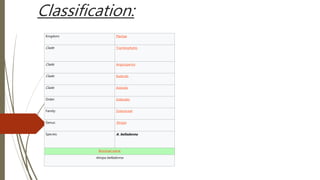
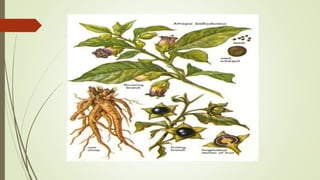
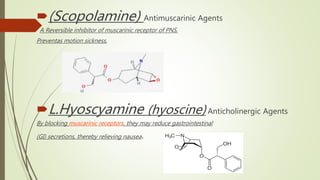
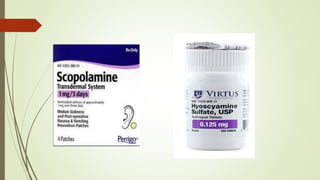
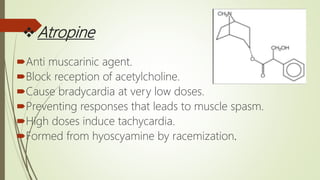
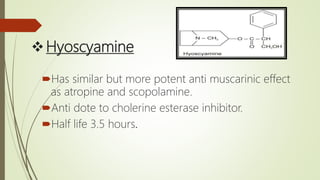
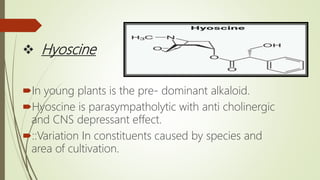
The document provides information about the Solanaceae family, also known as the potato family. It discusses key details about the family, including that it contains around 90 genera and 2000 species of flowering plants. 14 genera and 52 species are found in Pakistan. Common features among members include herbs, shrubs, vines with simple leaves and bisexual flowers. Many members are used for their alkaloid content, as ornamentals, medicines, and some are edible or toxic weeds. Examples like belladonna, henbane, jimsonweed, and peppers are described in more detail.