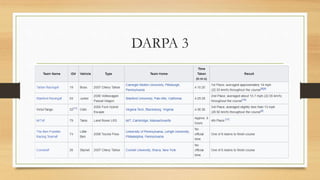
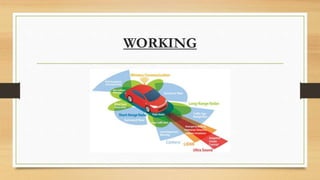
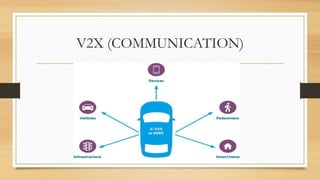
The document discusses the history and development of self-driving cars. It begins with early concepts in the 1920s and progresses through milestones like the DARPA Challenges. Key technologies that enable self-driving functionality are described, including sensors like LIDAR and radar, computer vision, and vehicle communication systems. Challenges remaining include operating in all weather and unpredictable urban environments. Potential applications and pros are outlined, such as increased safety, reduced traffic and emissions. Cons include security issues, potential job losses, and difficulties with sensing in adverse conditions like snow. Leaders in the field like Waymo are leveraging advances in AI and deep learning to progress towards fully autonomous vehicles.