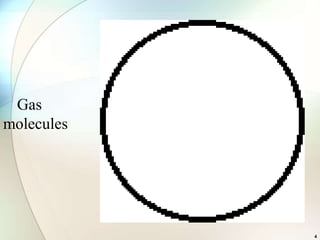
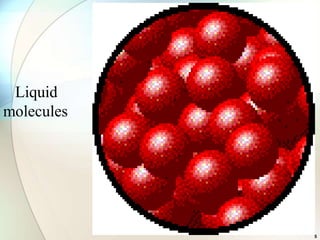
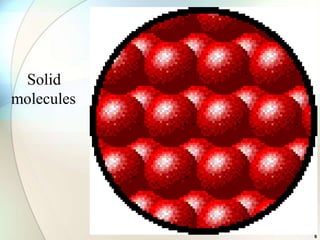
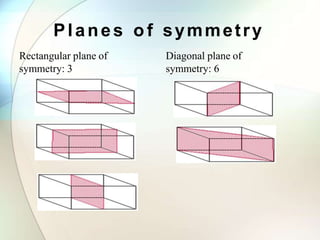
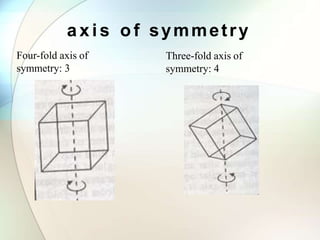
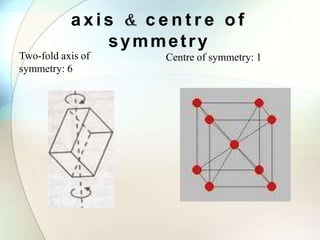
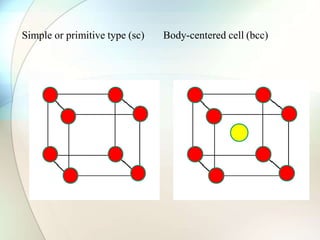
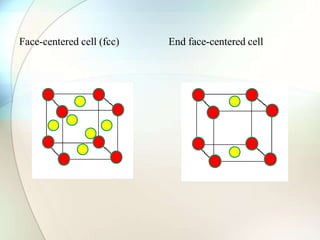
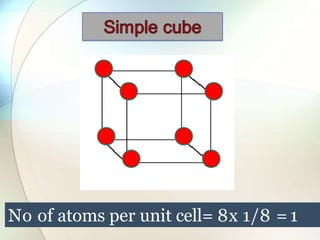
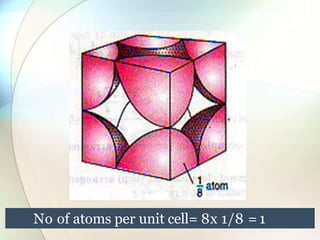
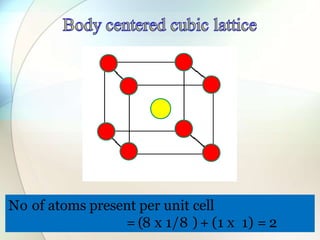
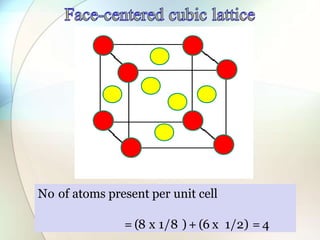
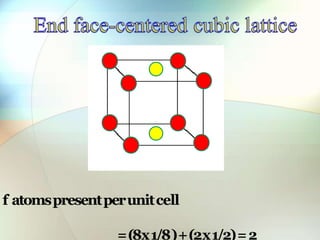
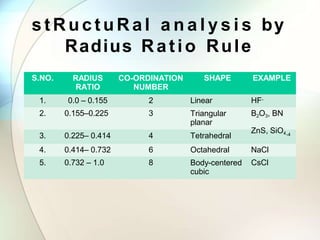
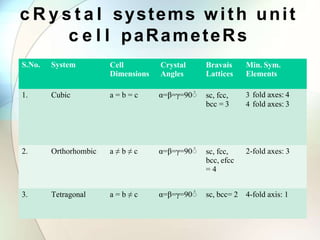
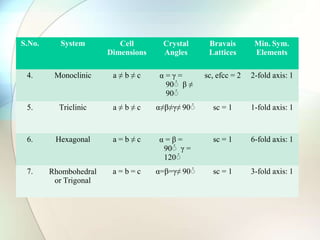
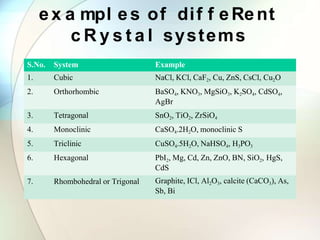
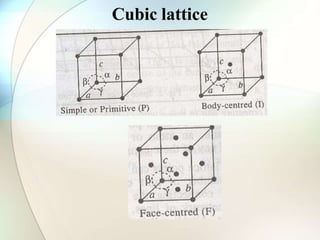
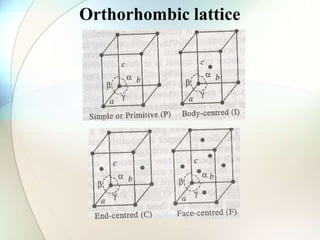
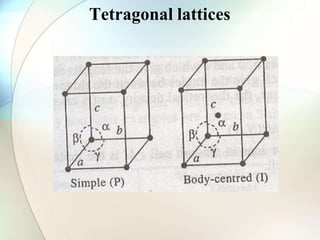
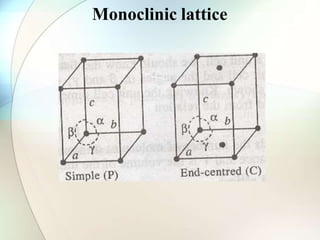
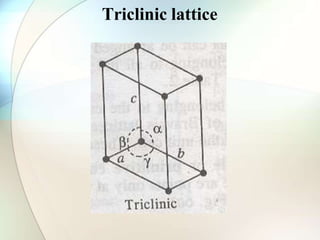
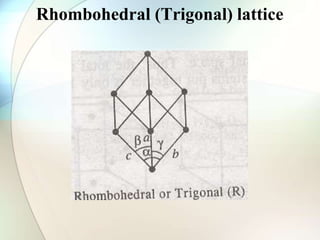
