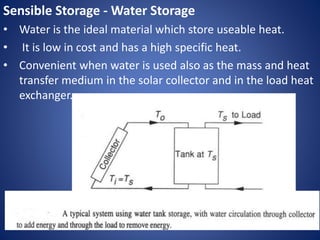
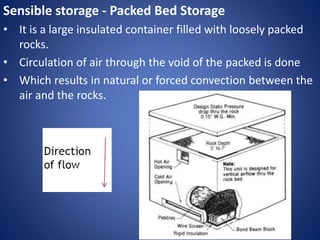
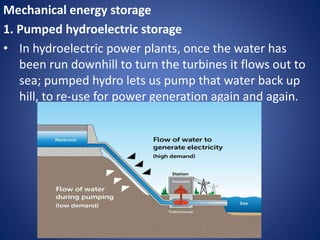
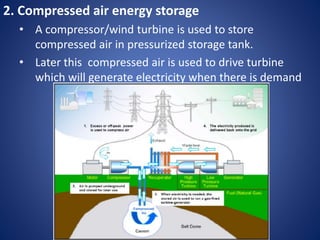
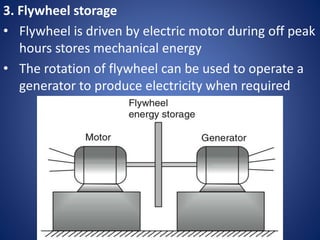
The document outlines various solar energy storage systems, including thermal, electrical, chemical, mechanical, and electromagnetic storage. It details methods such as sensible and latent heat storage, electrical storage using capacitors and batteries, and mechanical methods like pumped hydroelectric and flywheel storage. Additionally, it highlights criteria for effective energy storage materials and the operational principles behind each storage technique.