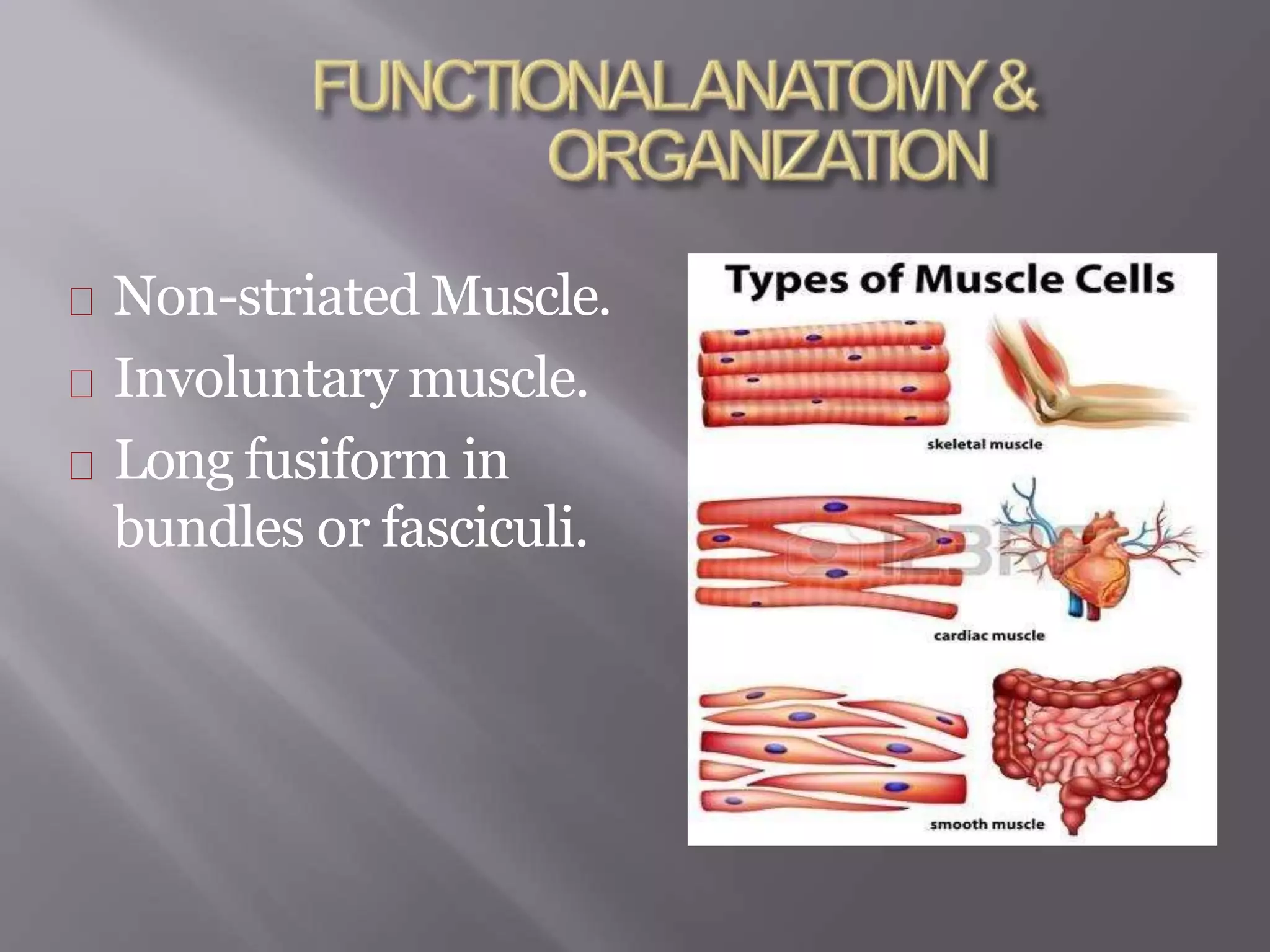
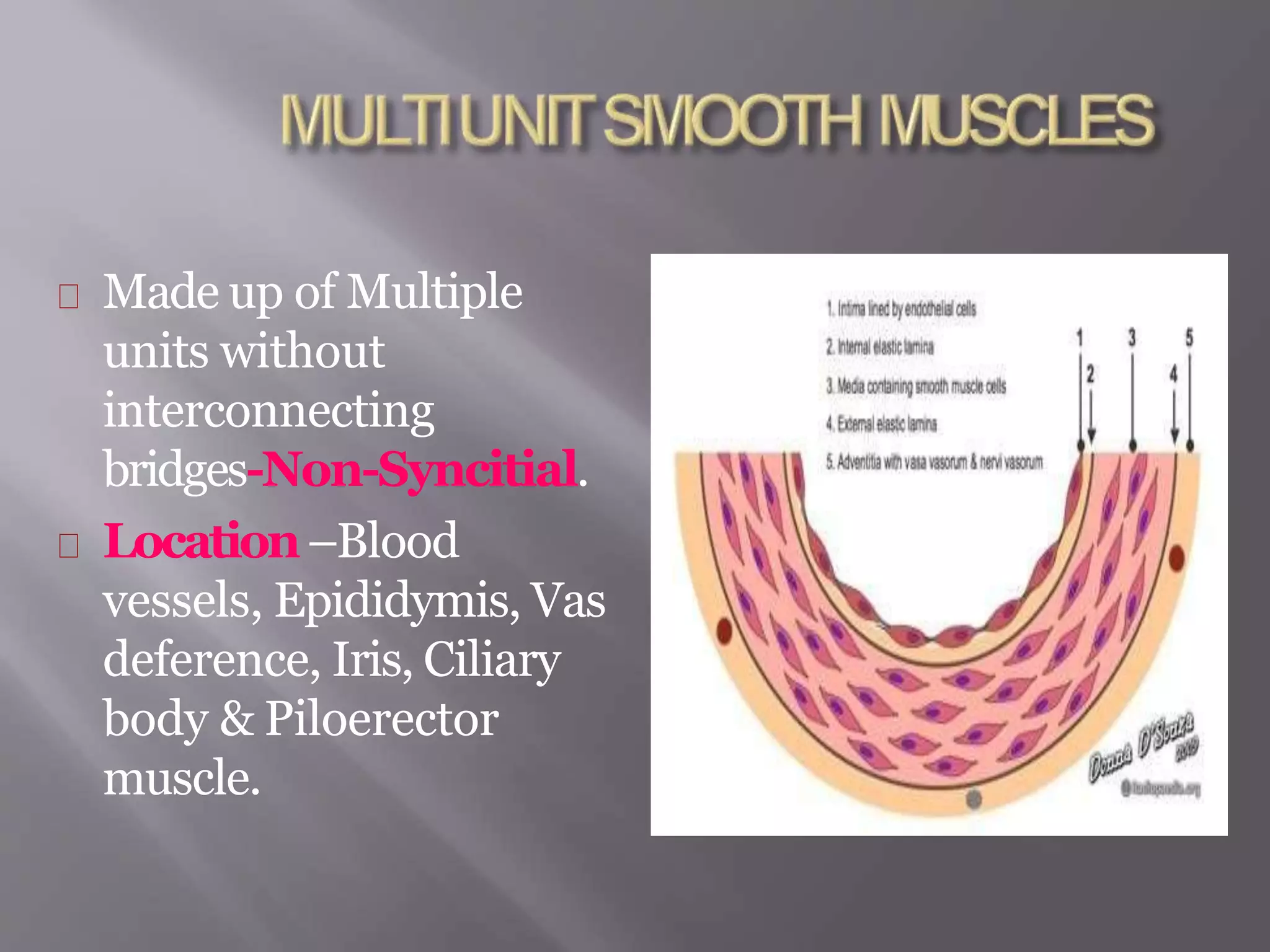
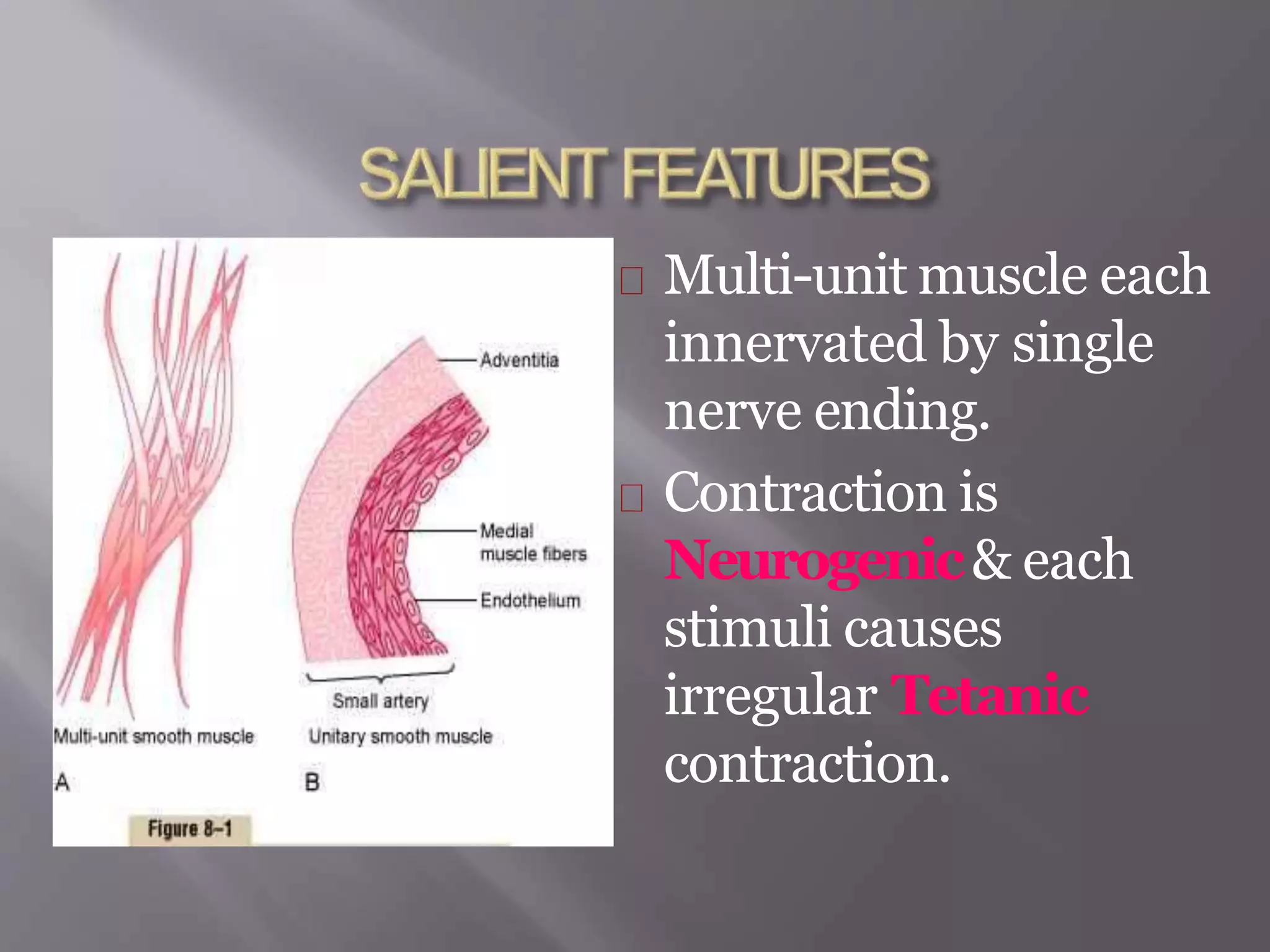
