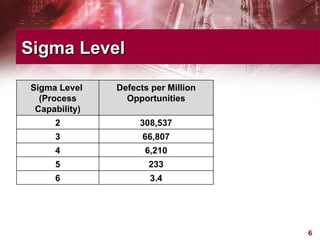
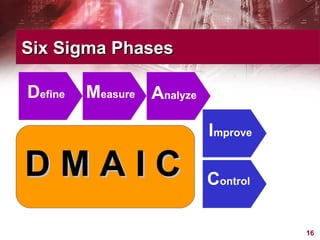
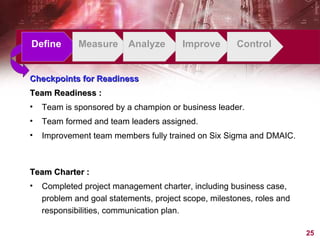
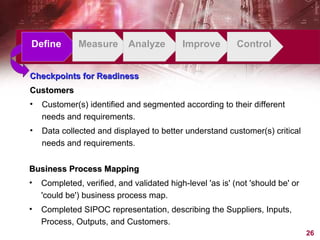
This document provides an overview of Six Sigma, including what it is, why companies use it, and the typical phases and tools involved. Six Sigma is a statistical approach to process improvement that aims for near perfect production quality. It follows the DMAIC cycle of Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control phases to reduce defects. Key tools include process mapping, design of experiments, measurement system analysis, and XY matrices. The goals are to save money by reducing costs and increasing customer satisfaction through lower defect rates.