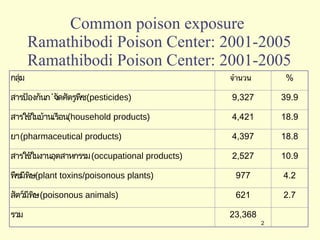
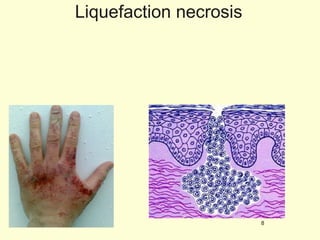
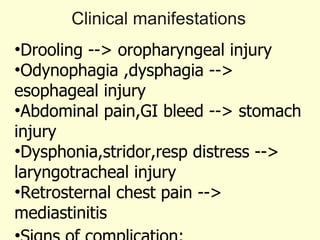
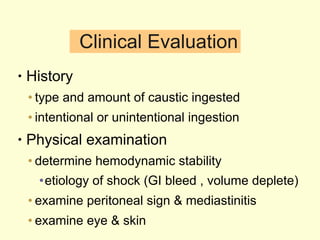
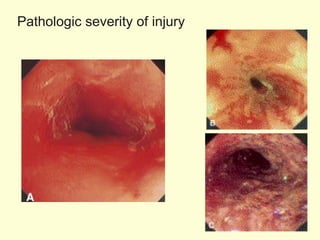
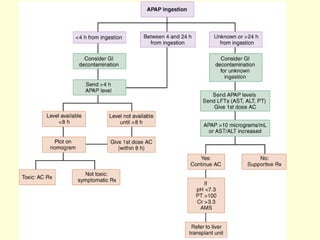
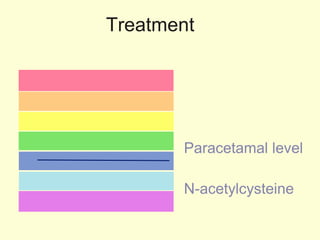
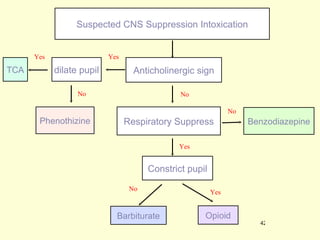
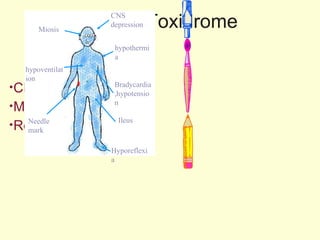
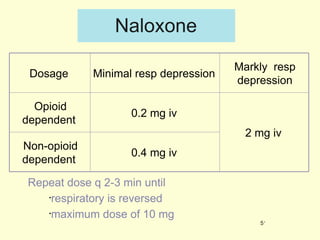
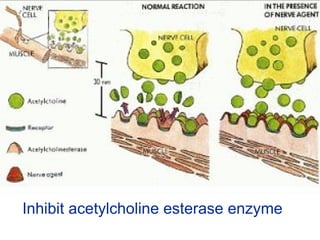
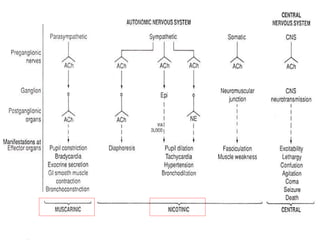
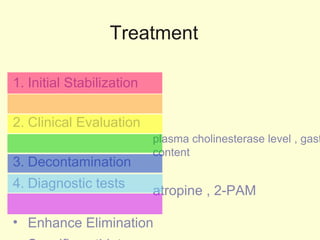
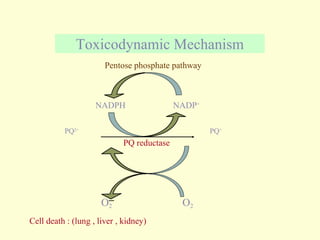
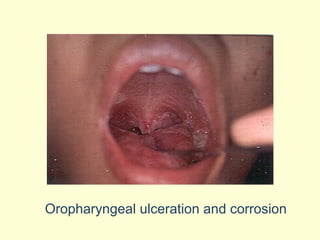
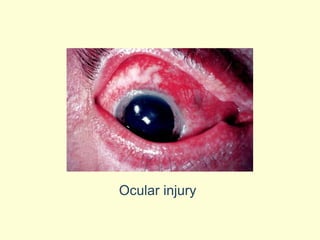
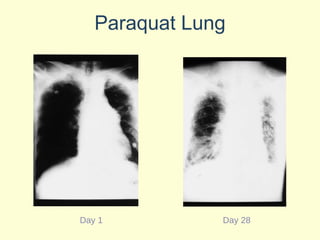
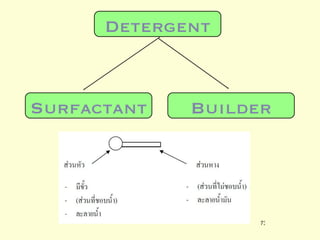
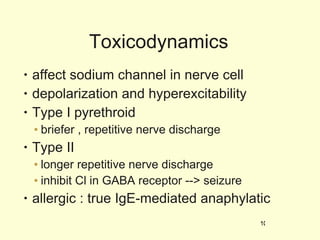
A 5-year-old boy ingested approximately 5 mouthfuls of shampoo 30 minutes prior to arriving at the hospital. Upon arrival, he reported slight tongue numbness but felt well otherwise with no vomiting, dyspnea, or abdominal pain. Shampoo contains surfactants like nonionic surfactants which are condensation products of fatty alcohols and ethylene oxide that can cause minor oral irritation but are generally considered low toxicity at normal usage amounts.