Embed presentation
Download to read offline



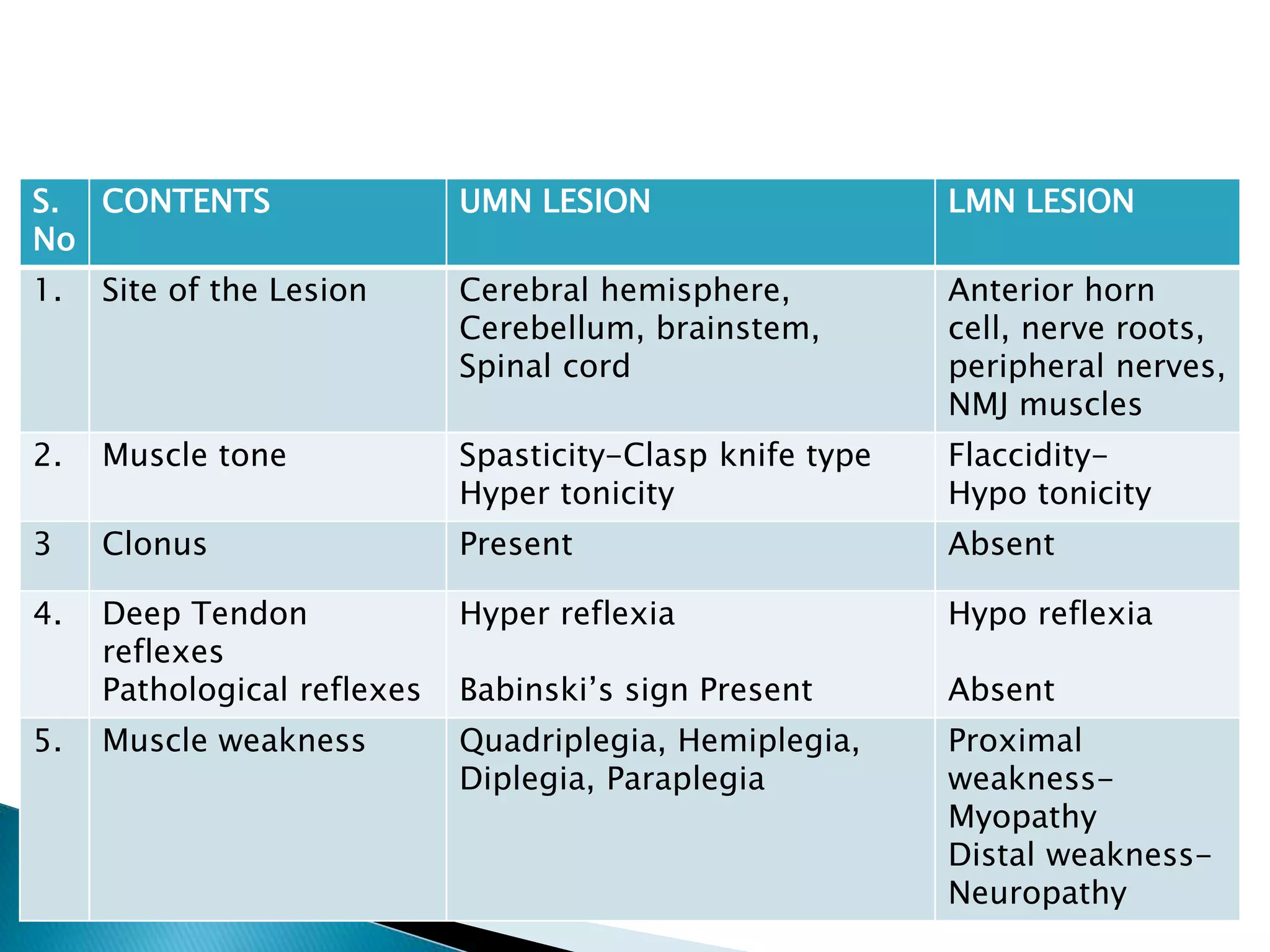
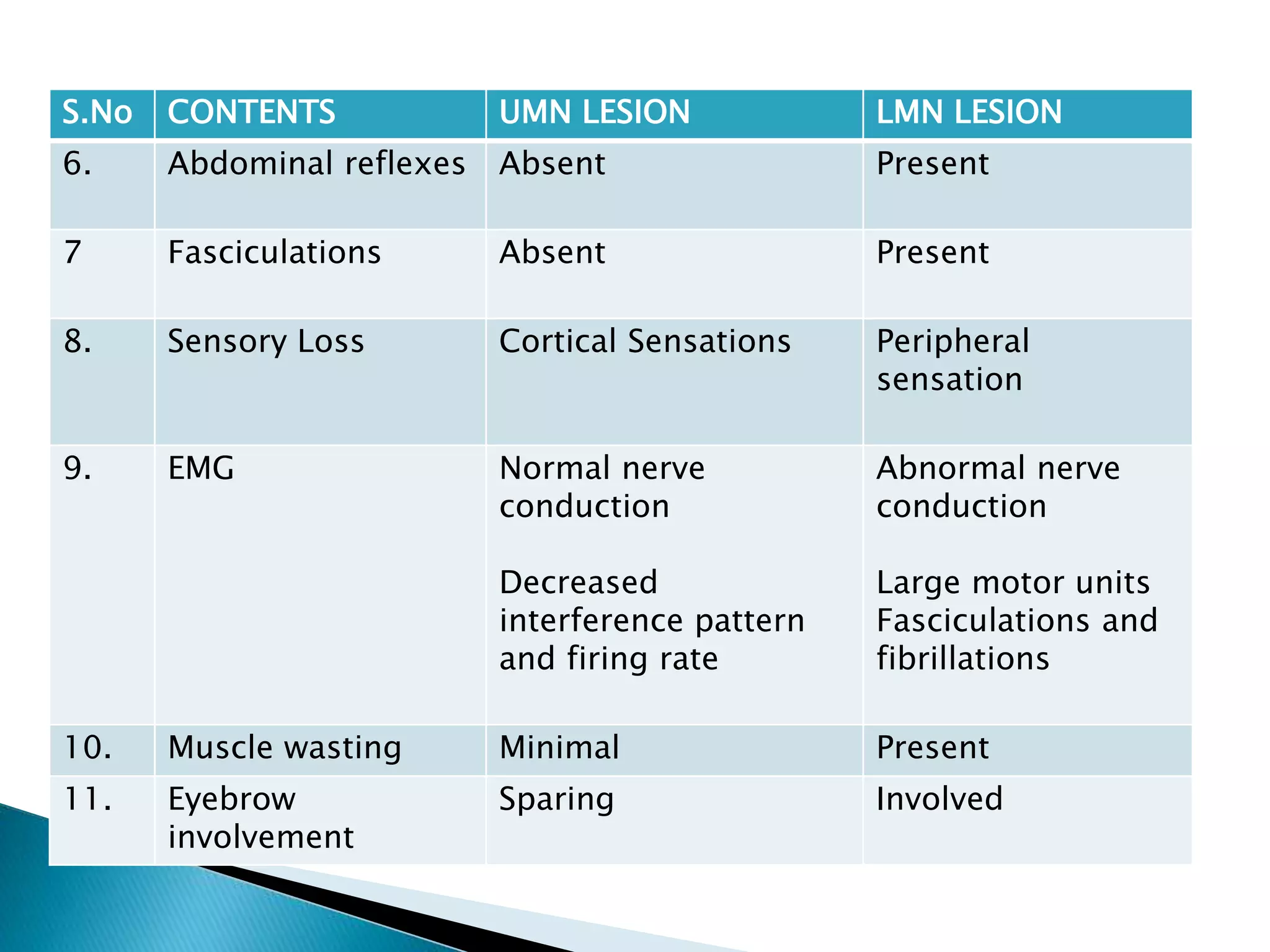

Upper motor neuron lesions occur in the cerebral cortex or brainstem and cause symptoms such as spasticity, hyperreflexia, pathological reflexes like Babinski's sign, and minimal muscle wasting. Lower motor neuron lesions occur in the spinal cord, nerve roots, or peripheral nerves and result in flaccidity, hyporeflexia, absent reflexes, fasciculations, muscle wasting, and peripheral sensory loss. The main differences between upper and lower motor neuron lesions are in the site of the lesion and the resulting muscle tone, reflexes, and patterns of weakness and sensory involvement.





