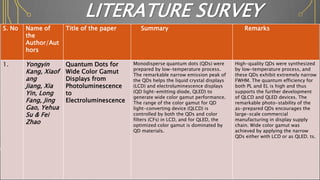
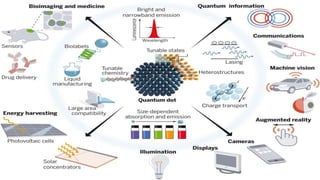
The document presents an overview of quantum dots and their applications in various display technologies, highlighting their advantages over traditional displays like CRT and LCD. It discusses the structure and properties of quantum dots, their integration in LED backlighting for LCDs, and innovations such as micro-LED and quantum dot-enhanced displays that improve color accuracy and energy efficiency. The potential for quantum dots to revolutionize display technology is emphasized, along with references to recent research and advancements in the field.




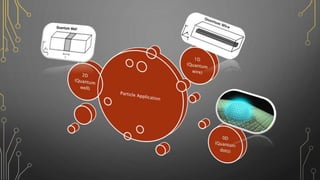



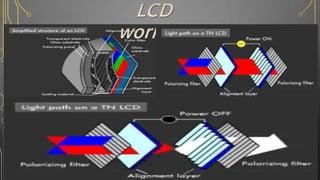

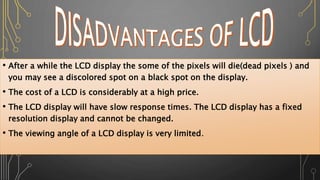
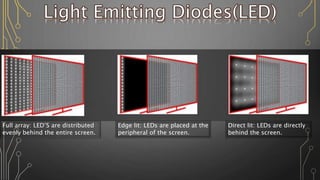





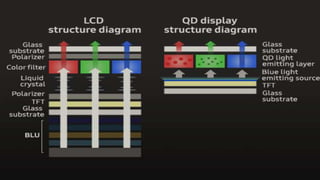


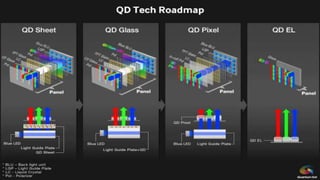

![The micro-LED
array with a single
pixel size of 20 ×
20 µm2 , and a
pitch of 25 µm
was fabricated, as
shown Figure.
The EL
(electroluminesce
nce) optical
microscopy image
of RGB NP pixel
micro-LED is
shown in Figure
References :- Chen, Z.; Yan, S.; Danesh, C. MicroLED technologies and applications:
Characteristics, fabrication, progress, and challenges. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2021, 54,
123001. [CrossRef]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nitin001full-230415062736-0f7a66b9/85/Quantum-dot-displays-27-320.jpg)
![EL(Electroluminesce
nce) spectra of red
and green pixel
EL(Electroluminescen
ce) image of RGB
pixels.
References:- Ashoori, R.C. Electrons in artificial atoms. Nature 1996, 379,
413–419. [CrossRef]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nitin001full-230415062736-0f7a66b9/85/Quantum-dot-displays-28-320.jpg)