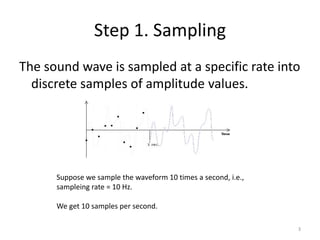
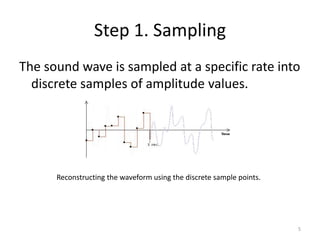
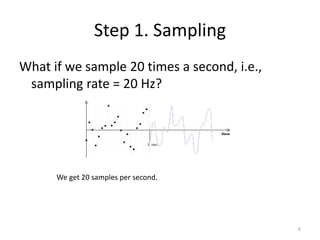
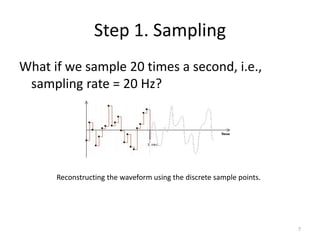
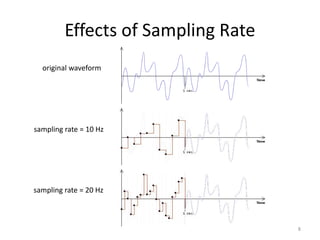
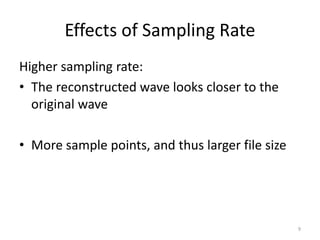
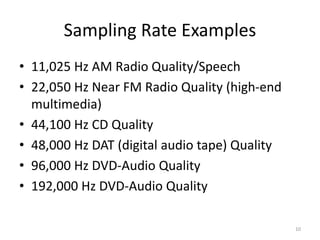
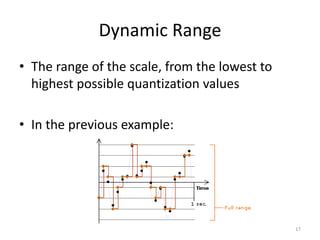
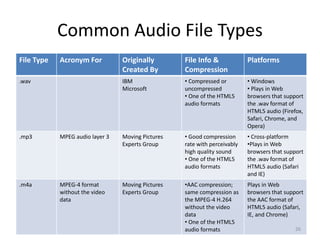
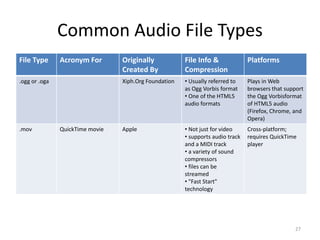
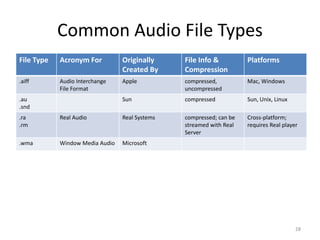
Digital audio involves sampling an analog sound wave into discrete digital samples. There are two main steps: 1) Sampling, where the amplitude of the sound wave is measured at regular intervals, and 2) Quantization, where the continuous range of amplitude values is divided into a finite number of levels. Key factors that affect audio quality include sampling rate, bit depth, file compression, and file format compatibility. A 1-minute CD quality audio file with a sampling rate of 44.1 kHz and 16-bit depth would be around 10 MB in size.