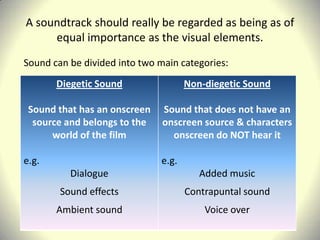
This document provides lesson objectives and materials for teaching students about the use of sound in media. It begins by explaining the key objectives: for students to understand diegetic and non-diegetic sound with examples; analyze how sound creates meaning in a TV drama clip; and use sound terminology. It then defines important sound terminology like diegetic, non-diegetic, sound effects, and voiceovers. Examples are provided of different sound clips to analyze meanings. The document aims to teach students how sound enhances emotional experience and meaning in media.