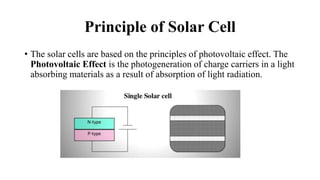
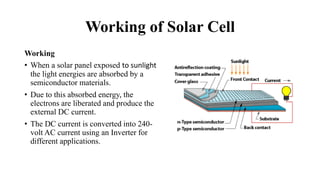
Solar cells convert sunlight into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect. They are constructed of layers of n-type and p-type semiconductors that form a p-n junction. When sunlight is absorbed, electrons are freed and produce an external DC current. There are three main types of solar cells: monocrystalline silicon cells have the highest efficiency around 14-17%; polycrystalline silicon cells have an efficiency of 13-15%; and amorphous silicon cells have the lowest efficiency of 5-7%. Solar cells have advantages of being renewable, clean, and requiring little maintenance but their initial costs remain high.