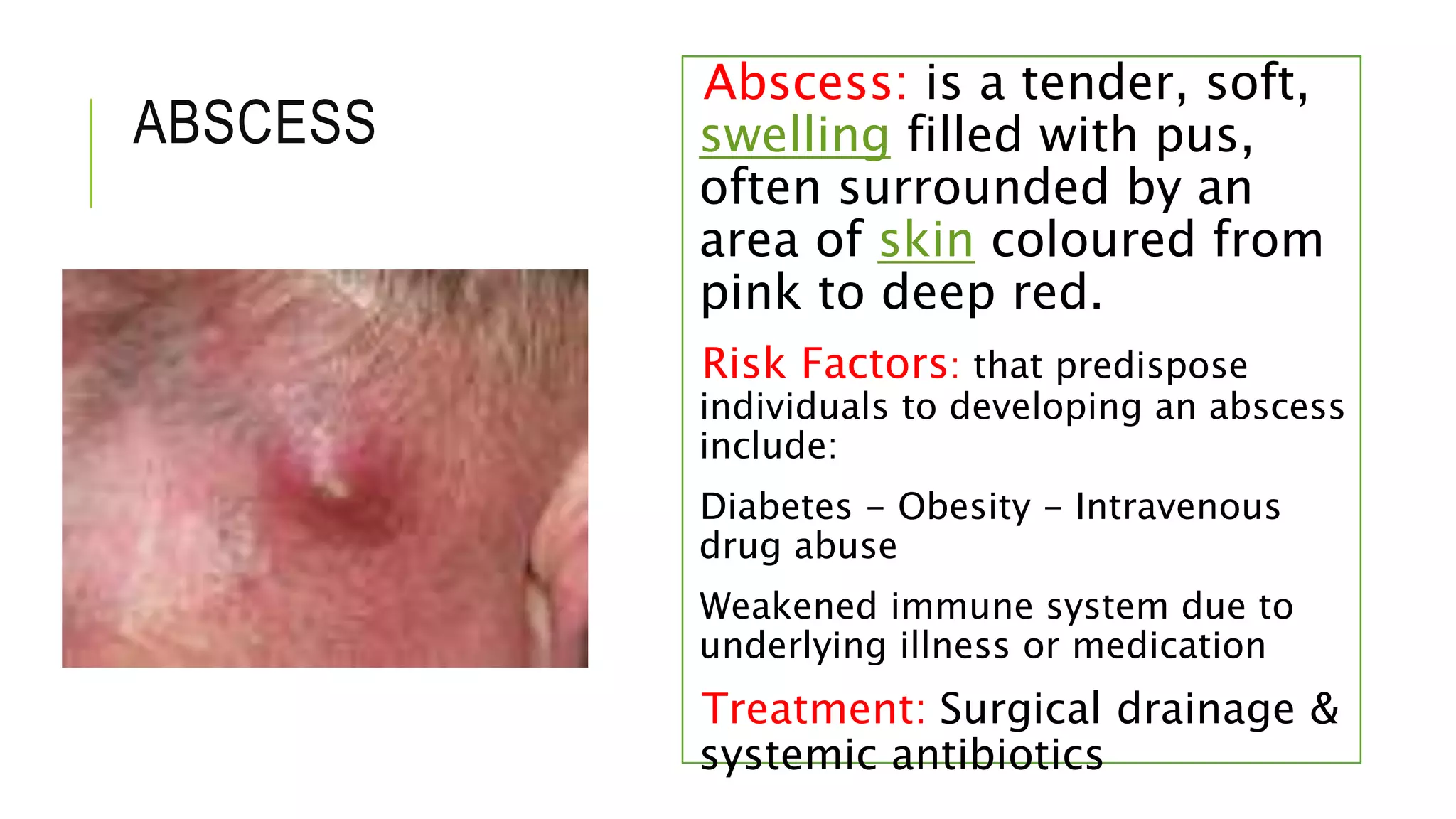
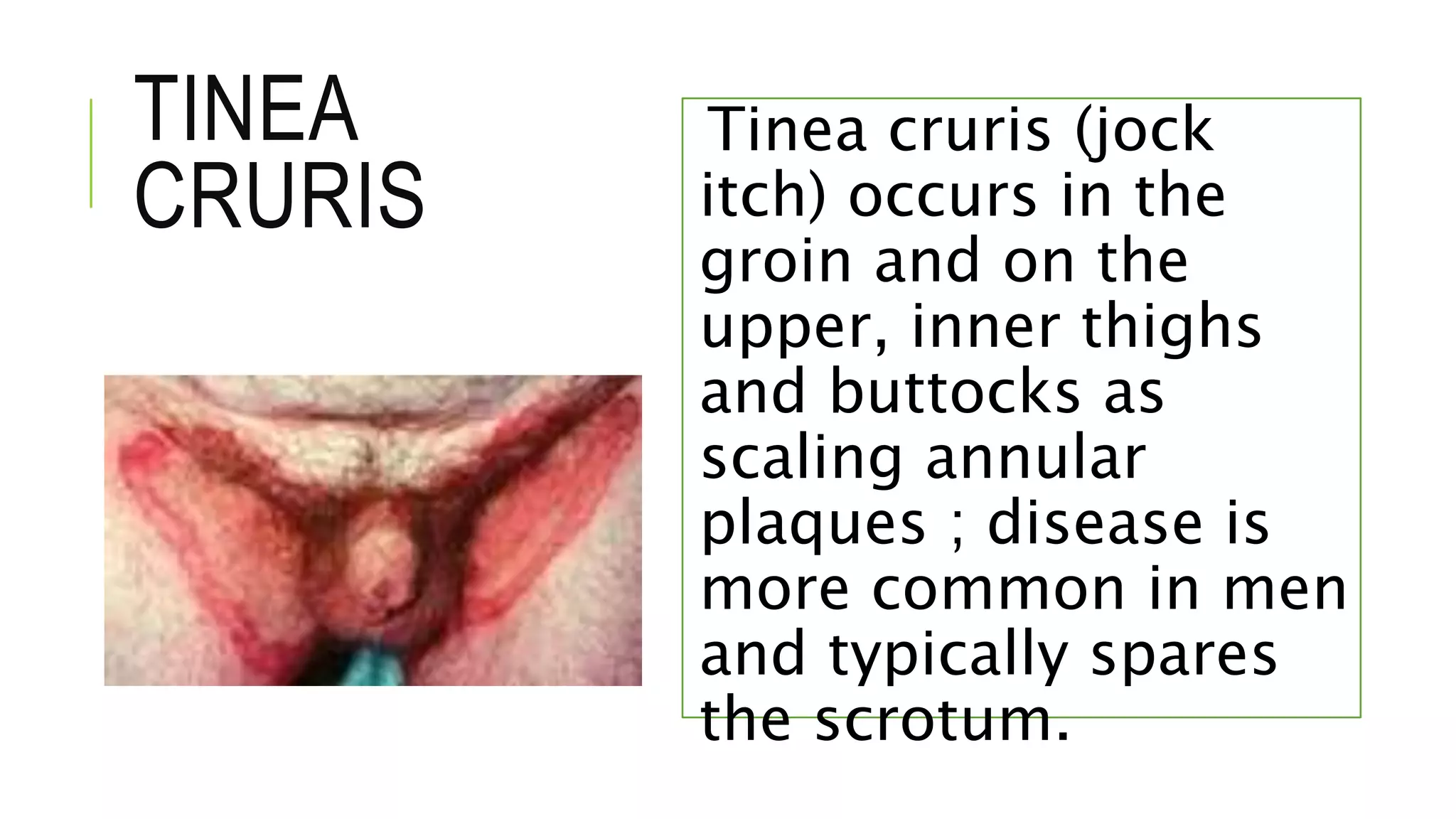
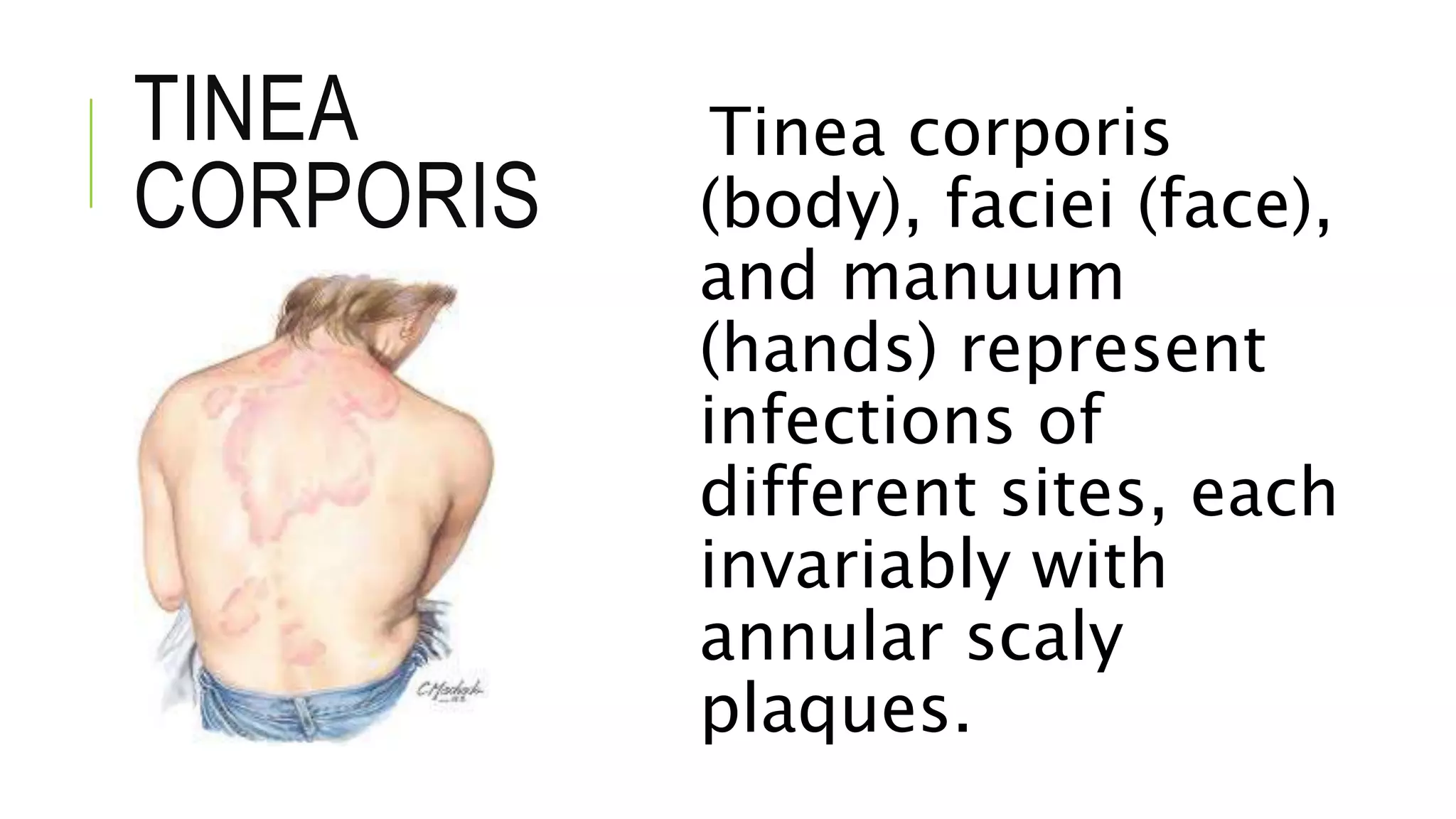
