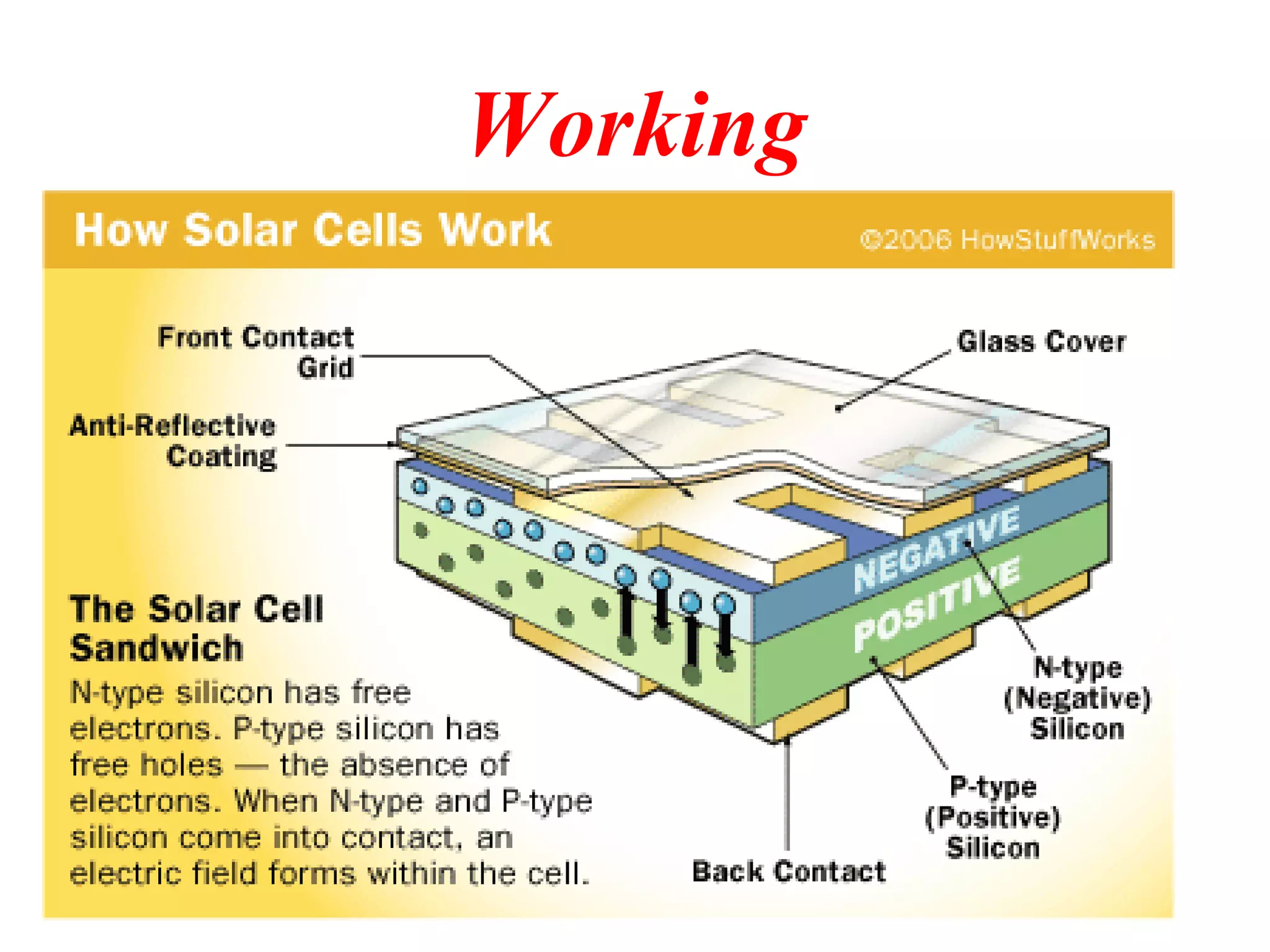
Solar cells, also known as photovoltaic cells, convert solar energy from the sun into electrical energy. They operate based on the photovoltaic effect where absorption of light by the solar cell's semiconductor material generates electron/hole pairs that can be harvested as an electric current. A typical solar cell consists of a thin wafer made from silicon with a positive and negative layer that form a p-n junction. When light hits the solar cell, photons are absorbed and electrons flow, generating direct current electricity that can be used or stored. The three main types of solar cells are monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and amorphous silicon cells which have varying efficiencies depending on the purity and structure of the