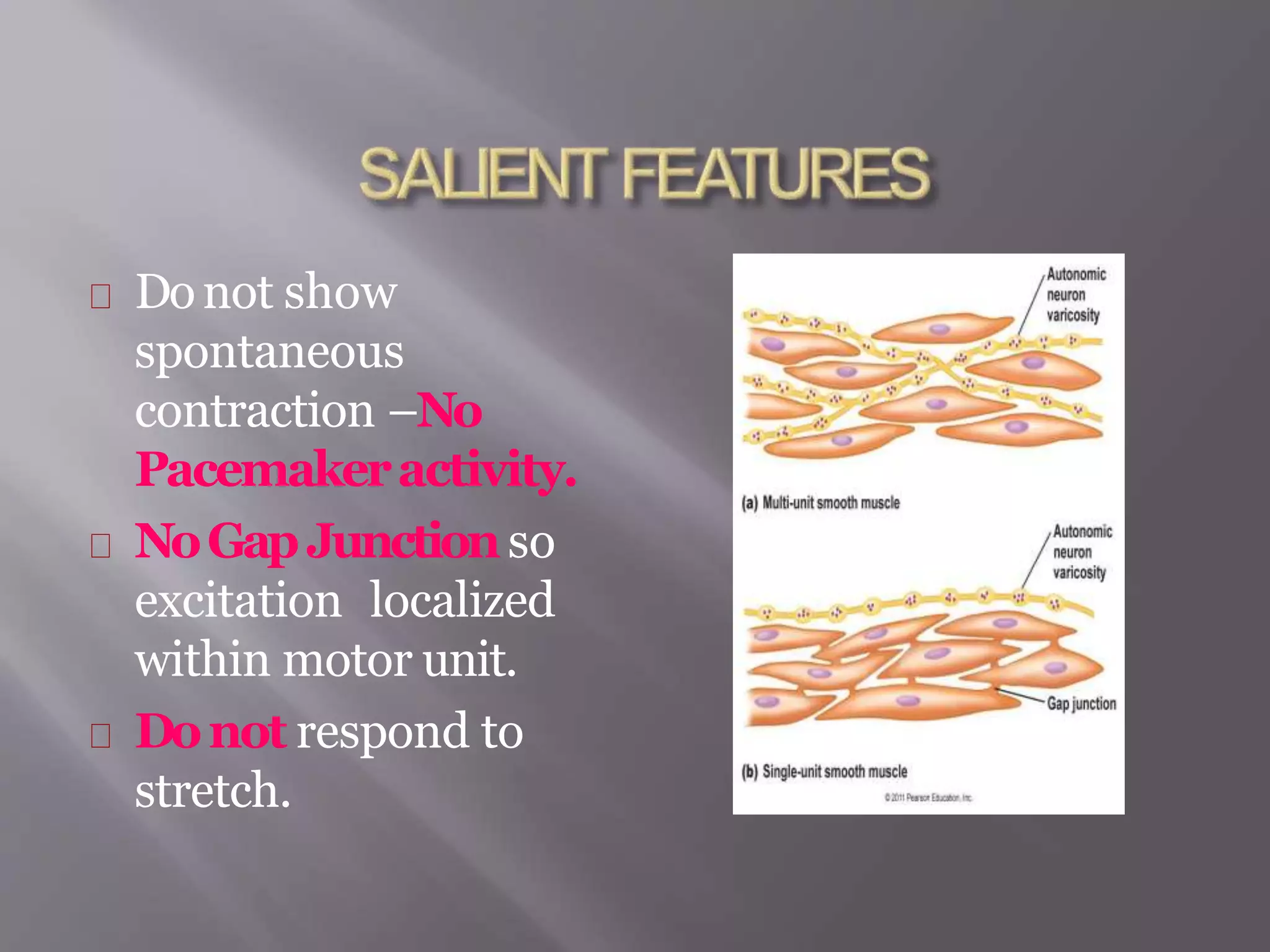
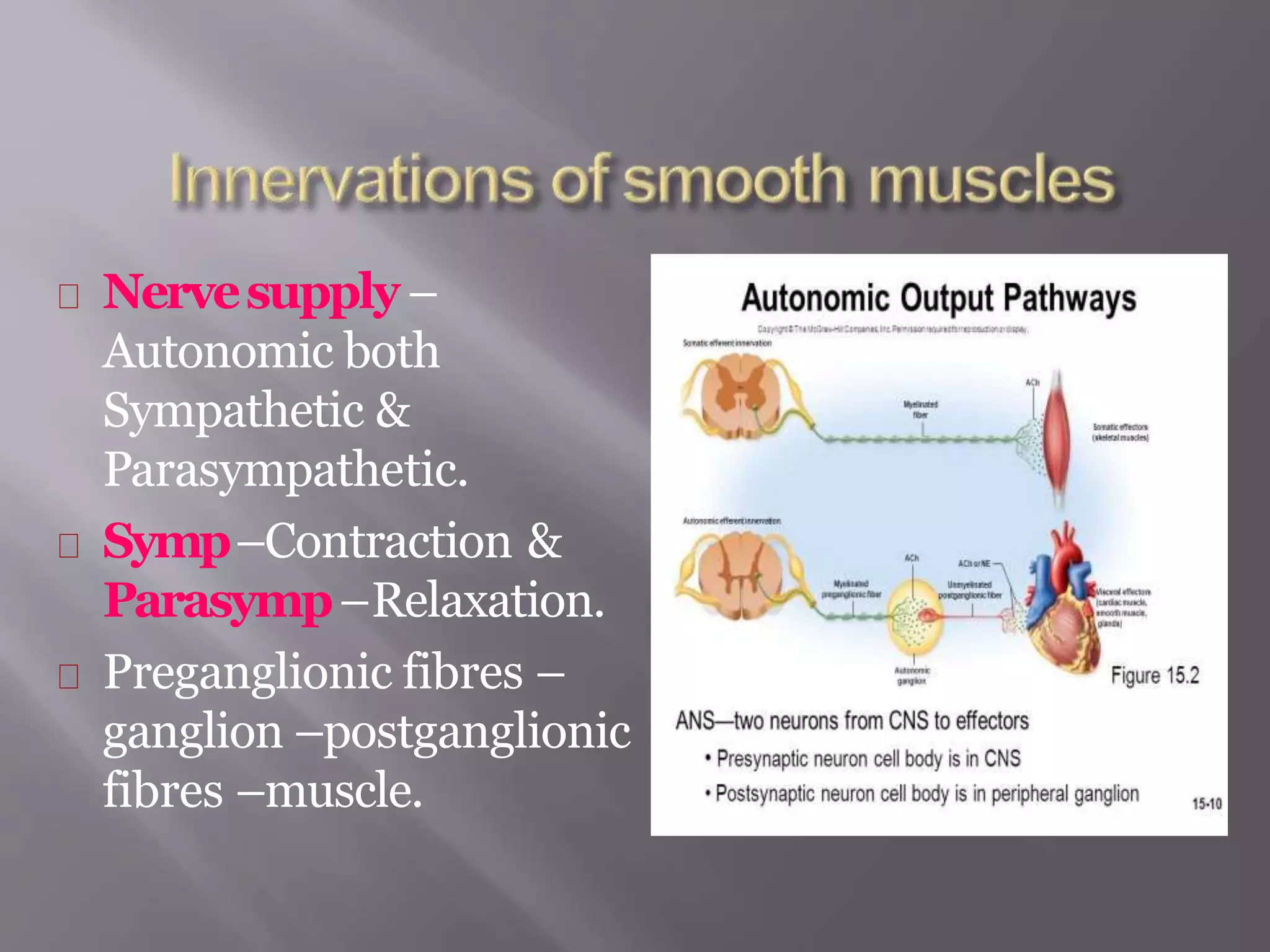
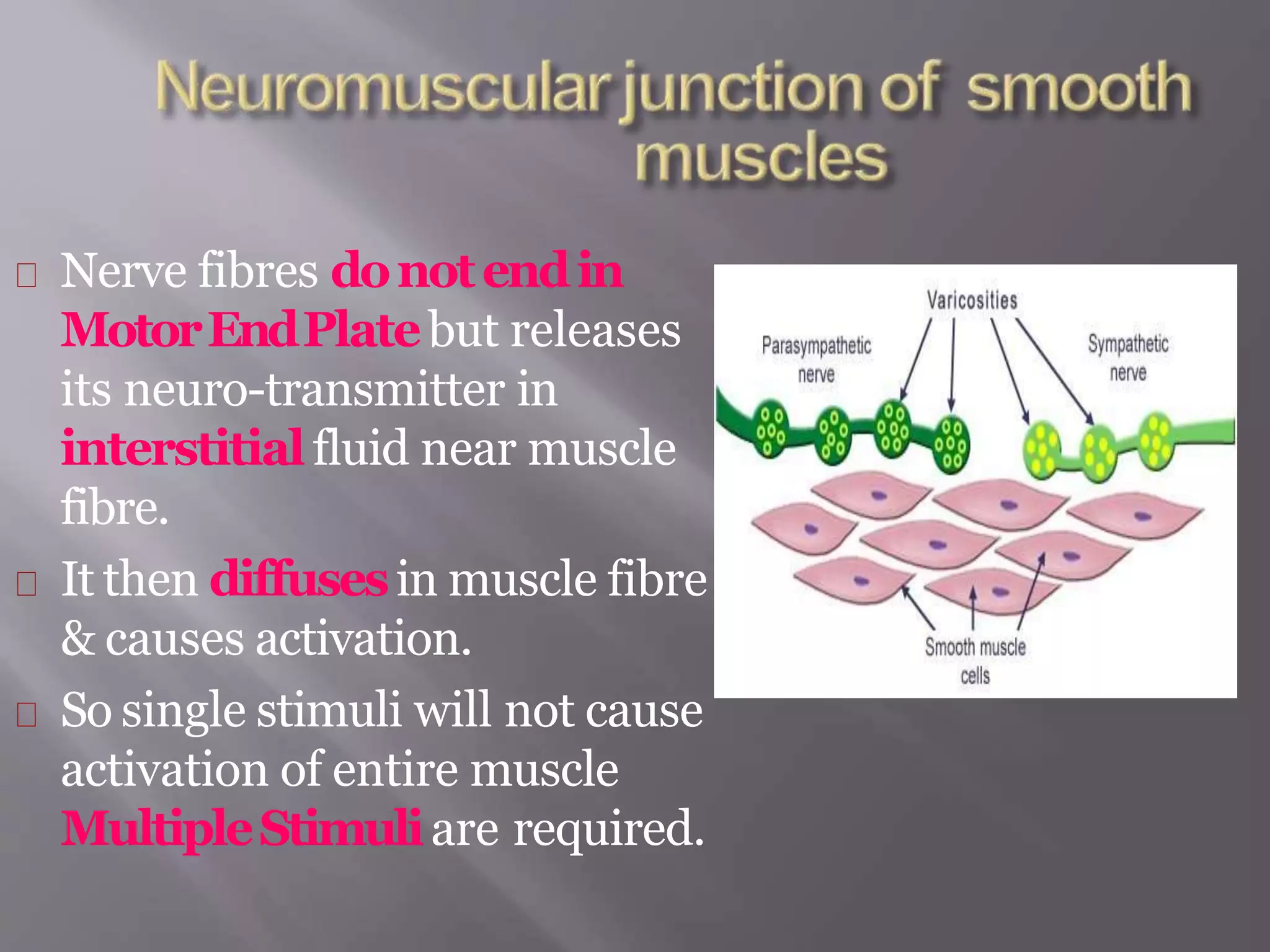
