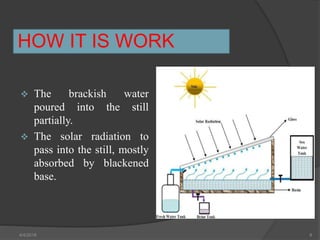
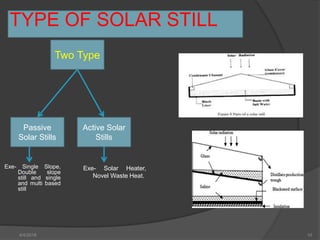
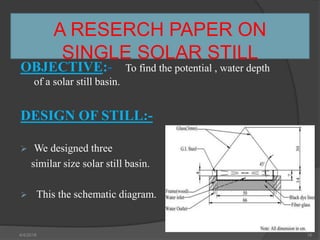
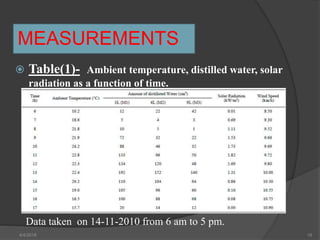
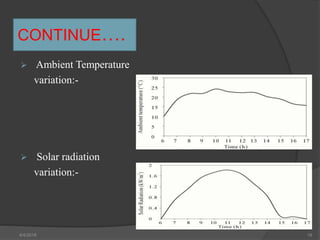
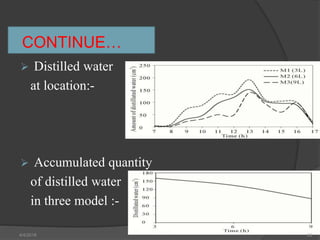
This document presents a summary of a student's research project on solar stills. It introduces solar stills as a method for purifying saline water using solar energy. It provides a brief history of solar stills, describes how they work through evaporation and condensation, and compares different types. The student's research is summarized as testing three solar still models with different water levels to determine maximum productivity. The conclusion is that less water in the still basin leads to higher efficiency. Solar stills provide an economical way to obtain drinking water in locations without other sources.