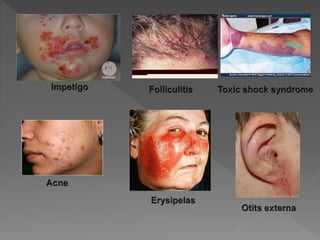
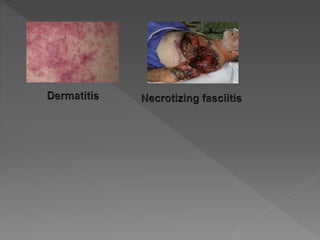
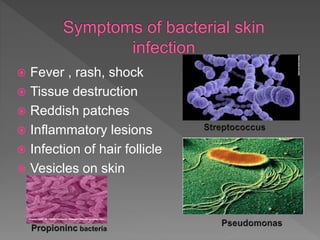
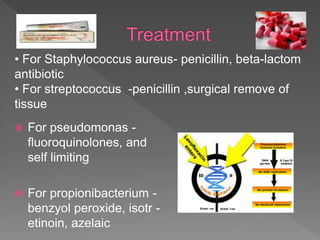
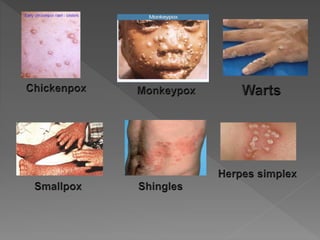
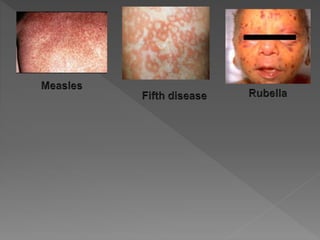
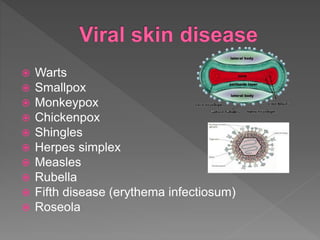
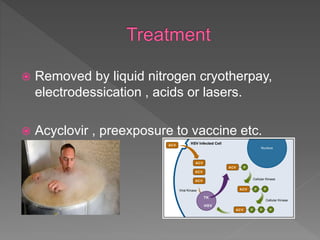
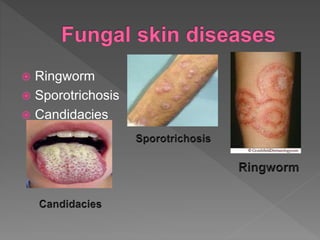
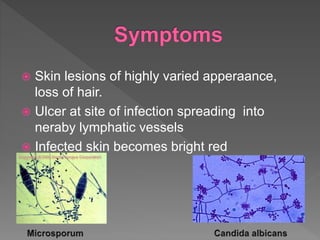
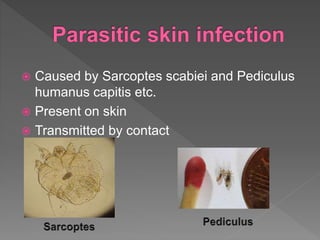
Types of skin infections include bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasitic. Common causes are Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Pseudomonas, fungi such as Microsporum and Trichophyton, and viruses like herpes simplex. Skin infections enter through breaks in the skin, hair follicles, mucous membranes, and can be transmitted via direct contact or fomites. Symptoms vary depending on the infecting pathogen but may include rashes, lesions, or pustules. Treatment involves antiviral medications for viruses, antifungals for fungi, and antibiotics for bacteria.










![Skin infection[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/skininfection1-170814065232/85/Skin-infection-1-24-320.jpg)