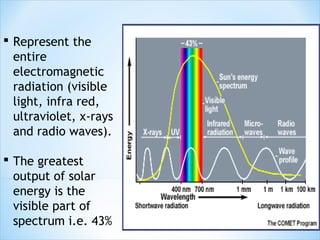
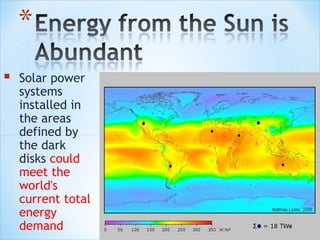
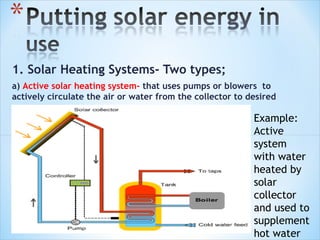
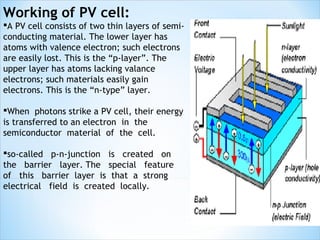
The document discusses various methods of harnessing solar energy, including solar heating systems, power towers, parabolic dishes, photovoltaic cells, and solar ponds. It also describes a case study of a "Solar Tuki" clean lighting alternative to kerosene lamps in Nepal. The advantages of solar energy are that it is renewable, environmentally friendly, and can provide independent power, while the main disadvantage is the high initial cost of solar systems.