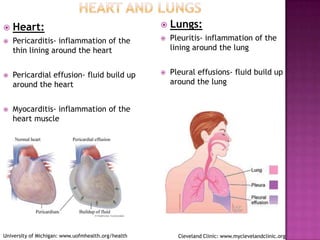
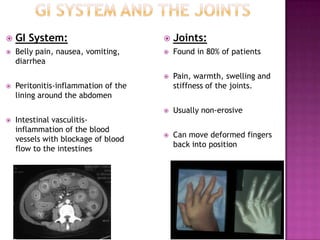
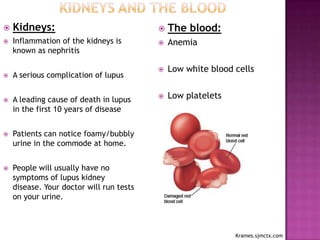
This document provides information about lupus and its treatments. It begins by noting that lupus can affect the body in many ways and medications are used to protect the body from lupus. It then discusses how lupus is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the body. It outlines the common symptoms and organ systems affected by lupus. The document concludes by describing several common medications used to treat lupus, including their purposes, side effects, and monitoring requirements.