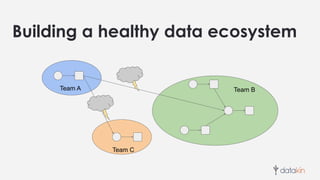
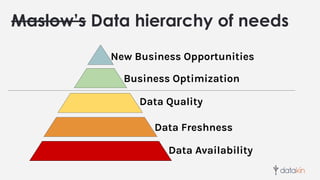
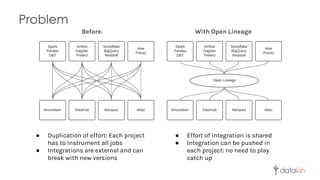
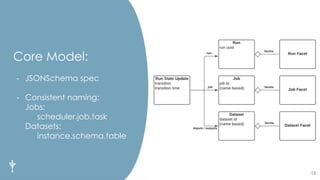
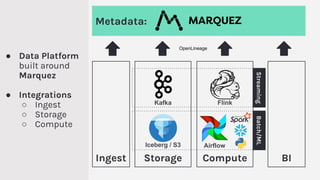
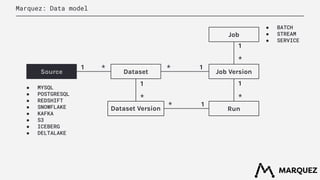
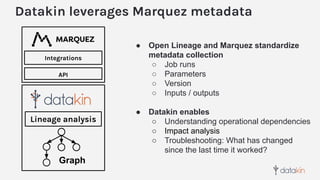
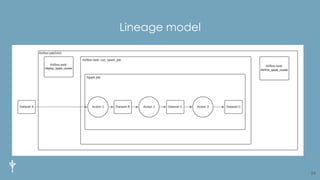
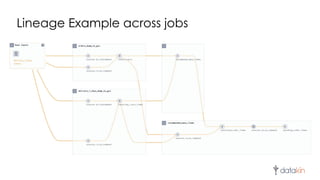
The document discusses the importance of metadata in data ecosystems and introduces OpenLineage, an open standard for lineage collection. It highlights the need for effective metadata management to avoid duplication and enhance collaboration across data pipelines, with an emphasis on integrations and observability in Spark. The document also outlines the core model and facets for metadata, detailing how OpenLineage and Marquez can facilitate understanding of data dependencies and support troubleshooting efforts.