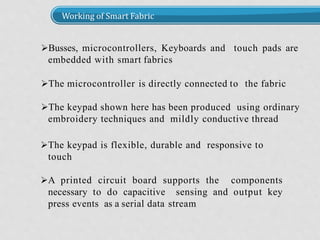
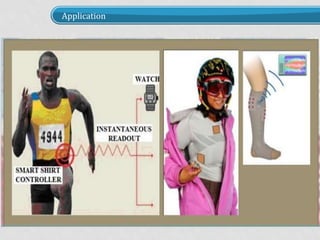
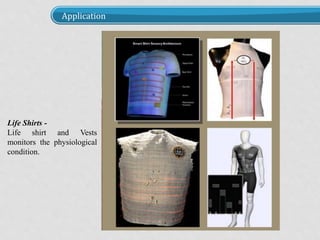
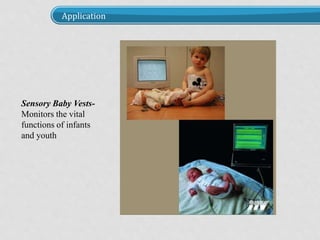
The document discusses smart fabrics and intelligent fabrics. It defines smart fabrics as fabrics that can sense environmental conditions or stimuli, while intelligent fabrics can both sense and react to stimuli. It describes different types of smart fabrics including aesthetic fabrics that change color and performance-enhancing fabrics for applications like sports. The document outlines how smart fabrics work using components like microcontrollers and sensors. It provides examples of applications of smart fabrics like life shirts that monitor physiology and sensory baby vests that monitor infant vital functions.