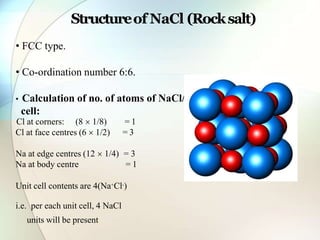
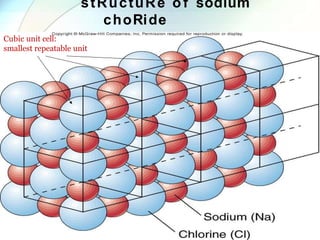
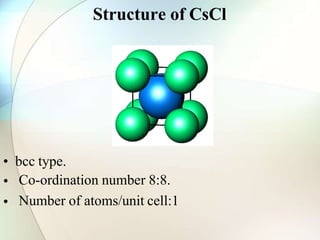
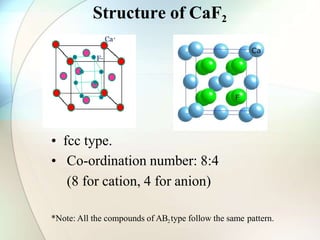
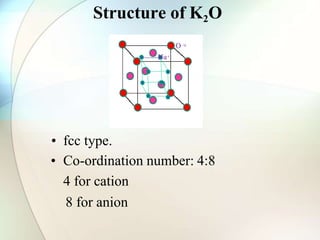
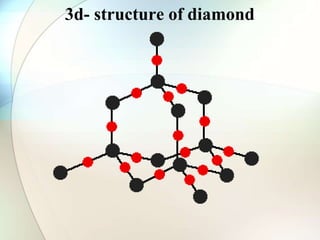
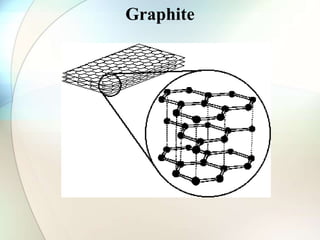
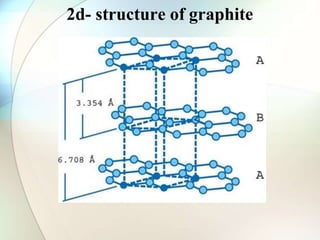
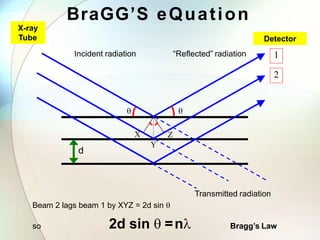
This document provides a summary of key topics in solid state chemistry, including the three phases of matter, types of solids (crystalline and amorphous), crystal structures (ionic, covalent, molecular, metallic), symmetry elements, Bragg's equation, and allotropes of carbon (diamond, graphite, fullerene). It describes characteristics of each topic in 1-3 sentences, with accompanying diagrams and examples. Key definitions include crystalline lattices, unit cells, coordination numbers, radius ratio rule for predicting structure, and the seven crystal systems.