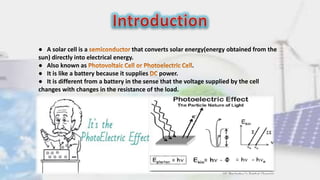
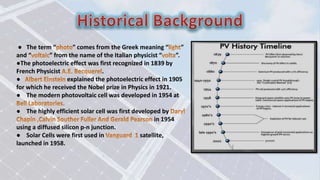
Solar cells convert sunlight directly into electrical energy. They work as a semiconductor that produces electricity when exposed to light, functioning similarly to how a battery produces electricity. The key components are a photovoltaic material like silicon that produces electrons and holes when struck by photons, and electrical conductors that carry the current. Solar cells have many applications and benefits like being renewable, clean, and able to provide off-grid power, but their initial costs remain high and they require large surface areas for average efficiency.