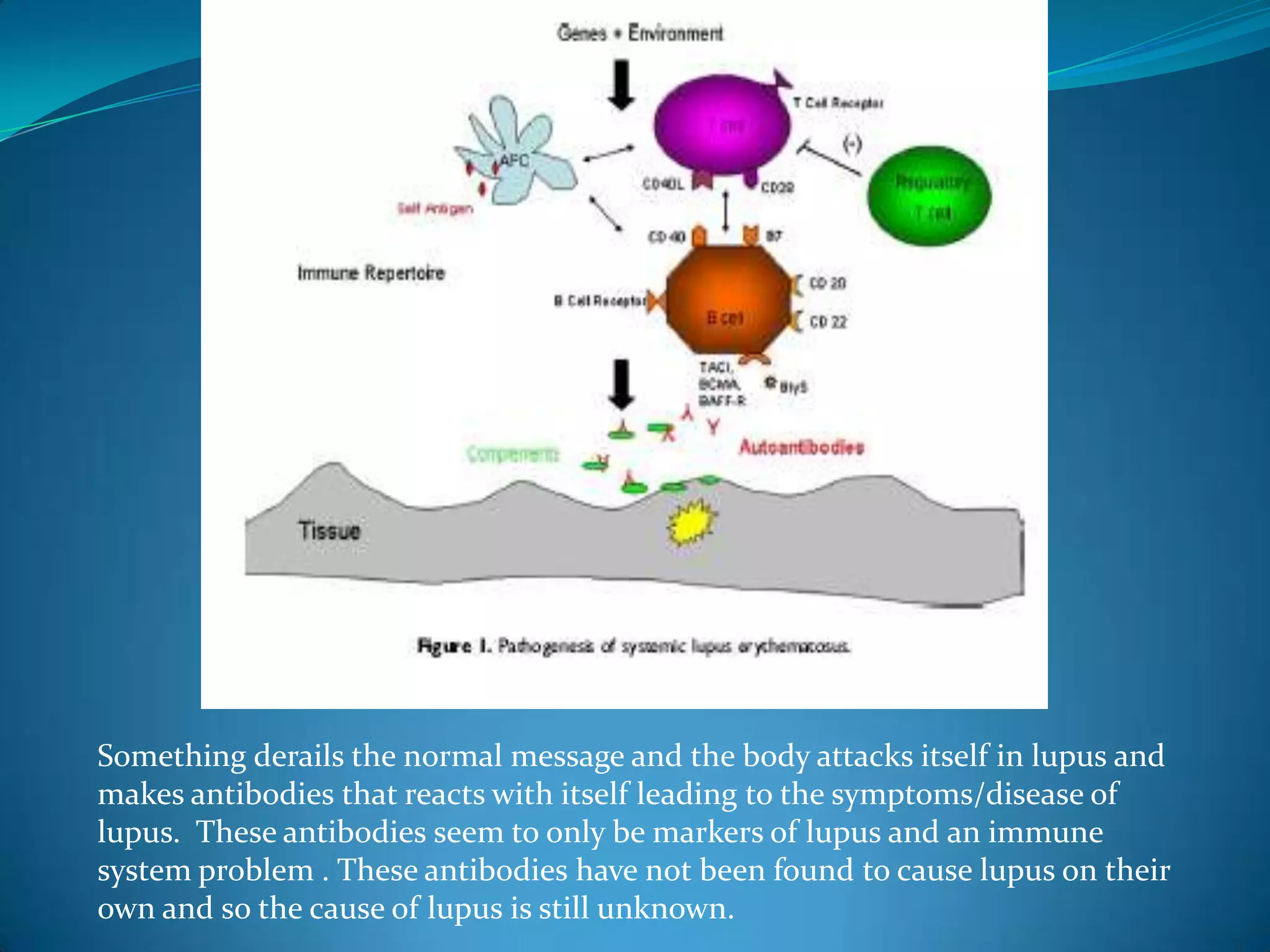
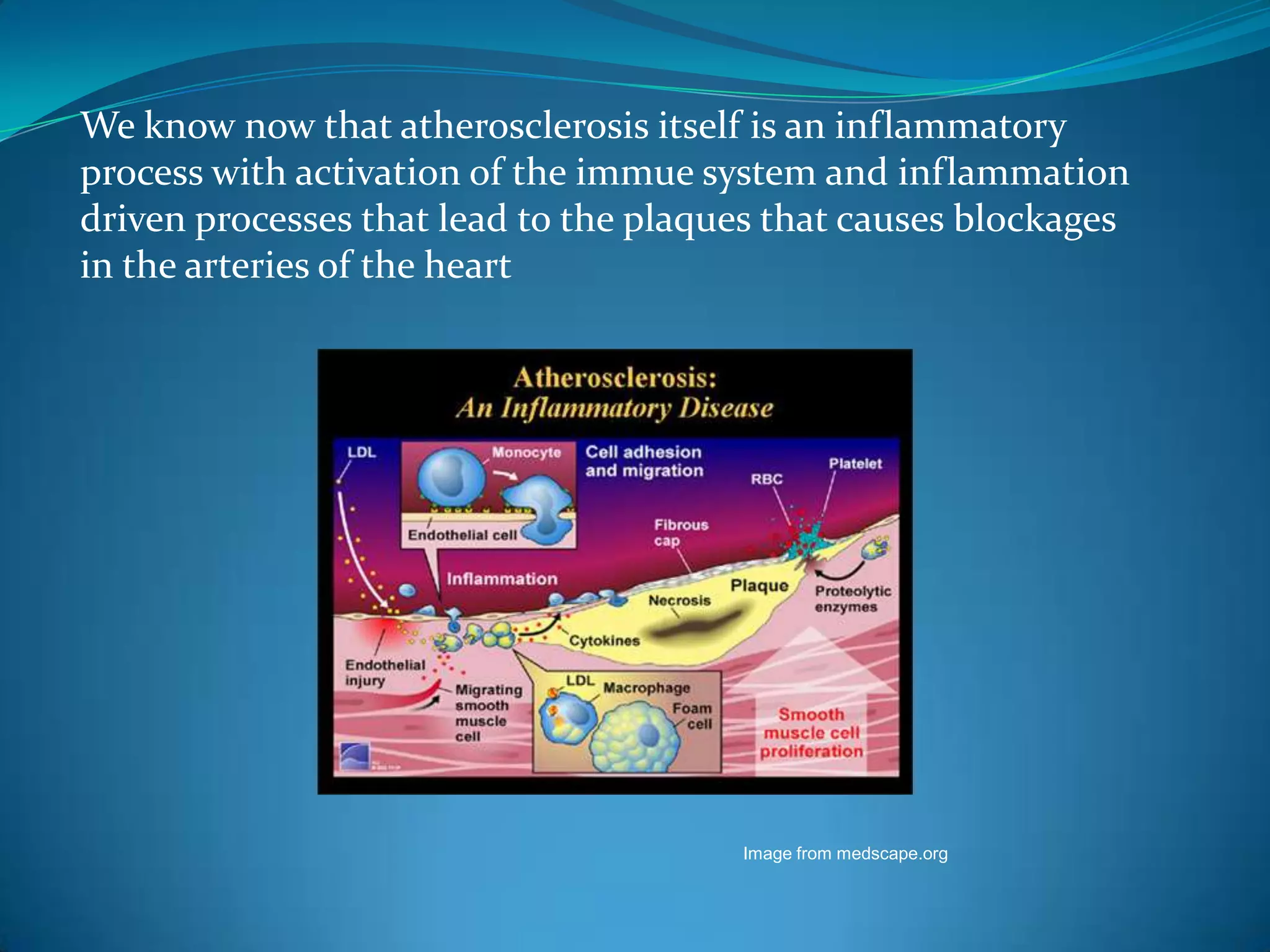
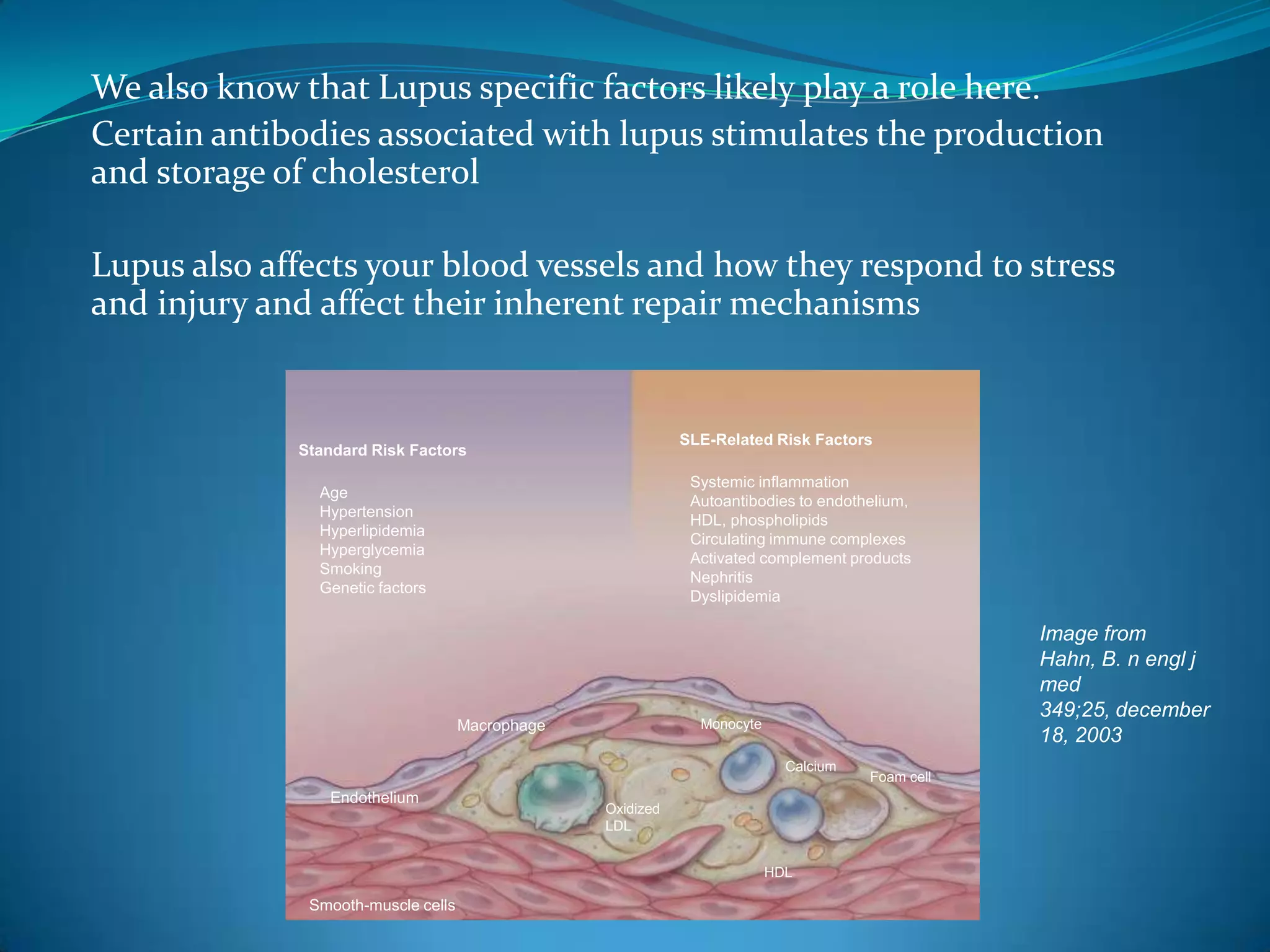
This document discusses systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and its effects on the heart. SLE is a chronic inflammatory disease that can affect multiple organs, including the heart. It can cause valvular heart disease, pericarditis, myocarditis, and conduction defects. SLE is also associated with an increased risk of accelerated atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease. Reasons for this include traditional risk factors, steroid use, inflammation from SLE, and certain autoantibodies that affect blood vessels and cholesterol levels. Screening and monitoring of cardiac involvement is important for lupus patients.