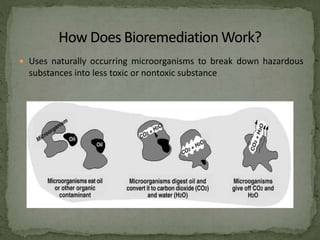
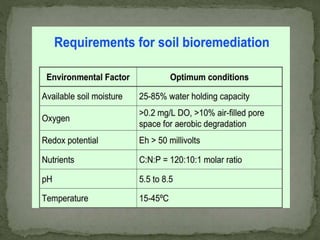
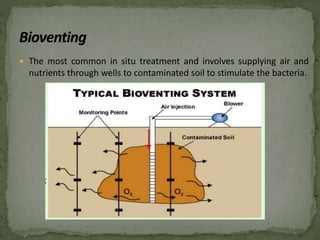
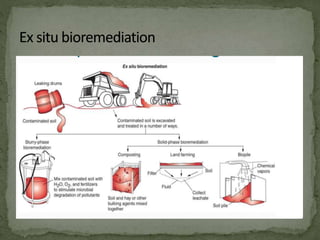
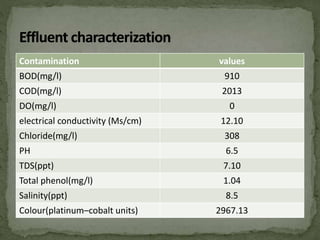
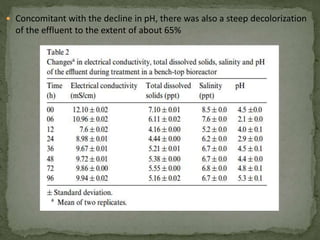
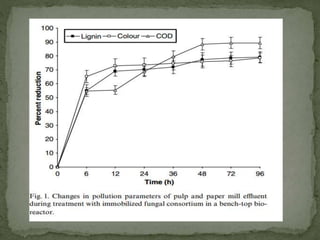
This document discusses bioremediation, which uses microorganisms to break down contaminants in soil and water. It can be used to treat sites contaminated with organic compounds by stimulating bacteria and fungi that are naturally present or introduced. The microbes use the contaminants for food and break them down into simpler, less toxic substances. Two types of bioremediation are discussed - in situ, which treats contaminants on-site without removing soil, and ex situ, which treats removed soil. Specific in situ techniques include bioventing, biosparging, and biostimulation. The document also summarizes a study that used a fungal consortium to treat wastewater from a pulp and paper mill, significantly