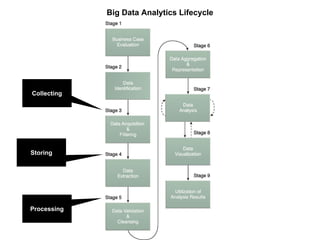
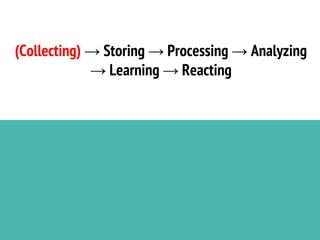
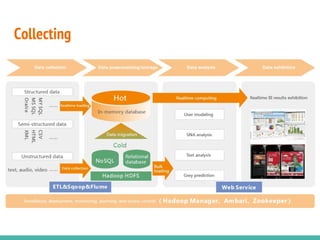
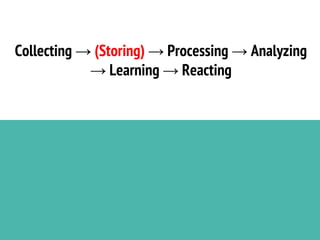
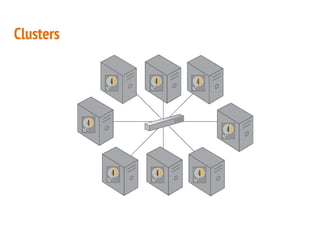
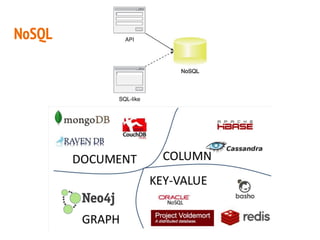
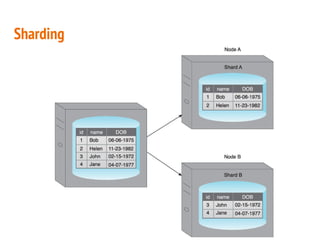
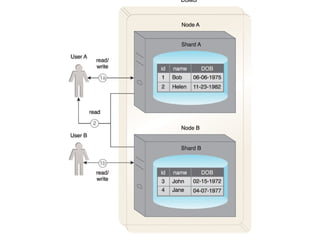
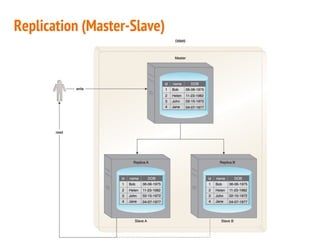
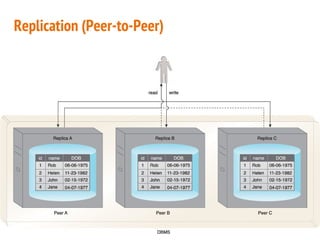
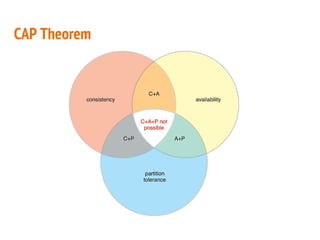
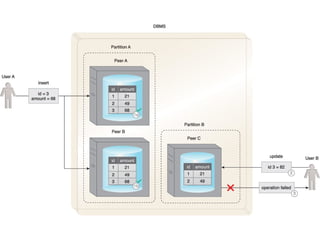
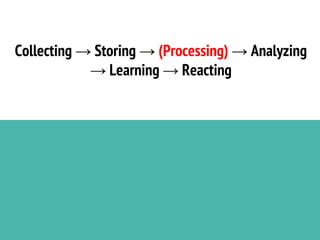
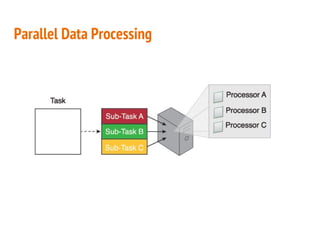
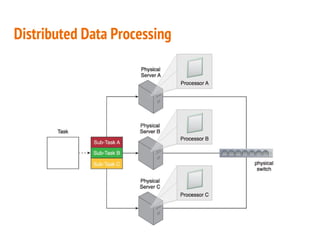
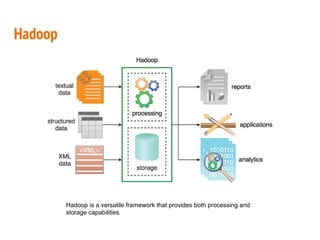
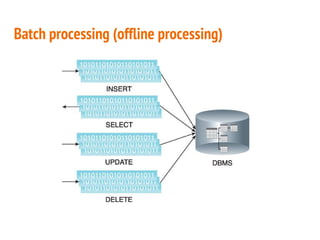
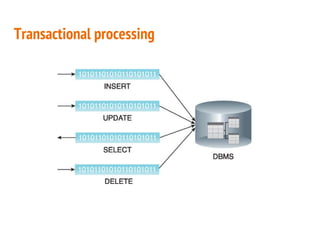
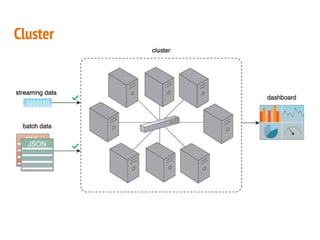
