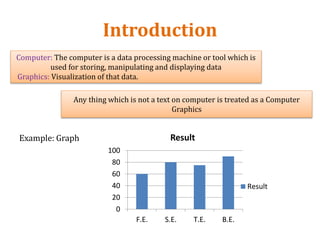
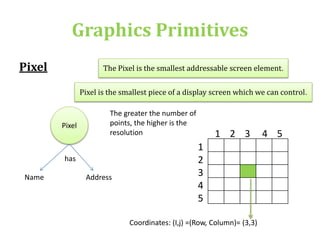
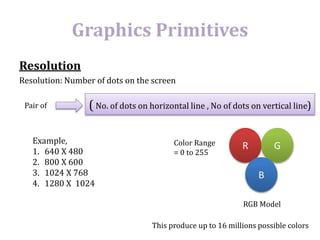
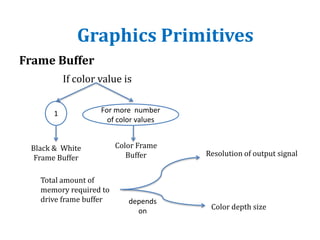
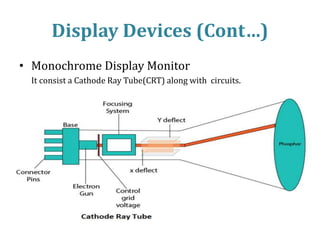
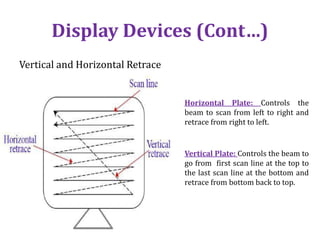
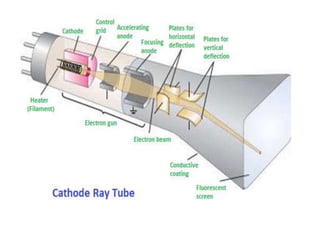
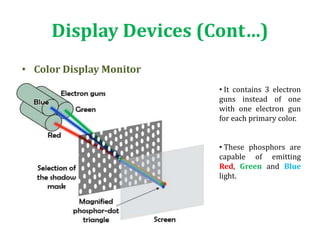
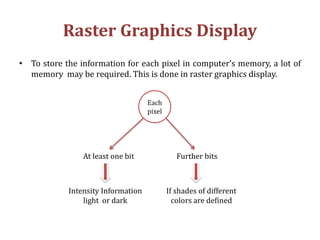
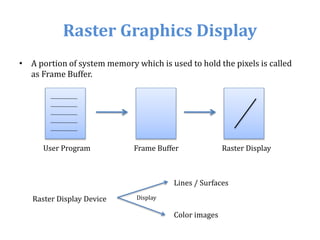
The document introduces computer graphics, covering topics such as graphics primitives, display devices, and their applications. It explains basic concepts like pixels, resolution, aspect ratio, and frame buffers, alongside the functioning of monochrome and color display monitors. Key applications include business software, TV channels, GUI animations, and computer games.