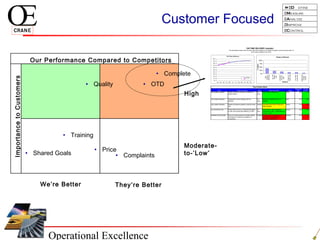
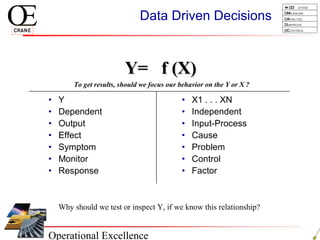
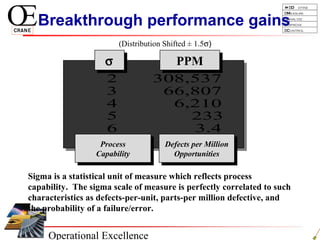
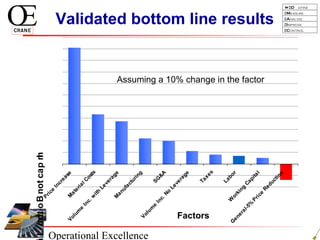
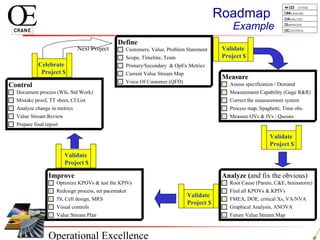
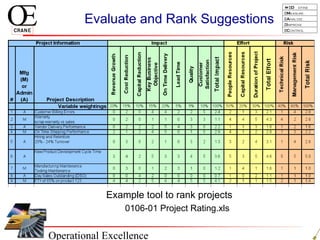
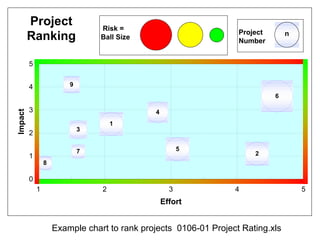
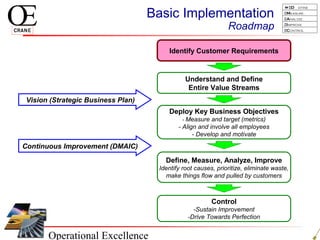
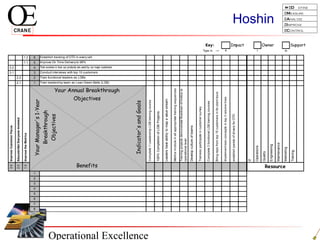
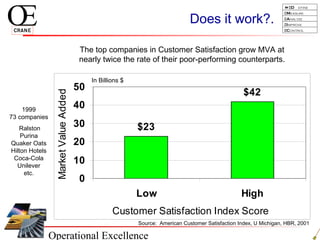
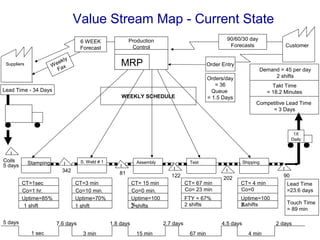
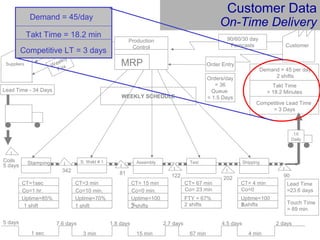
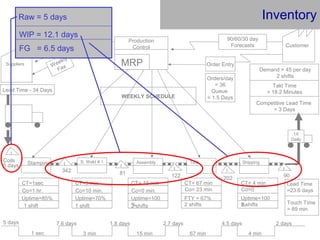
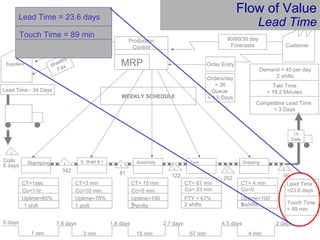
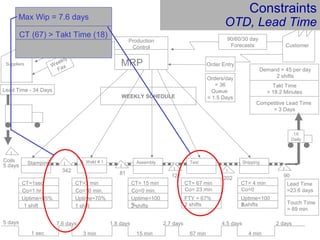
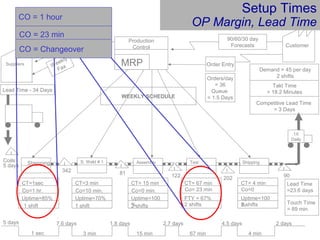
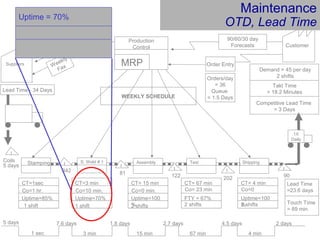
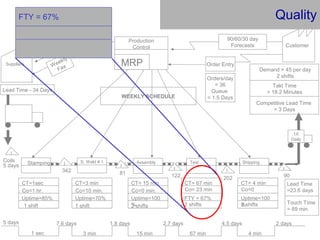
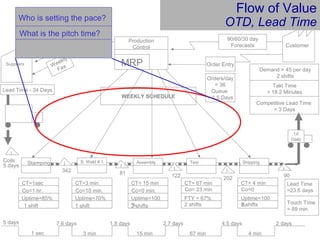
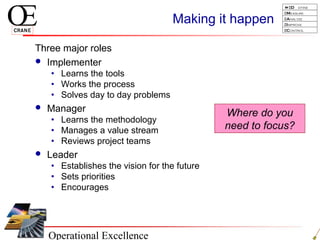
This document provides an overview of Six Sigma and operational excellence. It defines Six Sigma as a management methodology that is customer-focused, data-driven, and aims for breakthrough performance gains and validated bottom line results. The document outlines the Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control (DMAIC) methodology and how it relates to process improvement tools like Lean, Theory of Constraints, and Total Quality Management. It also provides examples of implementing a Six Sigma project, including defining the problem statement, measuring key metrics, analyzing data to identify root causes, improving the process, and controlling the results.