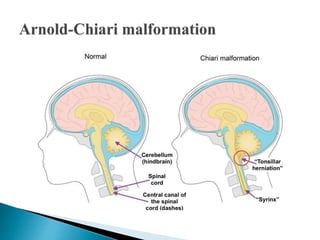
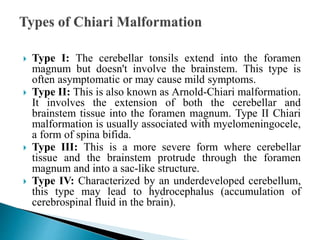
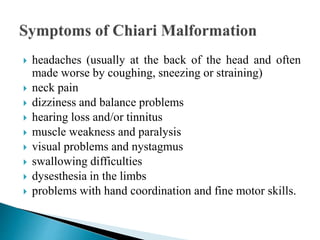
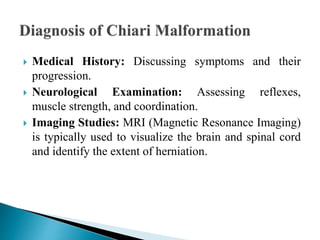
Arnold-Chiari malformation is a structural defect where the cerebellum, which controls balance, protrudes through the opening at the base of the skull. There are four types with varying severity, from type I where only the cerebellar tonsils extend through, to type IV with an underdeveloped cerebellum. Common symptoms include headaches, neck pain, dizziness, weakness, and difficulty swallowing. Diagnosis involves medical history, neurological exam, and an MRI to identify the extent of herniation. Treatment depends on the type but may include surgery to repair other issues, shunt placement, decompression, and physiotherapy to help manage symptoms.