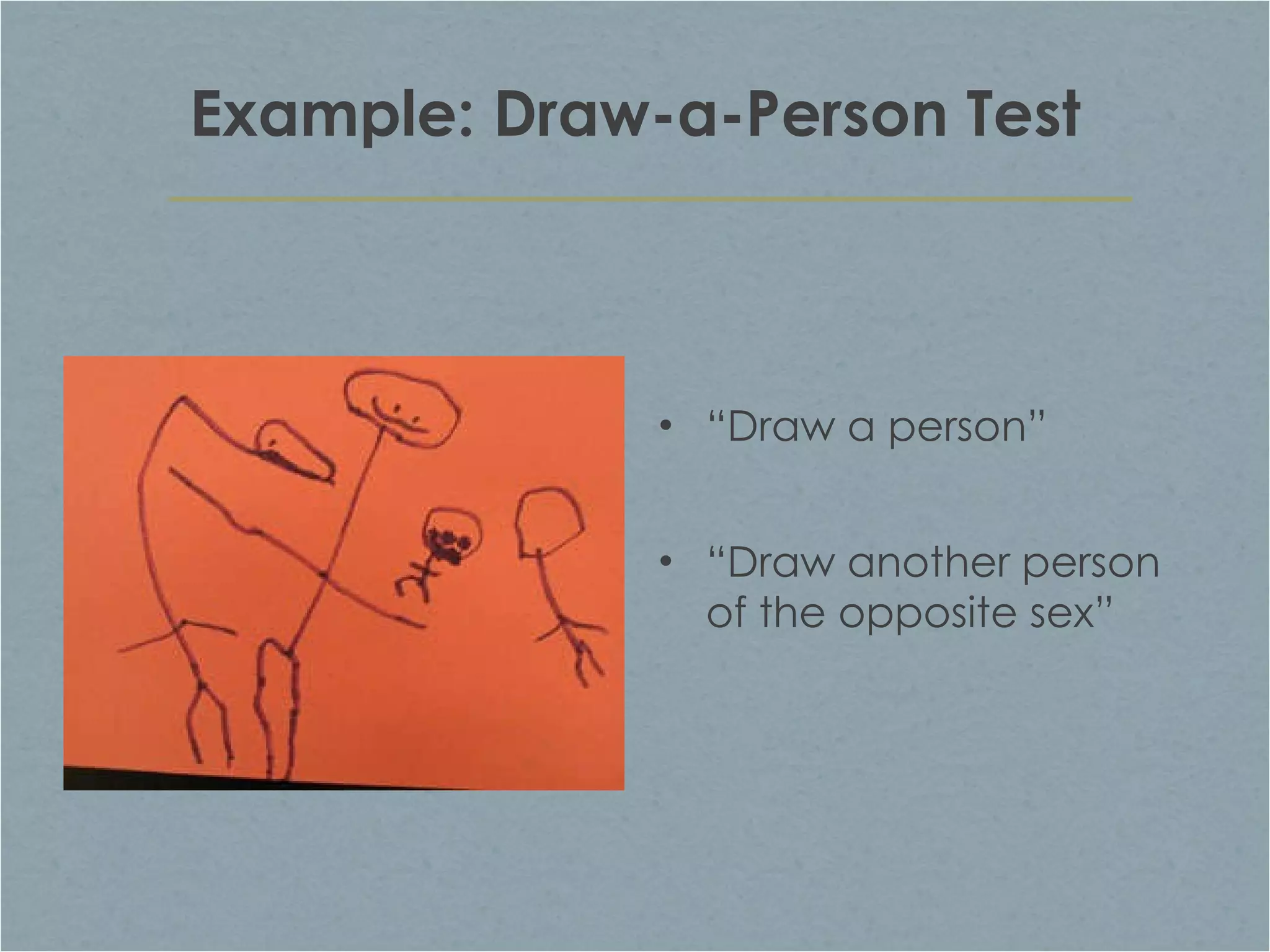
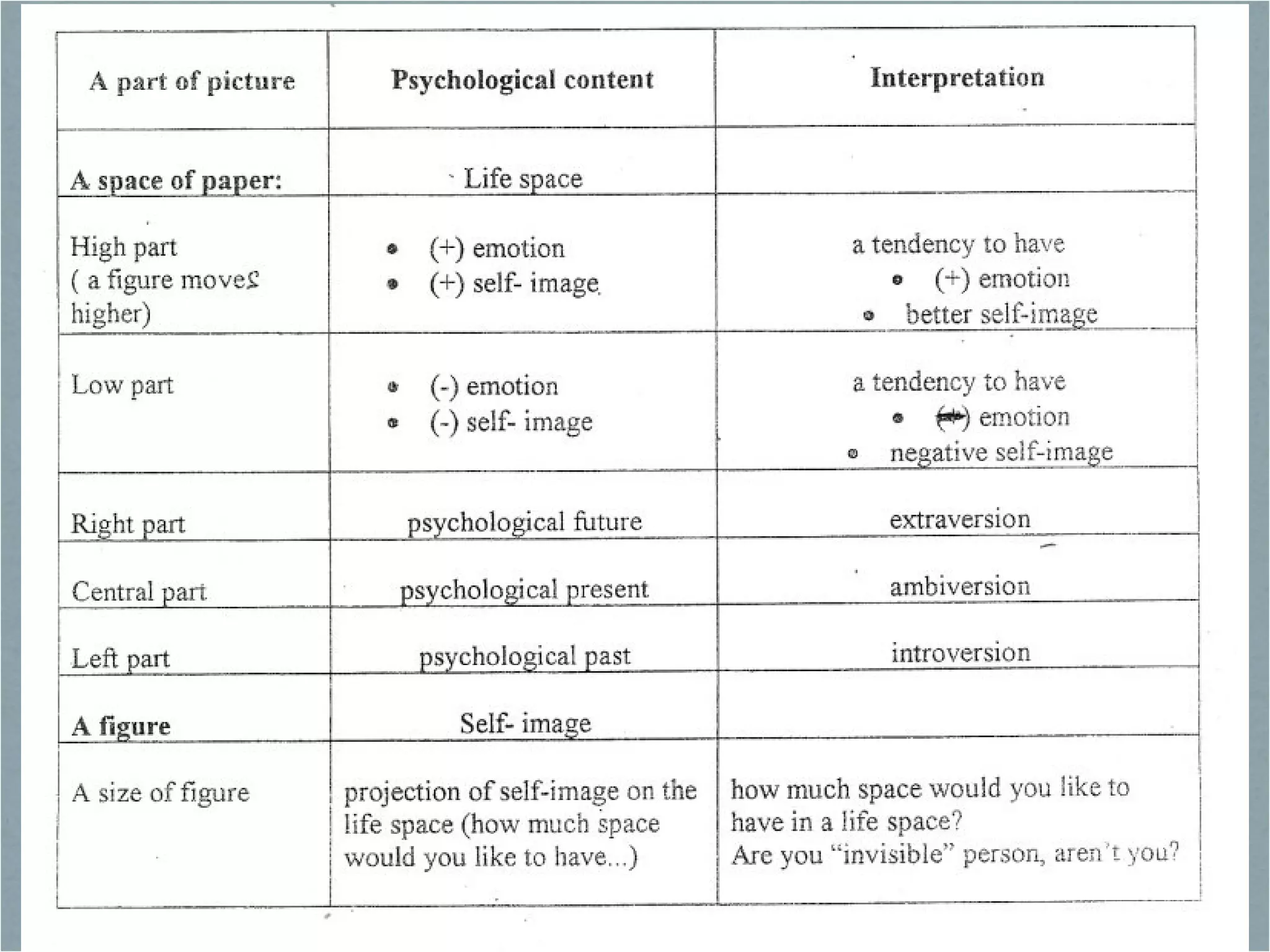
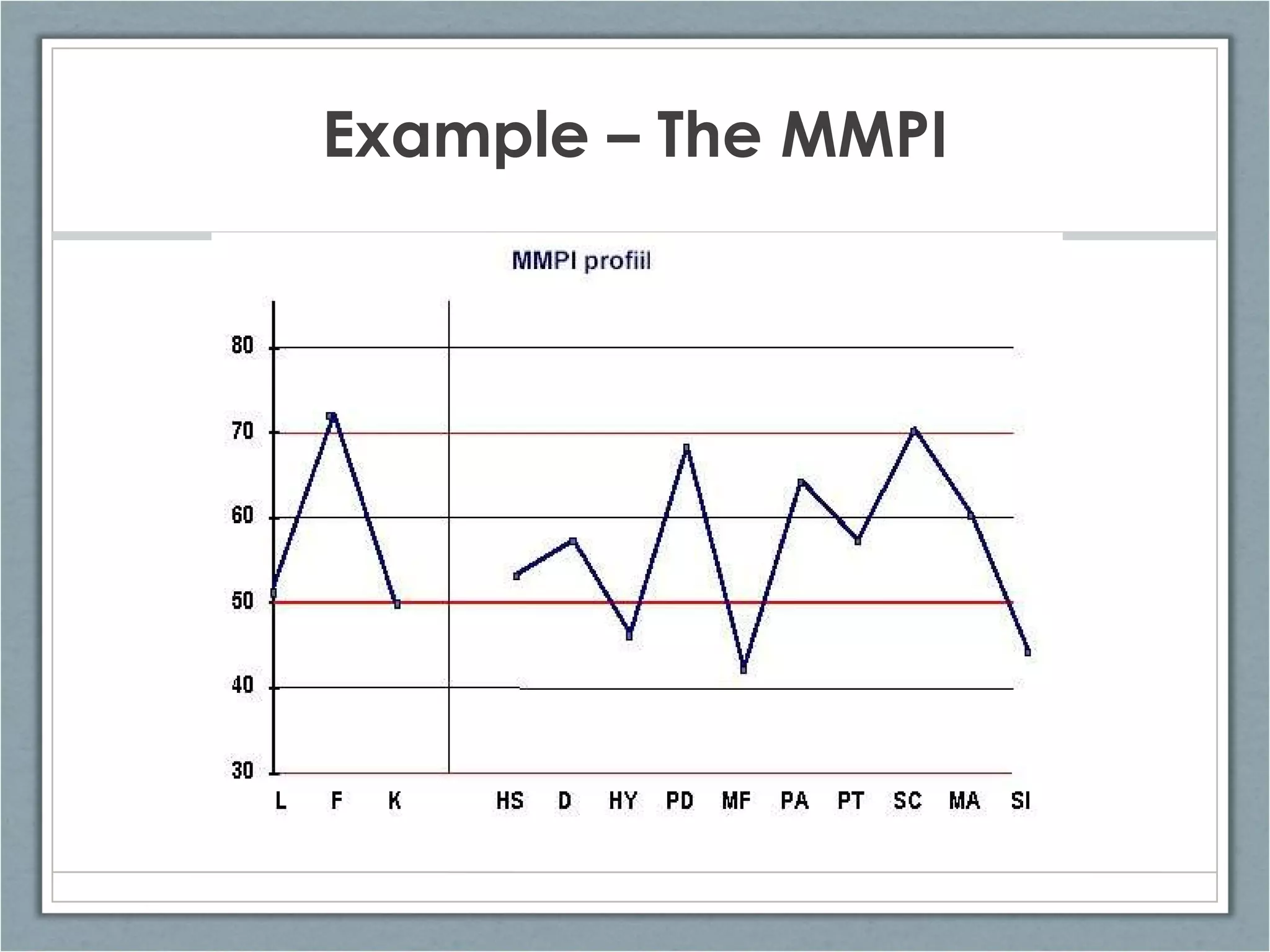
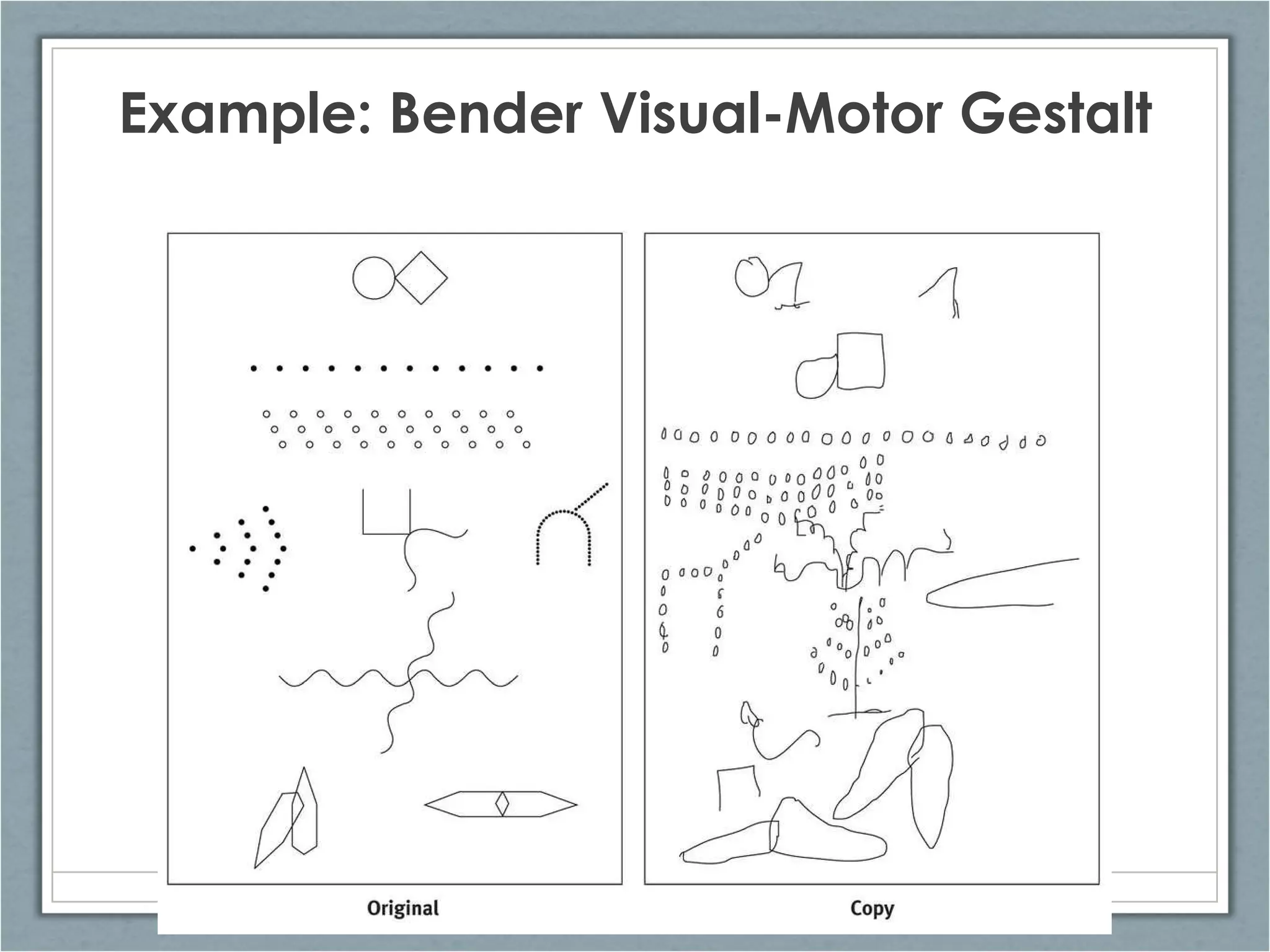
The document discusses clinical assessment and diagnosis in psychopathology. It describes the goals of assessment as understanding how and why a person is behaving abnormally and how they can be helped. Assessment tools should be standardized, reliable, and valid. Clinical interviews and psychological tests are common forms of assessment. Treatment decisions are based on assessment and diagnosis to determine an appropriate treatment plan. Research shows that therapy is generally effective compared to no treatment, and certain therapies are effective for specific disorders.