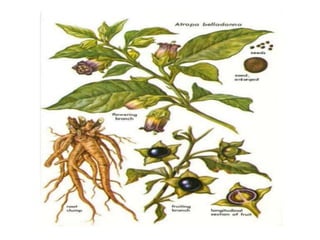
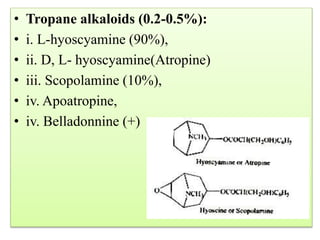
Hallucinogens are natural or synthetic substances that significantly alter one's consciousness by causing hallucinations such as seeing colors and objects that don't exist or experiencing altered perceptions of time, space, and senses. Some examples of hallucinogenic plants described in the document are belladonna, datura, morning glory, and psilocybin mushrooms. Belladonna contains tropane alkaloids that in large doses can cause effects like dilated pupils, blurred vision, and delirium. Historically, belladonna extracts have been used as a medicine to dilate pupils and as an antidote to other poisons, and it continues to be used recreationally as a hallucinogenic drug in some cases