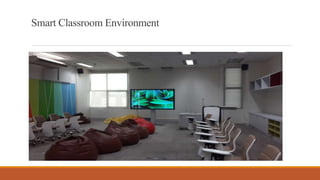
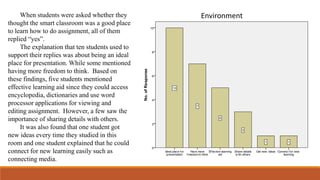
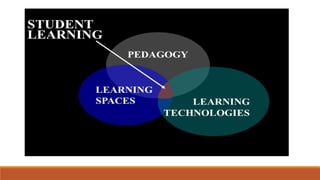
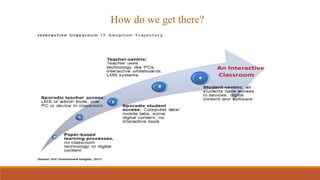
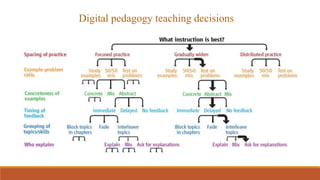
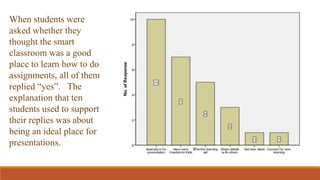
The document discusses the use of a smart classroom to support Thai students' learning. It describes the features of a smart classroom, including a smart whiteboard, smart tools, iPad charging, and connectivity. Students were asked if the smart classroom was a good place to learn assignments. All students replied yes, noting it was ideal for presentations and allowed freedom to think and access resources. The document advocates for an interactive learning environment and methodology in the smart classroom to nurture learning through varied contexts and spaced practice over time.