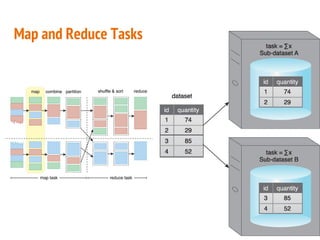
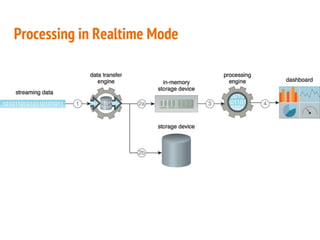
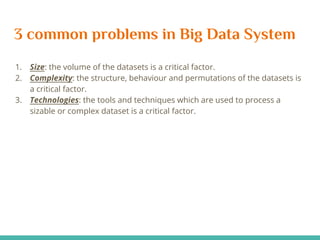
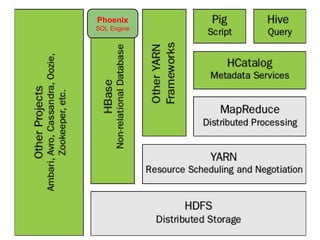
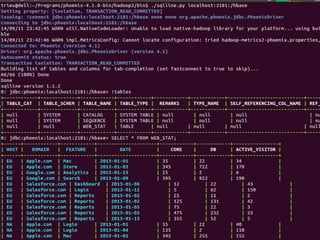
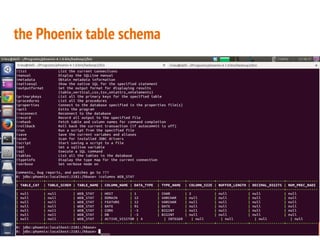
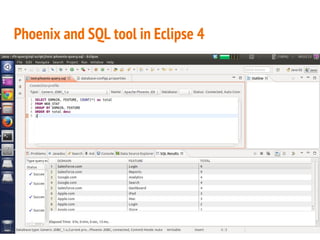
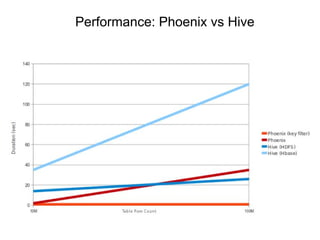
This document discusses the process of collecting, storing, processing and analyzing big data. It covers the key concepts and technologies for collecting data using tools like Apache Sqoop and Kafka, storing data using clusters, file systems, NoSQL databases and concepts like sharding and replication. It also discusses processing data using parallel and distributed processing with Hadoop, and analyzing data using Apache Phoenix which provides a SQL interface to query HBase databases.