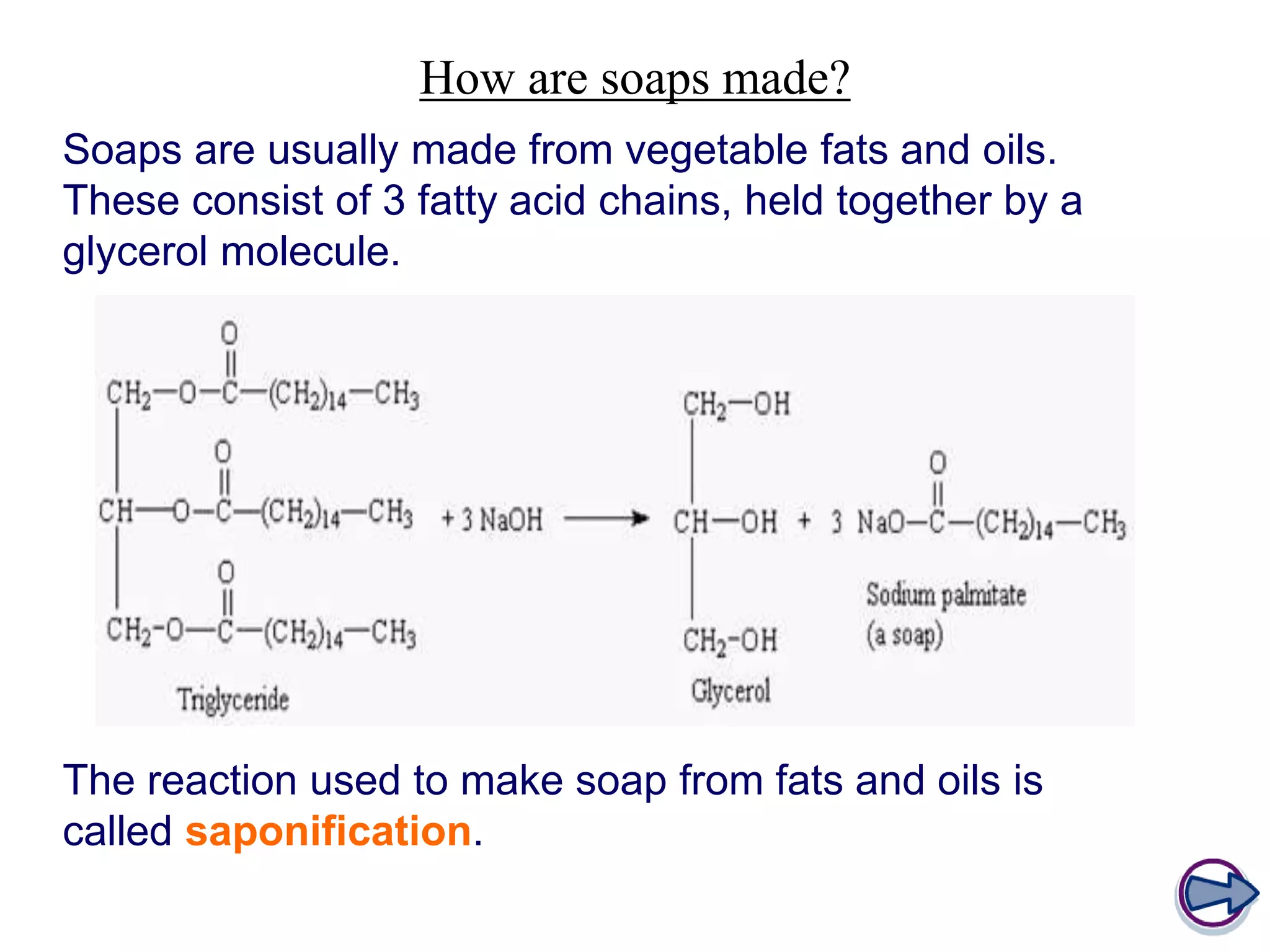
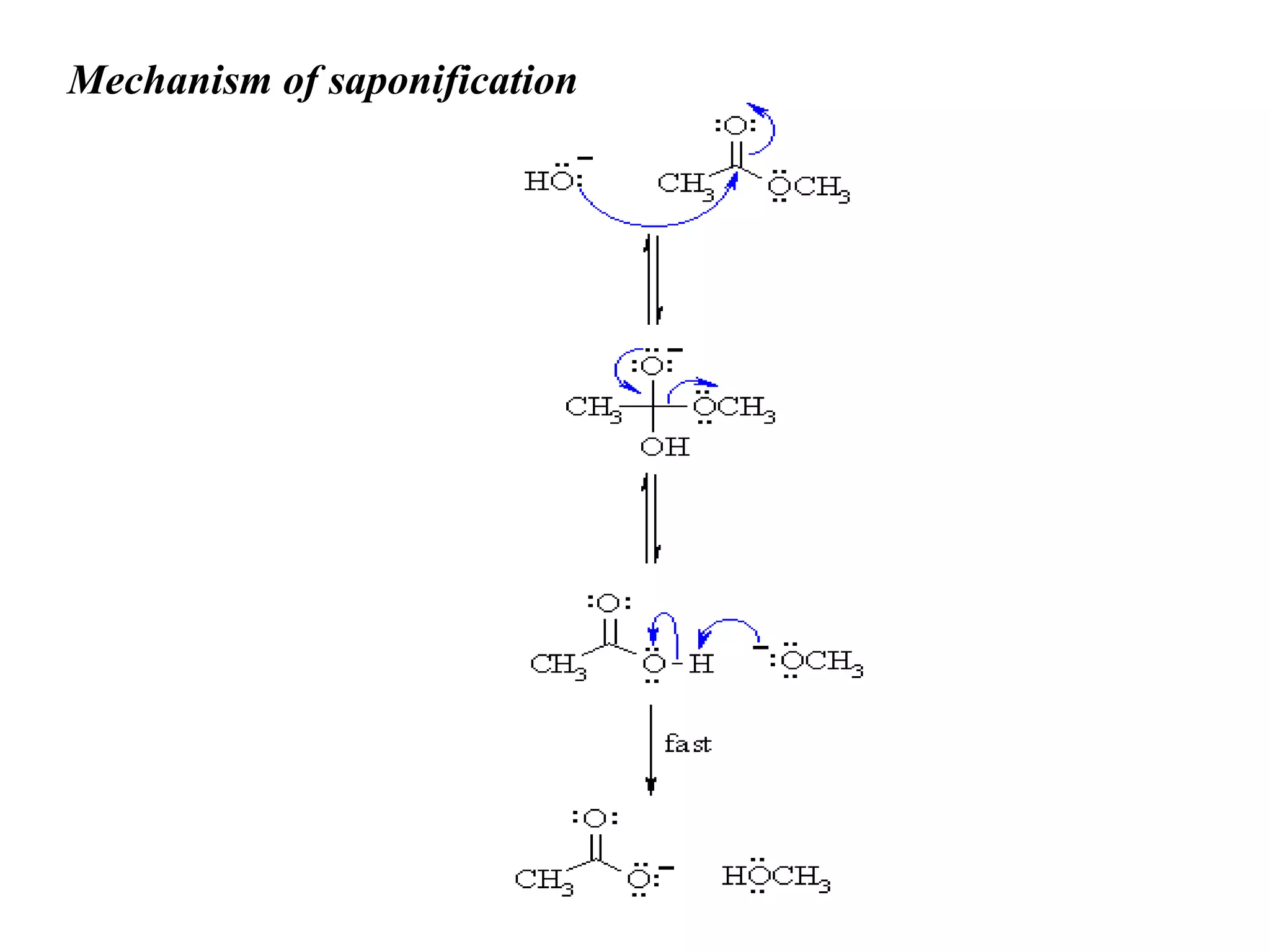
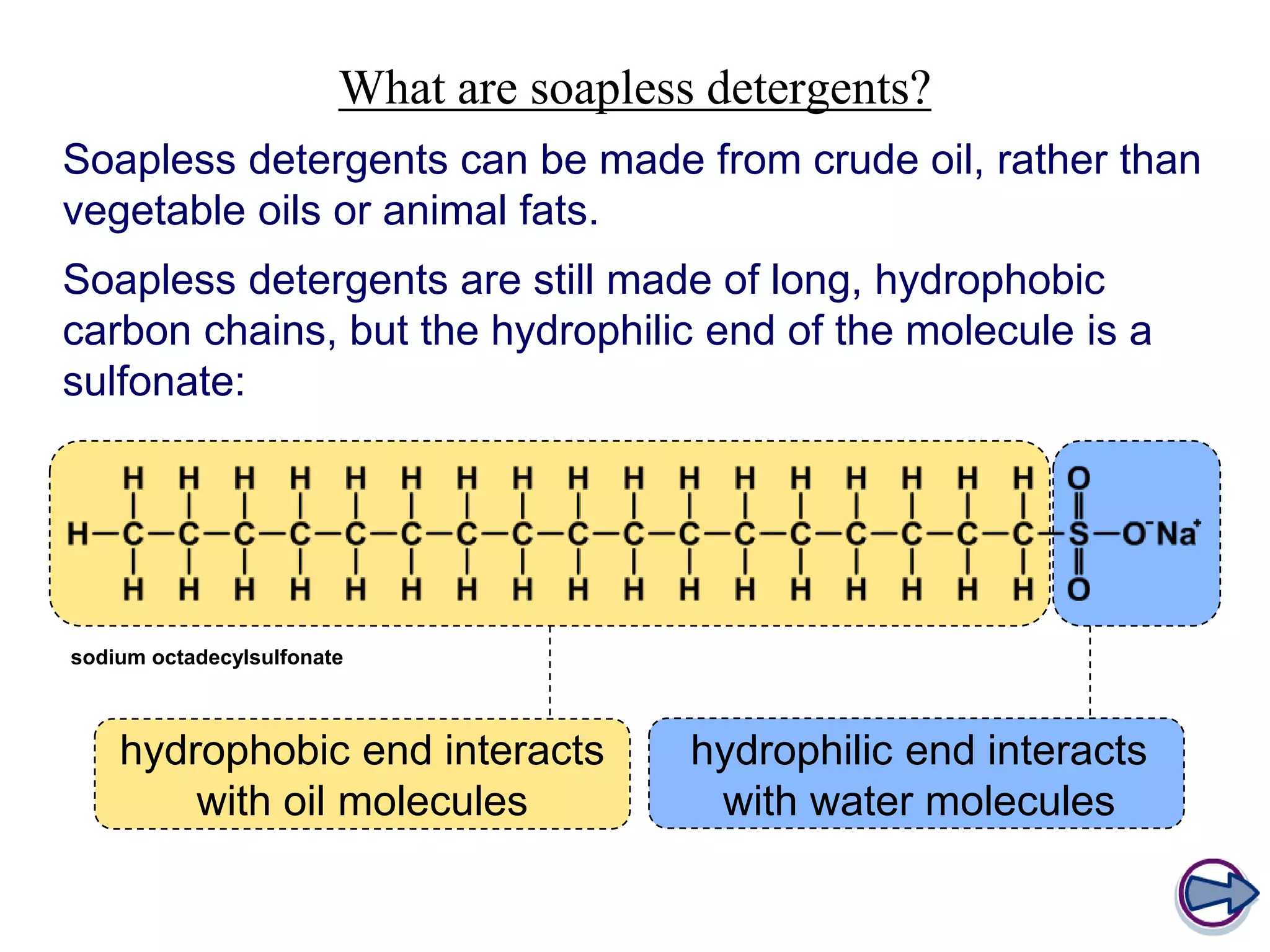
Soap is made through a chemical reaction called saponification where vegetable oils or animal fats are mixed with a strong alkali like sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. This produces soap (a salt of fatty acids) and glycerol. Soaps act as emulsifiers that allow oil and water to mix, helping to remove grease stains during washing. Soapless detergents can also be made from crude oil instead of vegetable/animal sources, and use a sulfonate group instead of fatty acid salts to emulsify oil in water.