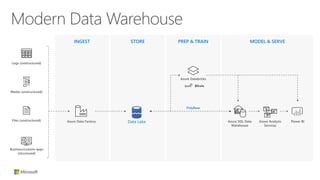
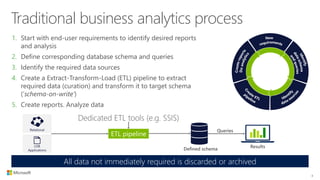
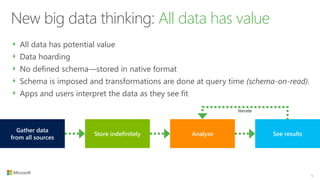
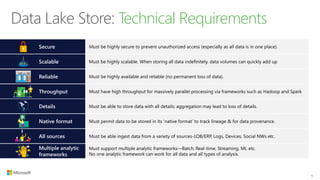
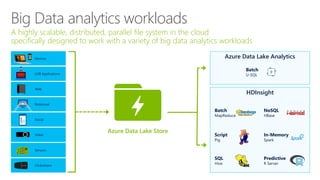
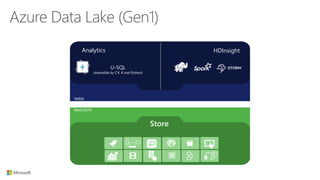
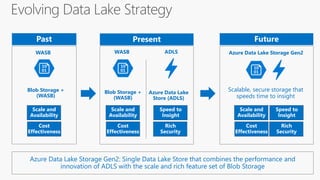
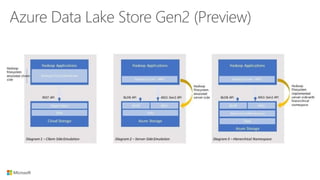
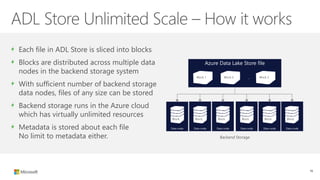
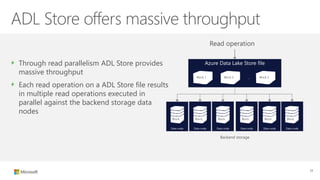
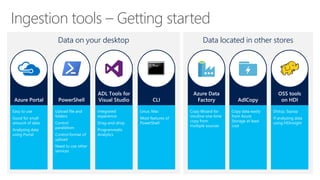
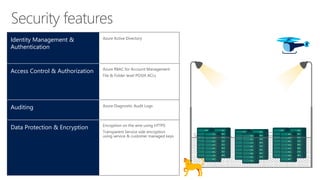
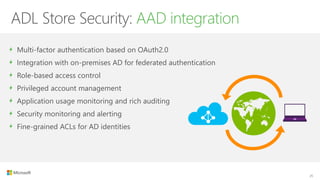
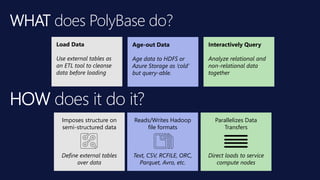
The document outlines the architecture and processes of Azure Data Lake Store, emphasizing the ingestion, processing, and analytics of data in various formats, both structured and unstructured. It highlights the importance of secure, scalable storage capable of supporting multiple analytic frameworks and high-throughput scenarios. Additionally, the document discusses the use of ETL processes, data management, and security features to handle big data efficiently while ensuring data integrity and availability.













![DROP EXTERNAL TABLE dbo.DimCurrency_external;
DROP EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT TSVFileFormat;
DROP EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT CSVFileFormat;
DROP EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE AzureDataLakeStore;
DROP DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL ADLCredential;
-- Create a Database Master Key.
--CREATE MASTER KEY;
-- Create a database scoped credential
CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL ADLCredential
WITH
IDENTITY = 'e785bd5xxxxxx-465xxxxxxxxxx36b@https://login.microsoftonline.com/72f988bf-86f1-41af-91ab-2d7cd011db47/oauth2/token',
--IDENTITY = 'app_id@oauth_token'
SECRET = 'eAMyYHQhgTn/aslkdfj28347skdjoe7512=sadf2=‘; --(This is not the real key!)
-- Create an external data source
CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE AzureDataLakeStore
WITH (
TYPE = HADOOP,
LOCATION = 'adl://audreydatalake.azuredatalakestore.net',
CREDENTIAL = ADLCredential
);
-- Create an external file format
CREATE EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT CSVFileFormat
WITH
( FORMAT_TYPE = DELIMITEDTEXT
, FORMAT_OPTIONS ( FIELD_TERMINATOR = ','
, STRING_DELIMITER = ''
, DATE_FORMAT = 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff'
, USE_TYPE_DEFAULT = FALSE
)
);
CREATE EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT TSVFileFormat
WITH
( FORMAT_TYPE = DELIMITEDTEXT
, FORMAT_OPTIONS ( FIELD_TERMINATOR = ''
, STRING_DELIMITER = ''
, DATE_FORMAT = 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff'
, USE_TYPE_DEFAULT = FALSE
)
);
-- Create an External Table
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [dbo].[DimCurrency_external] (
[0] [int] NOT NULL,
[1] [varchar](5) NULL,
[2] [varchar](500) NULL
)
WITH
(
LOCATION='/Files/DimCurrency.csv'
, DATA_SOURCE = AzureDataLakeStore
, FILE_FORMAT = CSVFileFormat
, REJECT_TYPE = VALUE
, REJECT_VALUE = 0
);
--Query the file from ADLS
SELECT [0] as CurrencyKey, [1] as CurrencyCode, [2] as CurrencyDescription
FROM [dbo].[DimCurrency_external];
--Load file directly into DW with CTAS
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.tables WHERE name = 'stgCurrency')
BEGIN
DROP TABLE stgCurrency
END;
CREATE TABLE dbo.stgCurrency
WITH (DISTRIBUTION = ROUND_ROBIN)
AS
SELECT [0] as CurrencyKey, [1] as CurrencyCode, [2] as CurrencyDescription
FROM dbo.DimCurrency_external;
SELECT * FROM stgCurrency;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datalakestoragepresentation-180905171102/85/Data-Analytics-Meetup-Introduction-to-Azure-Data-Lake-Storage-28-320.jpg)