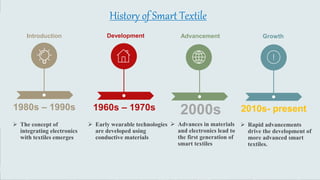
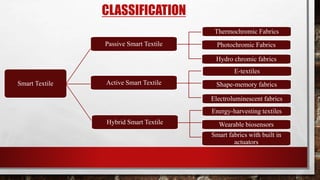
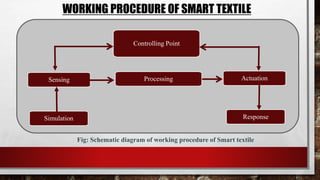
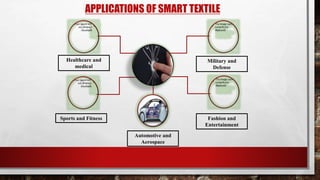
Smart textiles are materials that combine traditional textile components with advanced technologies to provide additional functionalities. They can sense and react to their environment or user inputs. Smart textiles are classified as passive, active, or hybrid. Passive smart textiles respond to stimuli without external power while active ones incorporate electronics and require power. Hybrid smart textiles combine passive and active elements. Potential applications of smart textiles include healthcare, sports, fashion, and more. Widespread adoption of smart textiles faces challenges regarding costs, data security, and infrastructure.