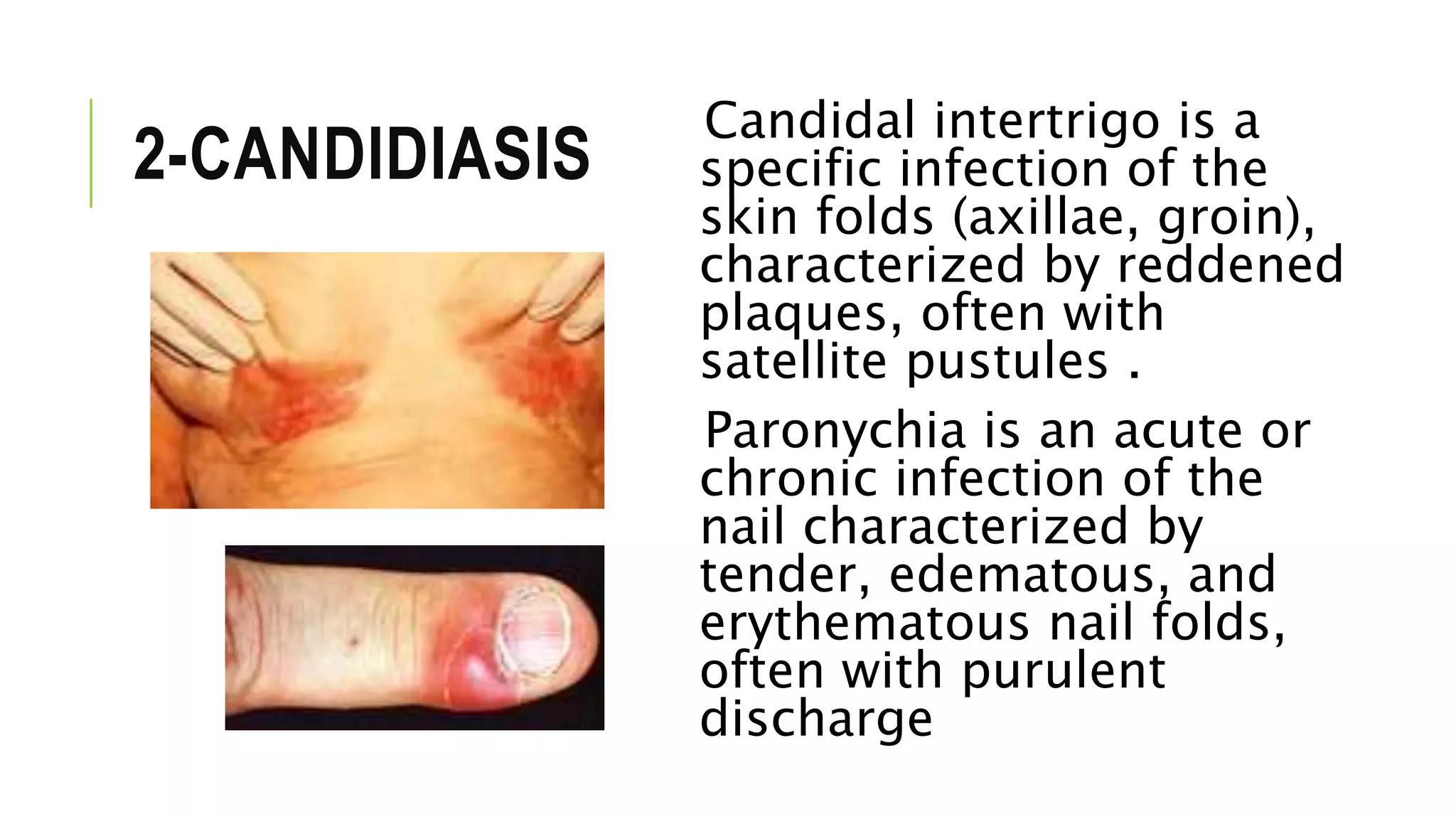
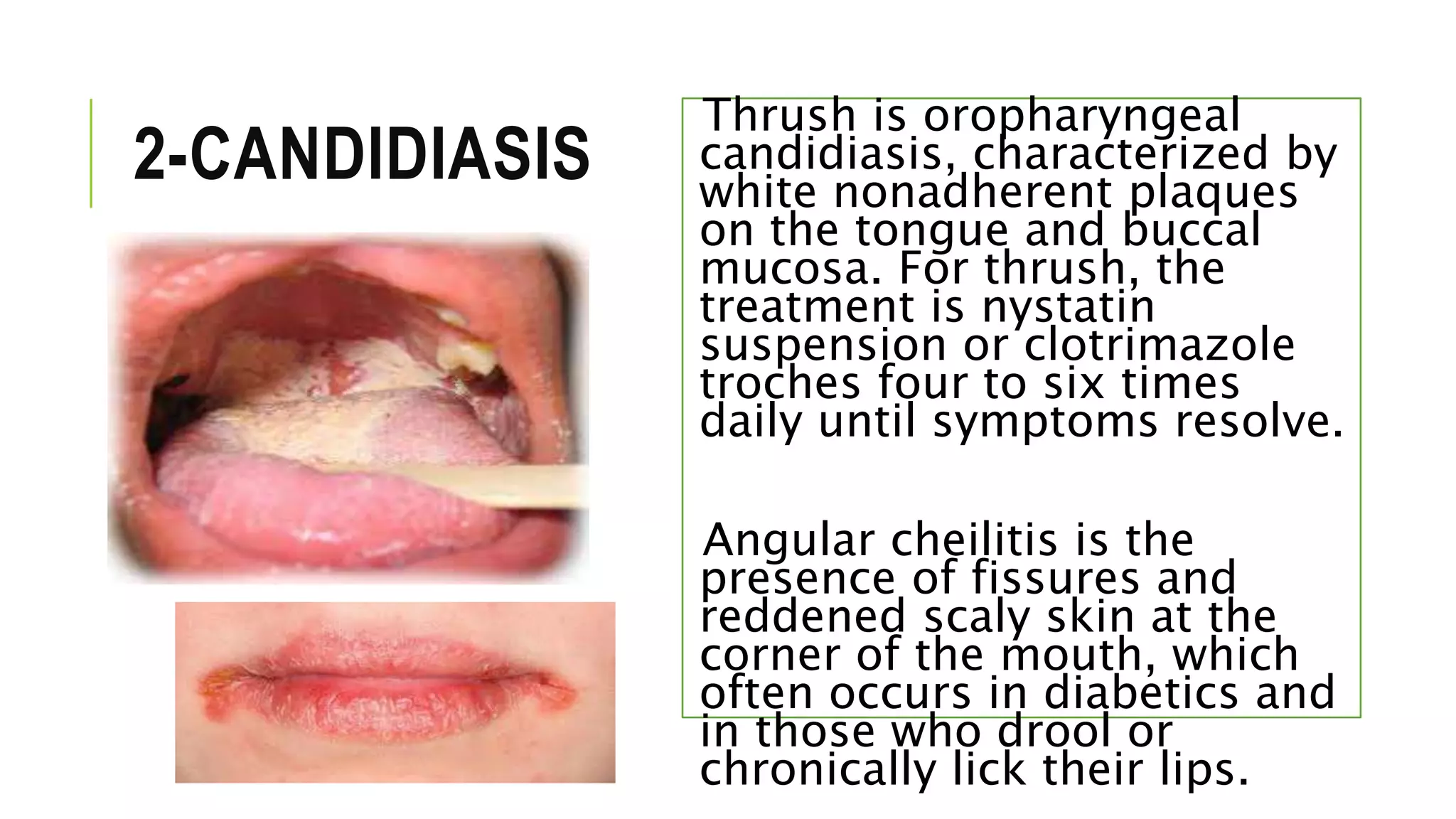
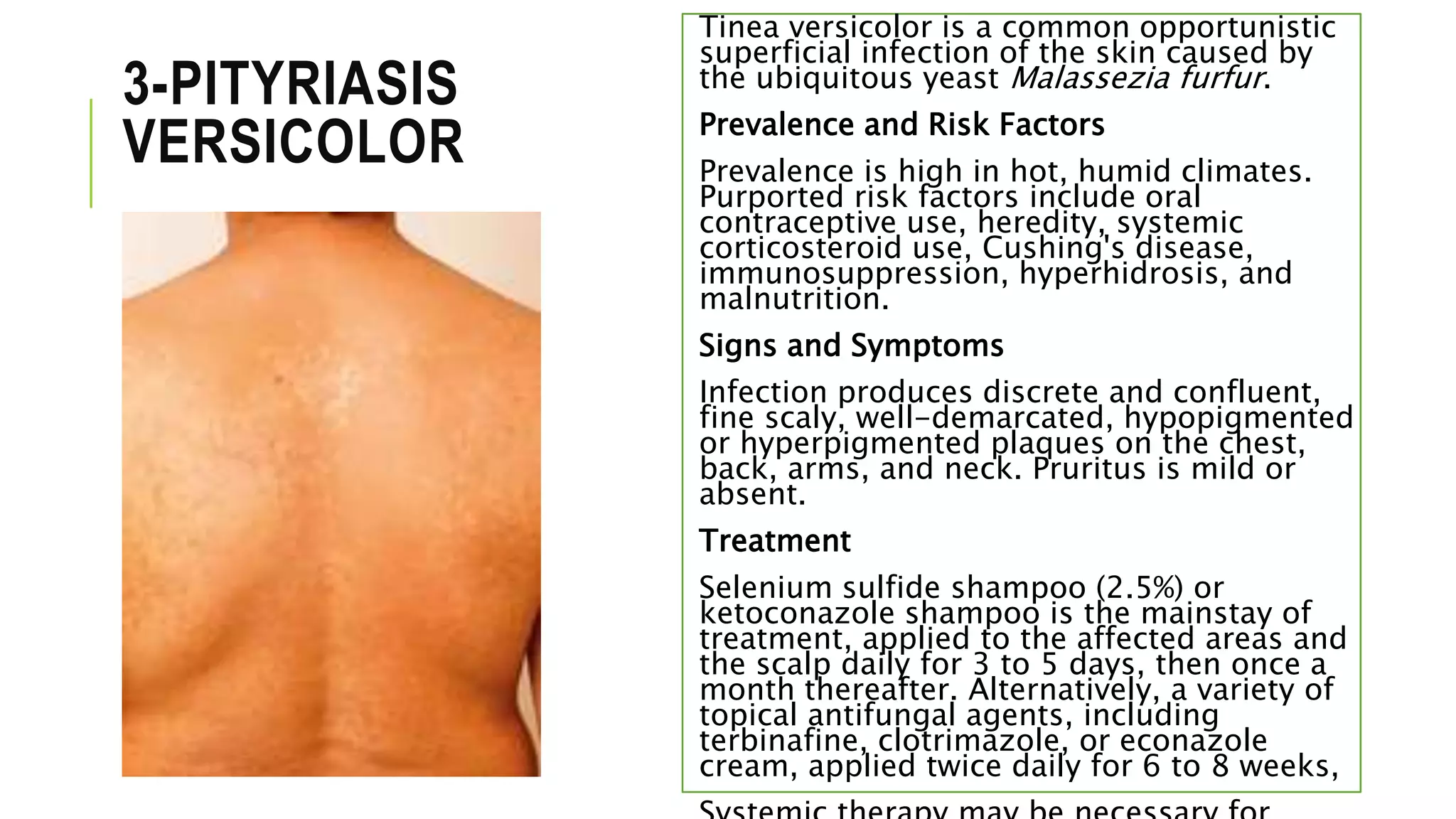
