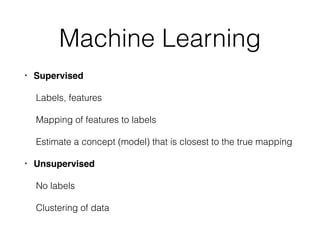
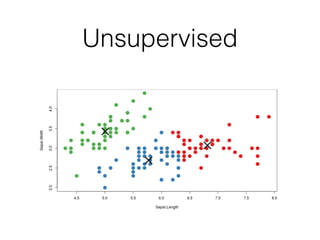
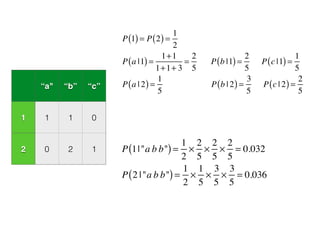
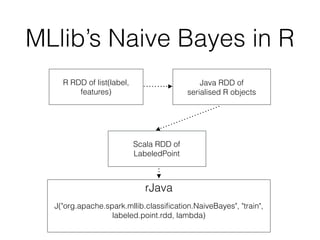
This document introduces R and its integration with SparkR and Spark's MLlib machine learning library. It provides an overview of R and some of its most common data types like vectors, matrices, lists, and data frames. It then discusses how SparkR allows R to leverage Apache Spark's capabilities for large-scale data processing. SparkR exposes Spark's RDD API as distributed lists in R. The document also gives examples of using SparkR for tasks like word counting. It provides an introduction to machine learning concepts like supervised and unsupervised learning, and gives Naive Bayes classification as an example algorithm. Finally, it discusses how MLlib can currently be accessed from R through rJava until full integration with SparkR is completed.







![Vector
• c(1, 2, 3, 4)
## [1] 1 2 3 4
• 1:4
## [1] 1 2 3 4
• c("a", "b", "c")
## [1] "a" "b" “c"
• c(T, F, T)
## [1] TRUE FALSE TRUE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparkr-141128041703-conversion-gate01/85/Introduction-to-SparkR-8-320.jpg)
![Matrix
• matrix(c(1, 2, 3, 4), ncol=2)
## [,1] [,2]
## [1,] 1 3
## [2,] 2 4
• matrix(c(1, 2, 3, 4), ncol=2, byrow=T)
## [,1] [,2]
## [1,] 1 2
## [2,] 3 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparkr-141128041703-conversion-gate01/85/Introduction-to-SparkR-9-320.jpg)
![List
• list(12, “twelve")
## [[1]]
## [1] 12
##
## [[2]]
## [1] "twelve"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparkr-141128041703-conversion-gate01/85/Introduction-to-SparkR-10-320.jpg)
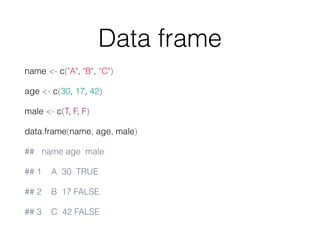





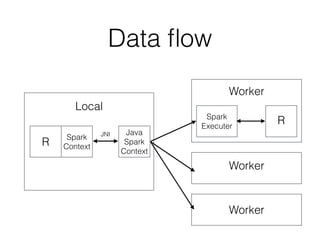
![Word count
lines <- textFile(sc, “/path/to/file")
words <- flatMap(lines,
function(line) {
strsplit(line, " “)[[1]]
})
wordCount <- lapply(words, function(word) { list(word, 1L) })
counts <- reduceByKey(wordCount, "+", 2L)
output <- collect(counts)
for (wordcount in output) {
cat(wordcount[[1]], ": ", wordcount[[2]], “n")
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparkr-141128041703-conversion-gate01/85/Introduction-to-SparkR-19-320.jpg)