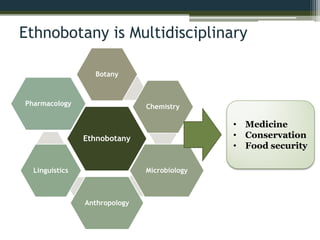
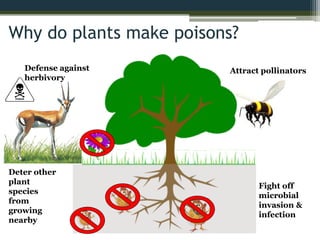
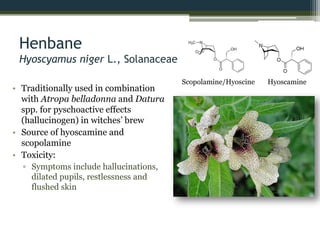
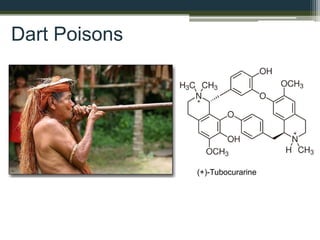
The document explores the relationship between poisonous plants and their medicinal uses through medical ethnobotany, detailing how various plants like cassava, pokeweed, and deadly nightshade can serve both as poisons and medicines depending on processing and dosage. It highlights historical uses, traditional remedies, and the chemical properties of these plants, illustrating the complex interplay of toxicity and therapeutic benefits while providing examples from history and mythology. Ultimately, the distinction between a poison and a medicine often hinges on dose and intent.




















![Poisons in Mythology
• Plant teratogen causes Cyclopia!
• Veratrum album L., V. californicum
Durand and V. viride Aiton,
Melanthiaceae [false hellebore] –
case of mistaken identity with other
hellebore (Helleborus spp.,
Ranunculaceae) used in ancient
Greek medicine as purgative
• Consumption during early pregnancy
(in humans and other animals – esp.
common in sheep) results in cyclopia
▫ Single eye, often missing nose
▫ Usually stillborn
• Responsible compound: cyclopamine](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deadlycuresv3-151229154036/85/Fernbank-Museum-Lecture-Deadly-cures-2015-25-320.jpg)





























![Rhus Dermatitis Plants
• Anacardiaceae
▫ Toxicodendron radicans (L.) Kuntze
[Poison Ivy]
▫ Toxicodendron diversilobum (Torr.
& A. Gray) Greene [Poison Oak]
▫ Toxicodendron vernix (L.) Kuntze
[Poison Sumac]
▫ Mangifera spp. [Mango]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deadlycuresv3-151229154036/85/Fernbank-Museum-Lecture-Deadly-cures-2015-57-320.jpg)
![Rhus Dermatitis Plants
• Anacardiaceae
▫ Toxicodendron vernicifluum
(Stokes) F.A. Barkley [Lacquer Tree]
▫ Anacardium occidentale L. [Cashew
Nut]
▫ Semecarpus anacardium L. f.
[Indian marking nut]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deadlycuresv3-151229154036/85/Fernbank-Museum-Lecture-Deadly-cures-2015-58-320.jpg)