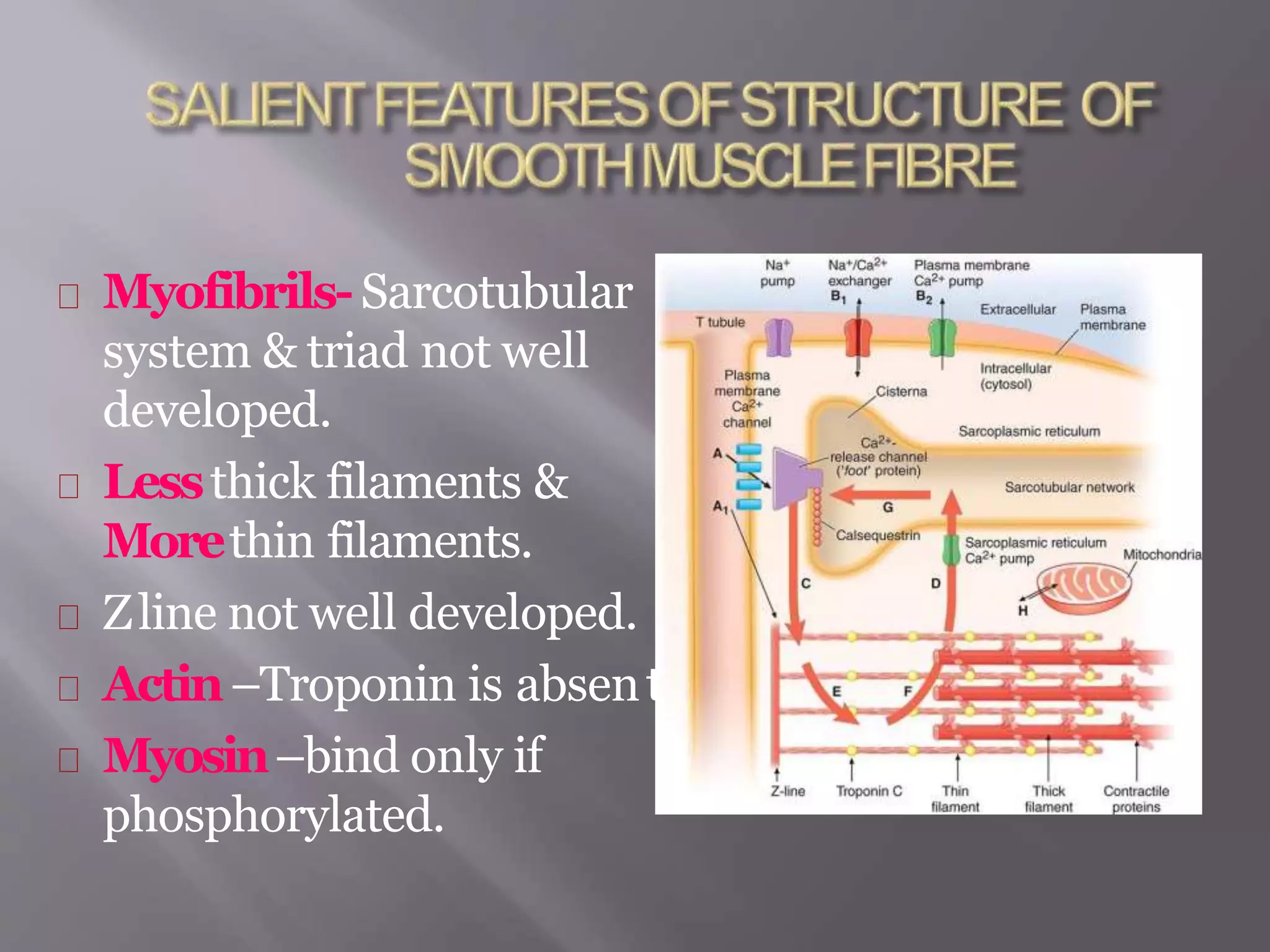
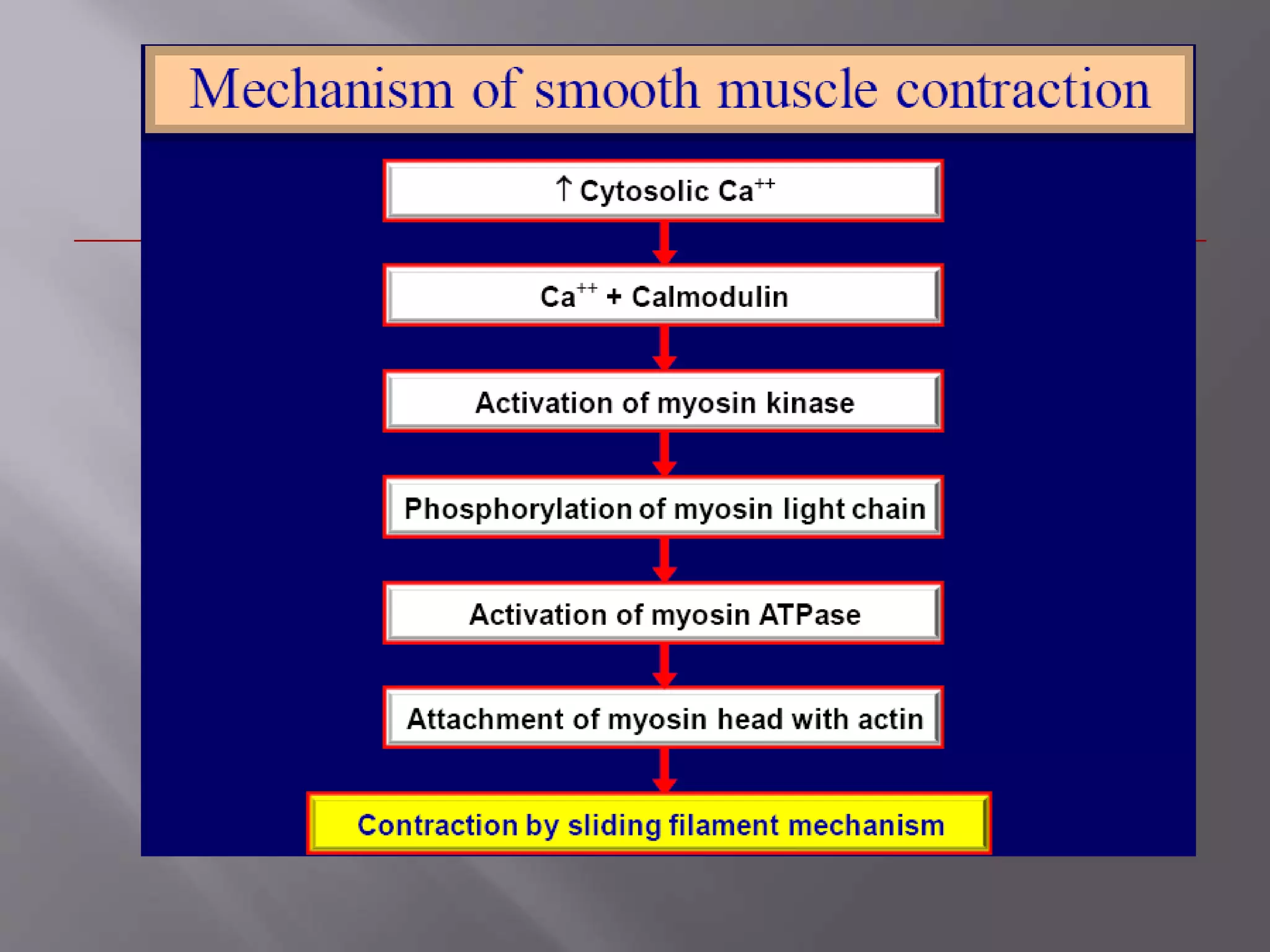
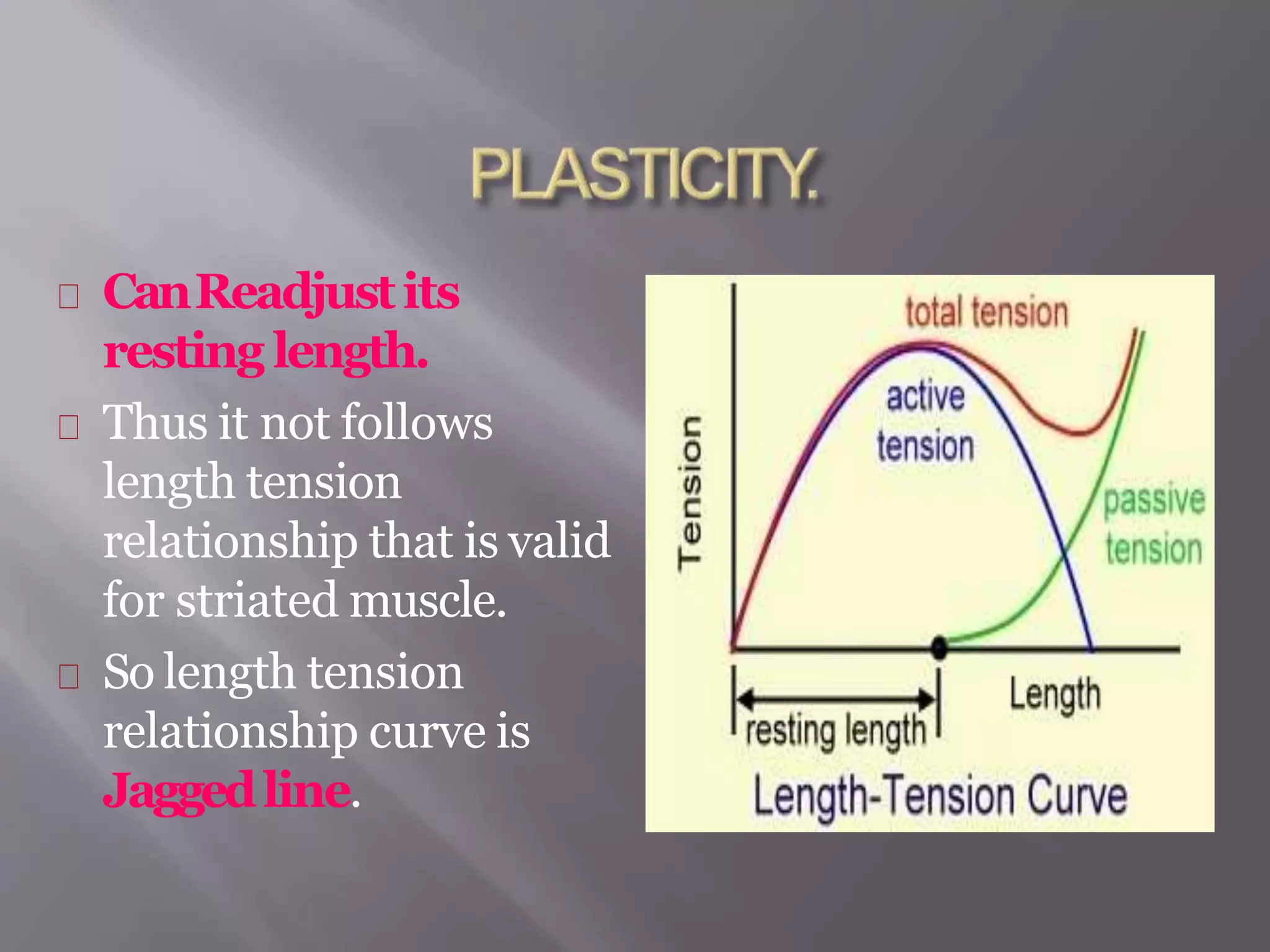
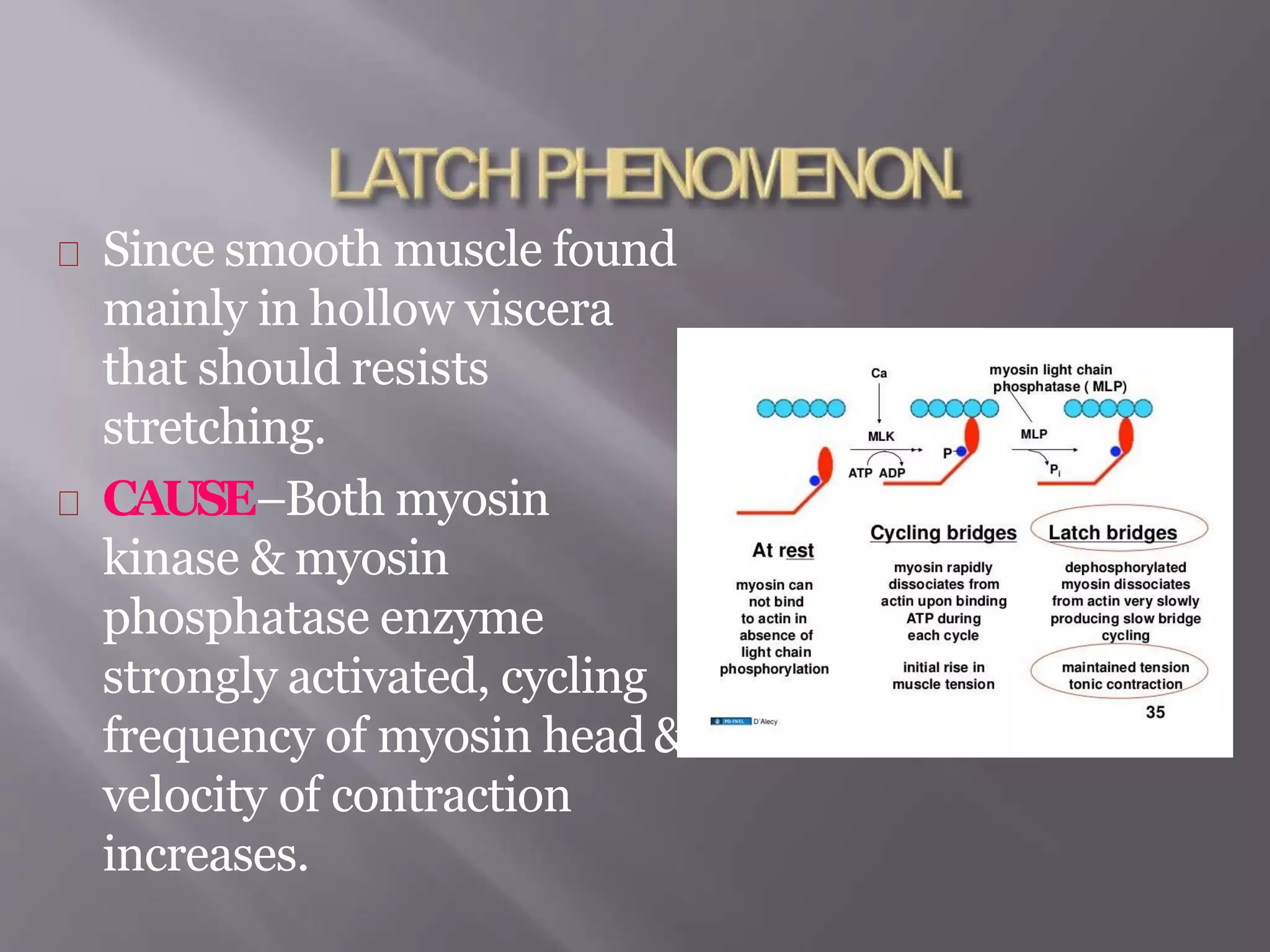
