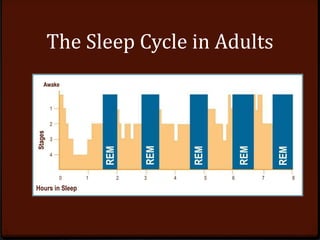
Sleep is essential to our overall health and well-being. It is key to our ability to perform cognitive and physical tasks, engage fully in life, and function productively and safely. The average sleep requirement varies by age, from 16-20 hours for infants to 6-8 hours for adults. There are two main types of sleep disorders - dyssomnias which affect sleep amount, timing or quality, and parasomnias which involve abnormal physical or experiential events during sleep. Sleep disorders can be treated through lifestyle modifications, behavioral therapies, medication, and treating any underlying medical conditions. Maintaining good sleep hygiene is important for promoting healthy sleep.