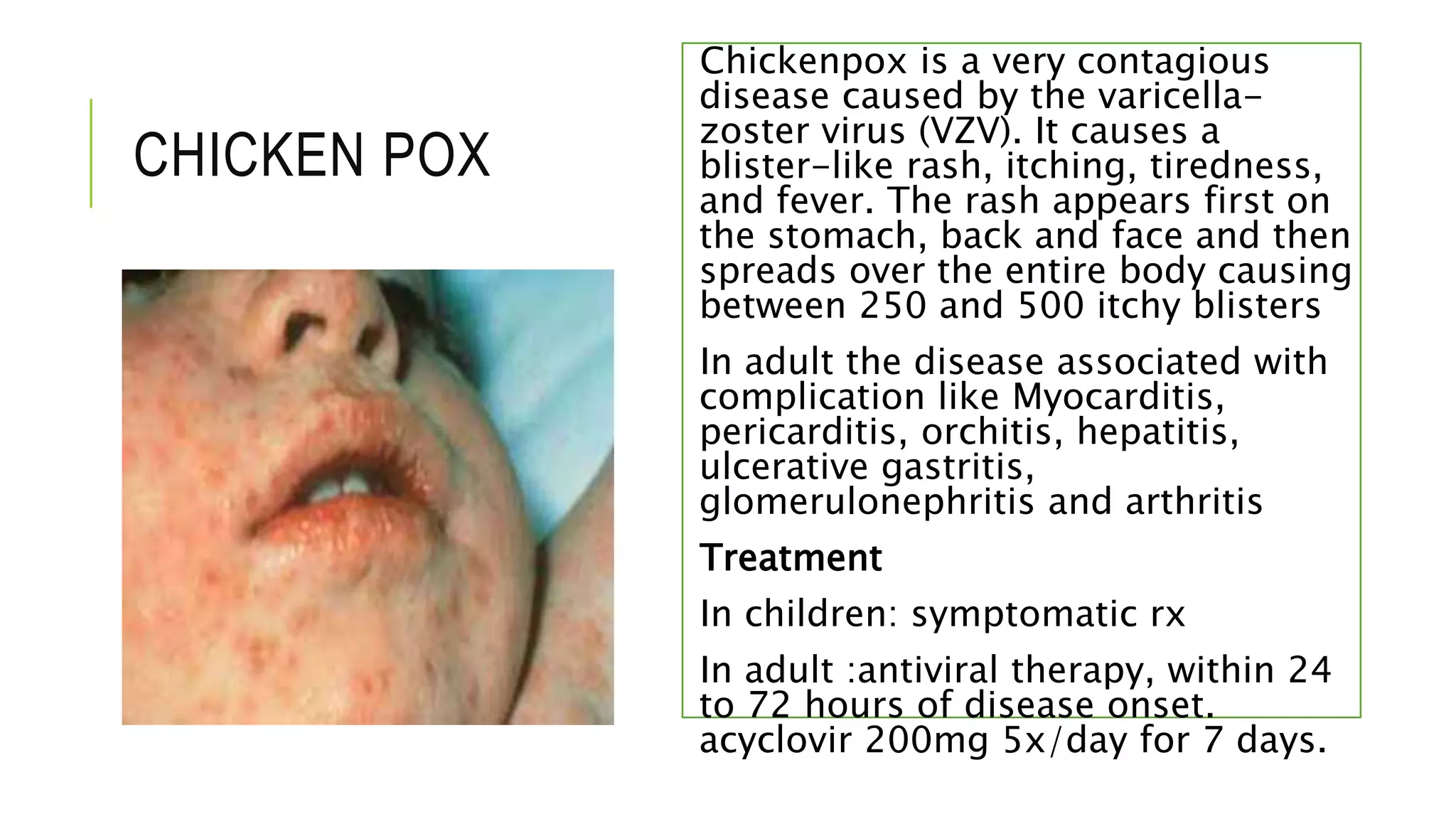
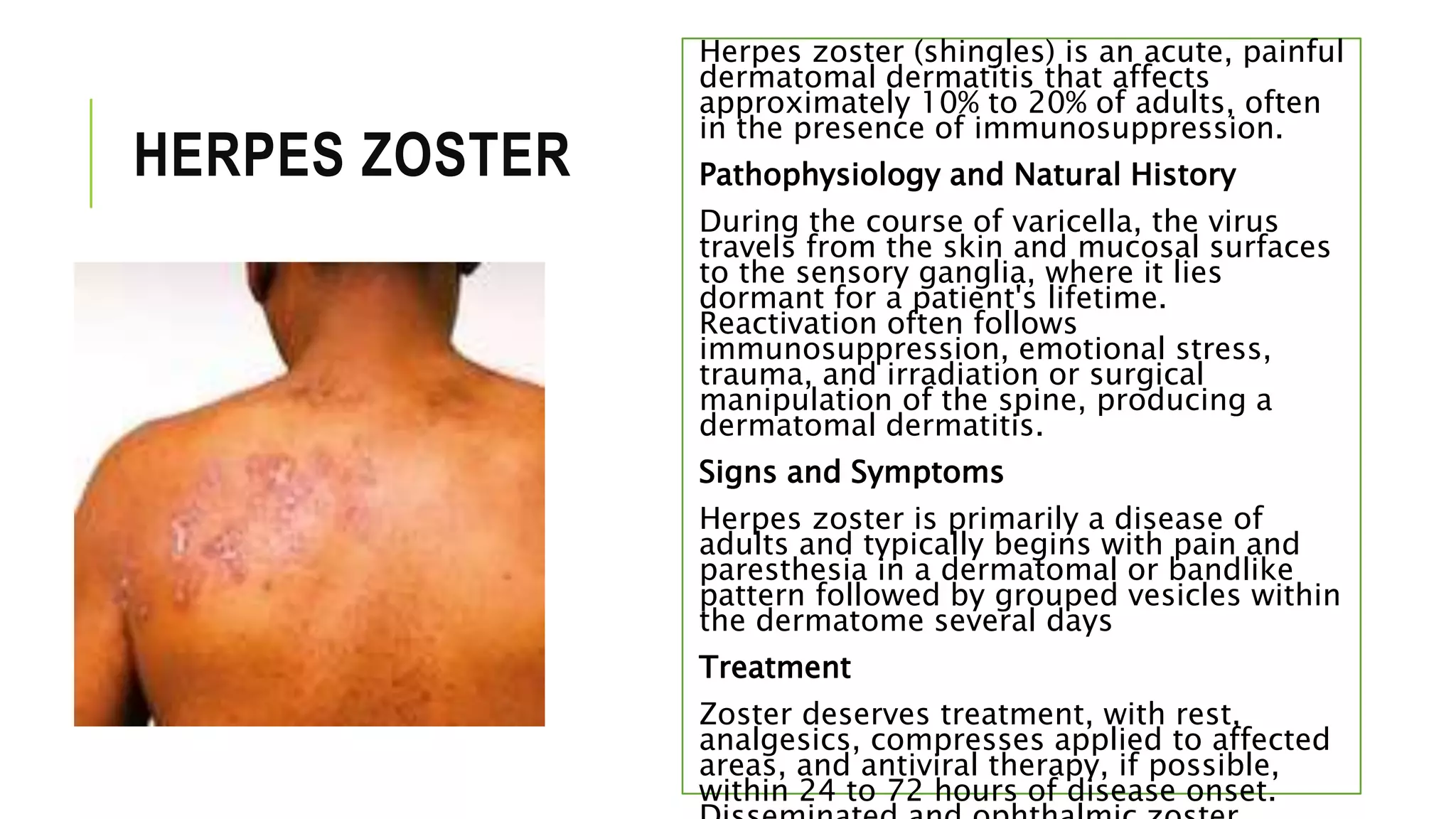
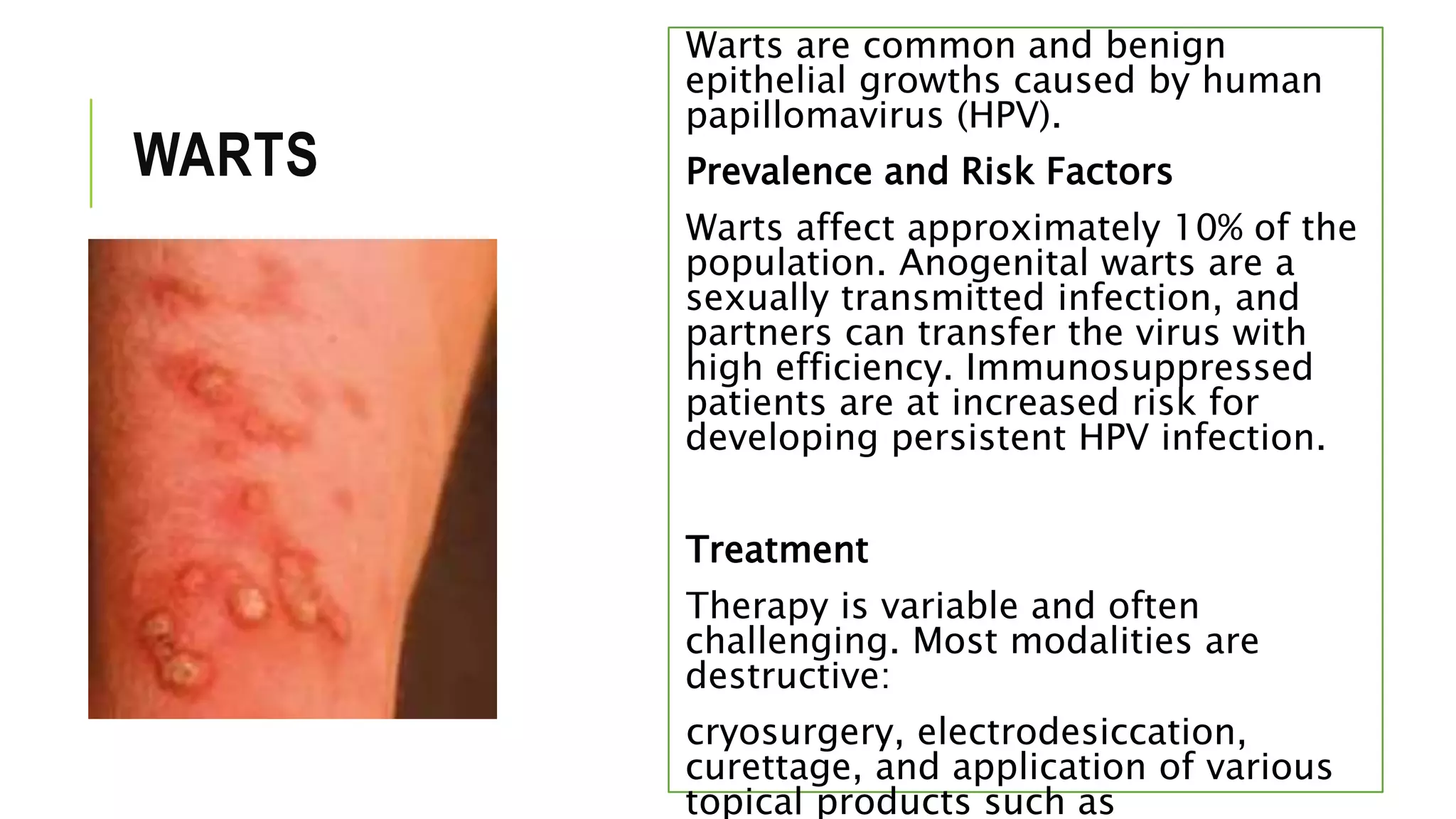