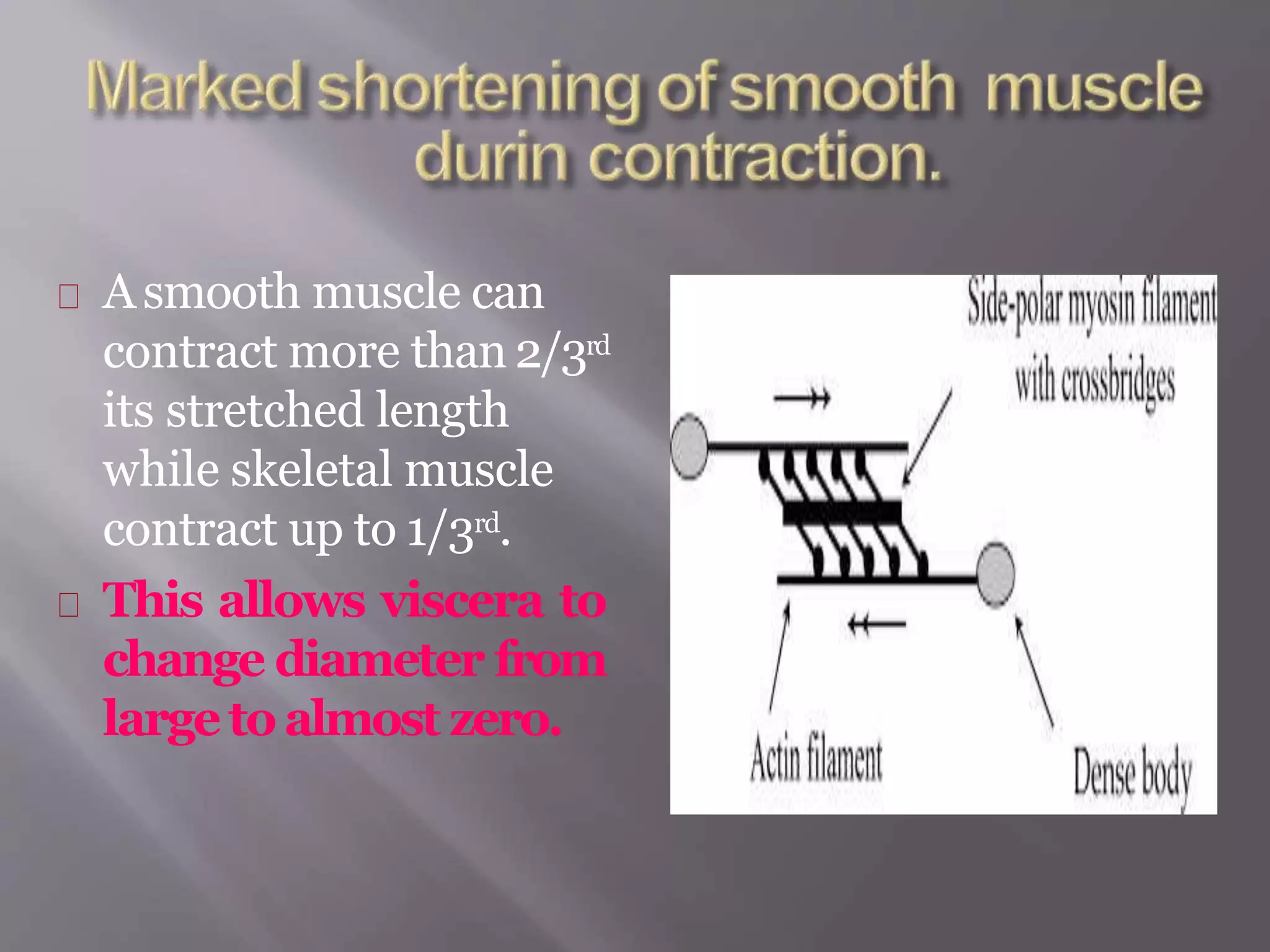
Smooth muscle is involuntary muscle found in hollow organs and blood vessels. It exists as single-unit or multi-unit smooth muscle. Single-unit smooth muscle contracts as a syncytium through gap junctions and has its own pacemaker activity. Multi-unit smooth muscle contracts through neural stimulation. Contraction is initiated by an action potential causing calcium entry, which activates myosin light chain kinase and cross-bridge cycling between actin and myosin for sustained contraction. Smooth muscle allows organs to change shape dramatically with less energy than skeletal muscle.