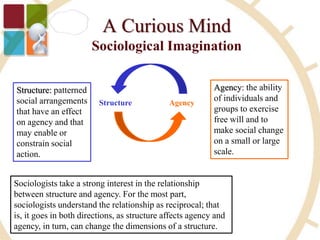
This document provides an overview and summary of the key topics covered in Week 1 of the SOC 100 Introduction to Sociology course. The week introduced students to the basic concepts of sociology including defining the sociological imagination, the relationship between structure and agency, and the six rules of critical thinking. It also reviewed the origins and early founders of sociology as an academic discipline and the major theoretical paradigms in sociology including functionalism, conflict theory, and symbolic interactionism. The document concludes by previewing the topics and assignments for Week 2.