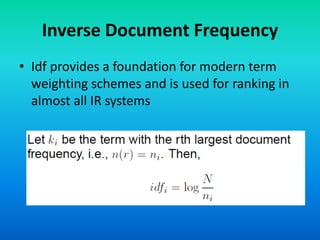
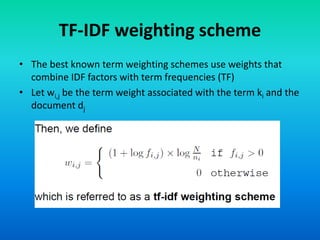
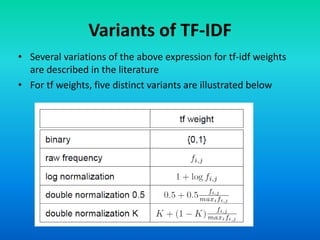
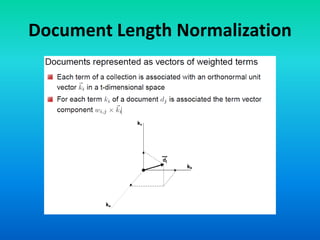
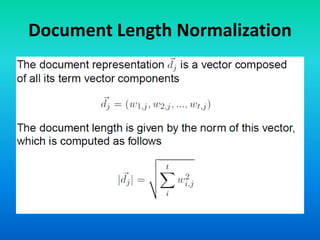
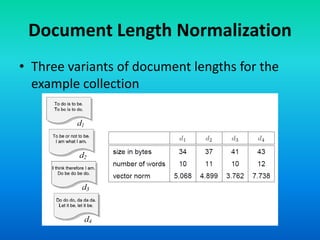
The document discusses the tf-idf weighting scheme in information retrieval, which combines term frequency and inverse document frequency to optimize term relevance in documents. It explores the concept of document exhaustivity and the importance of balancing the number of index terms assigned to a document to improve retrieval without introducing irrelevant matches. Additionally, it covers document length normalization as a method to adjust document rankings based on size, ensuring that different document lengths do not unduly affect retrieval outcomes.