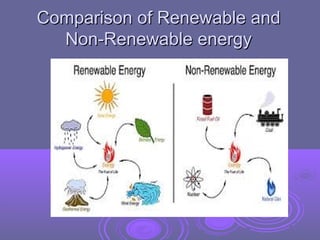
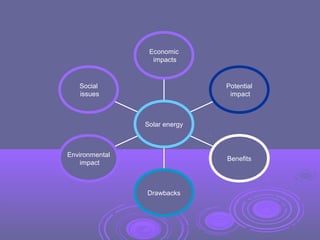
This document discusses renewable and non-renewable energy sources, focusing on solar energy. It defines renewable energy as coming from naturally replenished resources like sunlight, wind, and tides. Solar energy harnesses radiant light and heat from the sun using technologies like solar heating and photovoltaics. While solar energy is sustainable and has environmental benefits by not producing pollution, manufacturing solar panels requires energy and produces waste, and solar technology is currently inefficient and expensive compared to fossil fuels. The document also discusses the economic, social, and potential impacts of solar energy.