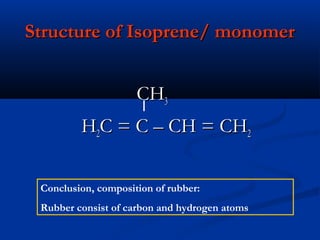
Natural rubber is a natural polymer obtained from the latex of the rubber tree Hevea brasiliensis. It is composed of polyisoprene, which is a long chain of the monomer isoprene. Latex is a white fluid that is coagulated to form solid natural rubber through the addition of bacteria or acids that lower the pH. Vulcanization improves the properties of natural rubber by adding sulfur to form cross-links between polymer chains, making the rubber more durable and elastic.