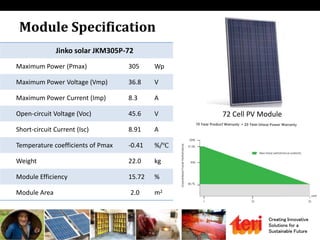
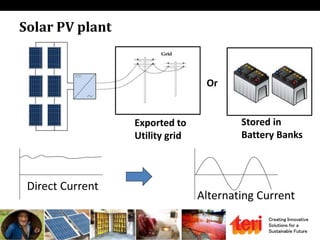
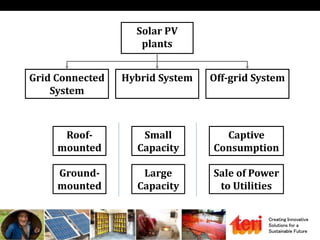
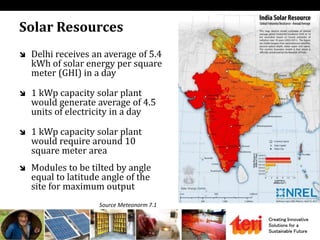
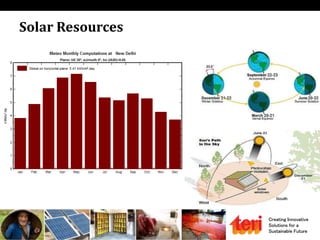
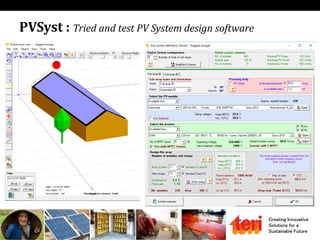
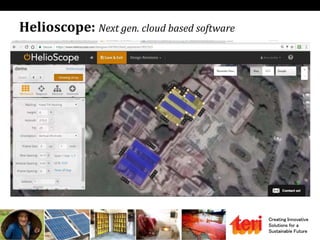
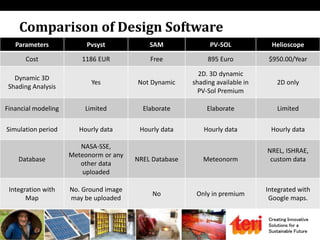
The document discusses designing rooftop solar photovoltaic systems. It covers requirements for solar power plants like space needs and solar radiation levels. Key steps in design include assessing the site for available roof area and energy needs, selecting suitable solar modules, and estimating annual energy generation considering factors like losses. Software tools can help with tasks like component selection, system sizing, and generation simulation. Dynamic 3D modeling is important for accurate shading analysis to optimize rooftop system design.