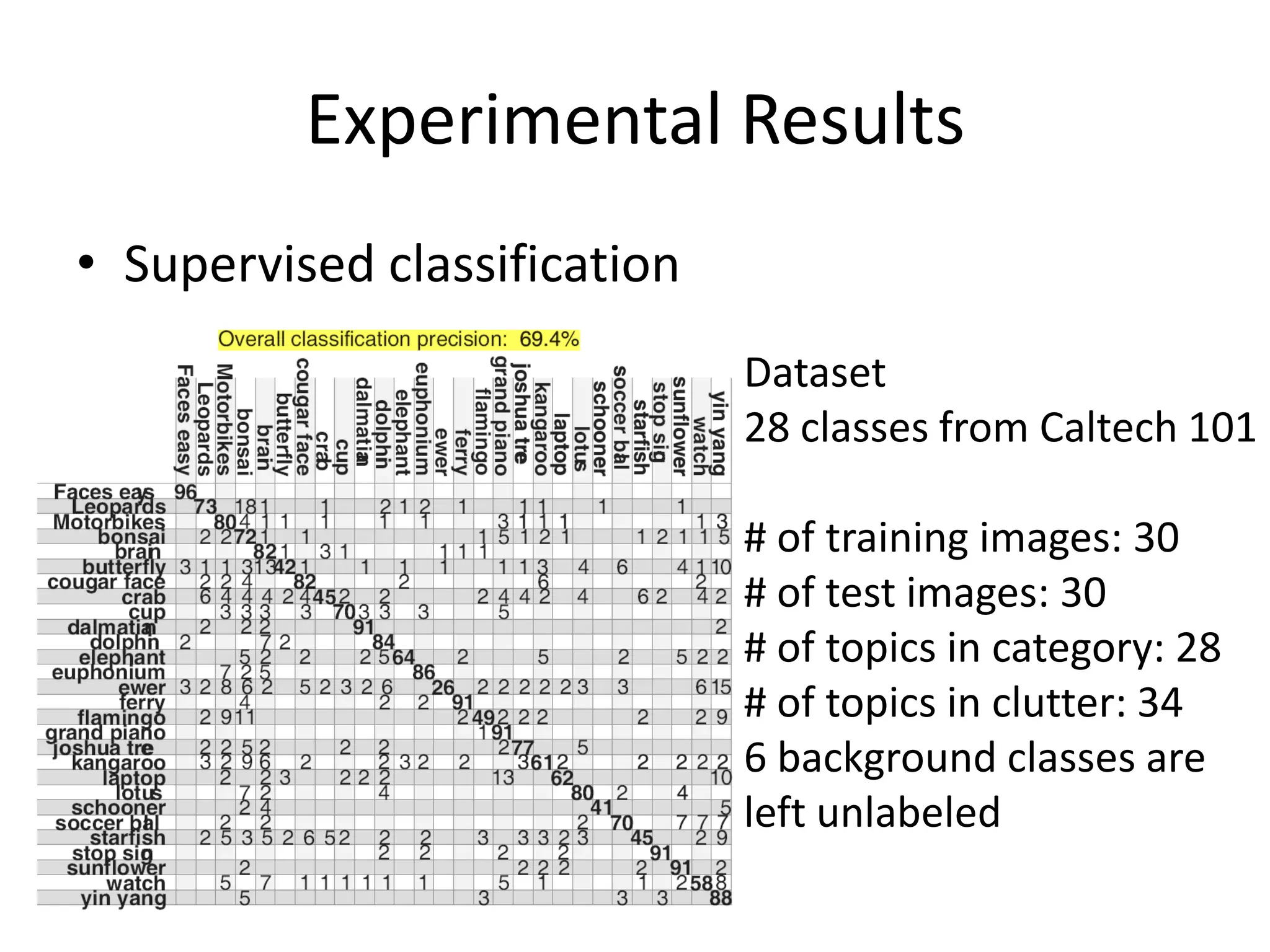
The document summarizes a research paper on spatially coherent latent topic modeling for concurrent object segmentation and classification from images. The proposed model represents images as a collection of regions, each associated with a latent topic. It incorporates spatial relationships between regions by encouraging neighboring regions to take on similar topics. The model is trained using variational message passing to maximize the log likelihood of image data. Experimental results show the model can segment objects even under occlusion and achieve good performance on supervised classification tasks using natural scene images.