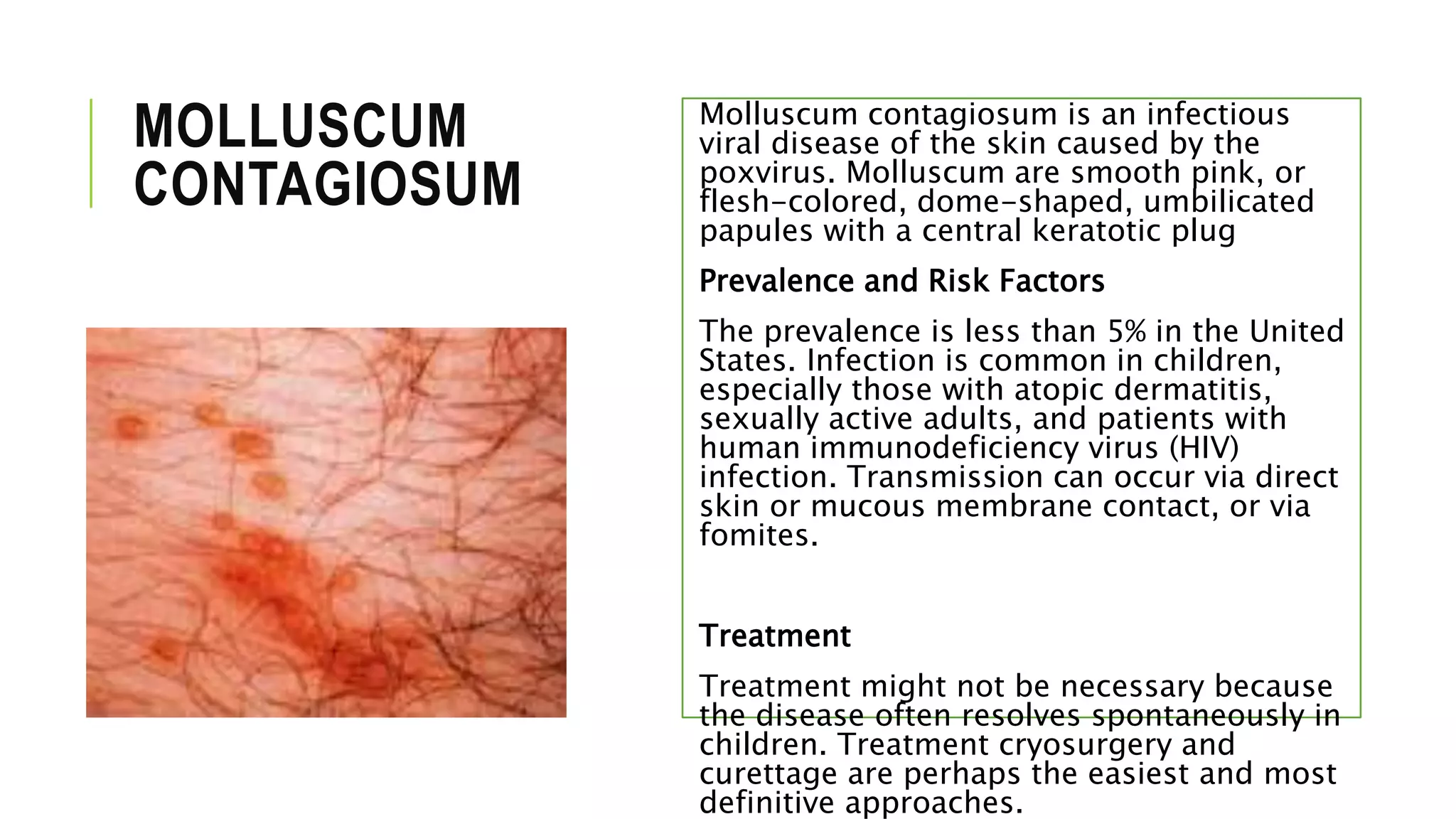
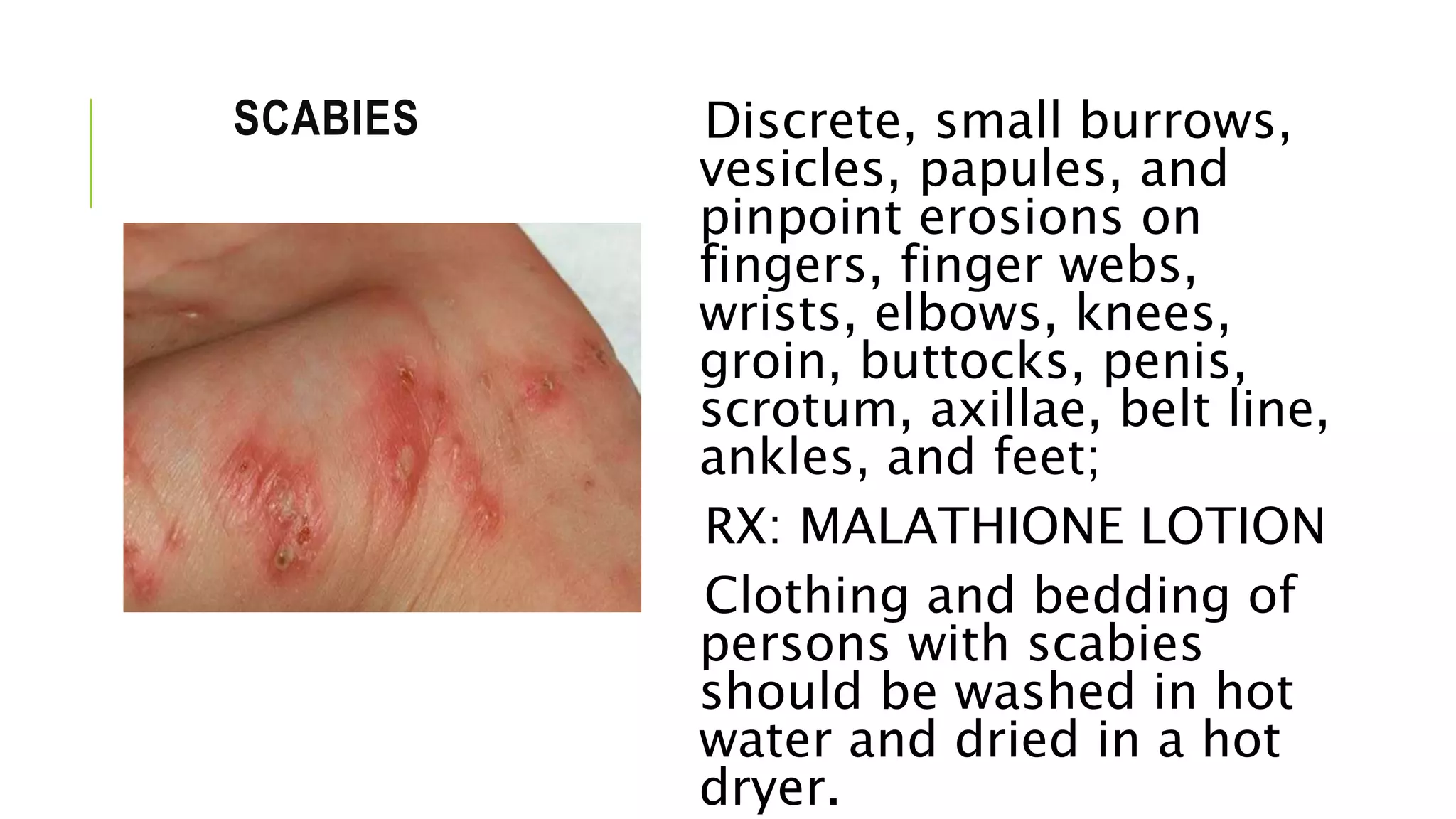
This document provides information on common skin infections, including their causes, presentations, and treatments. It discusses bacterial infections like impetigo, folliculitis, and cellulitis; viral infections like herpes, shingles, and warts; and fungal infections like ringworm and candidiasis. For each type of infection, the document describes typical signs and symptoms and recommends first-line treatment approaches, which generally involve topical or oral antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungals depending on the infecting pathogen.