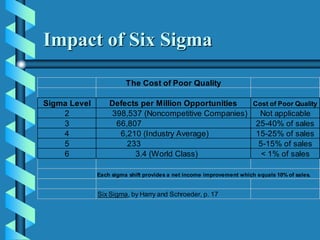
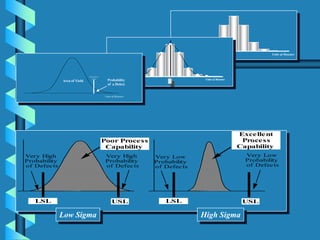
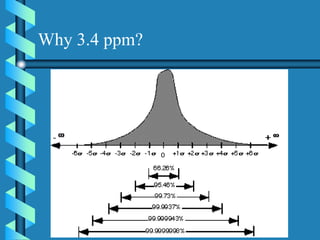
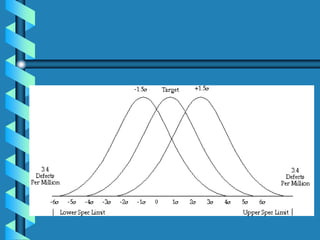
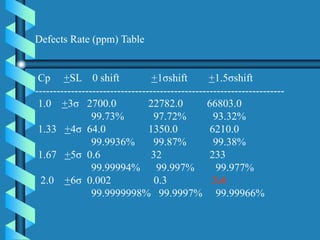
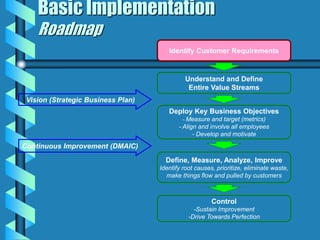
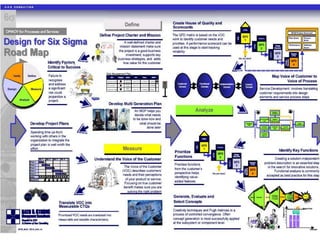
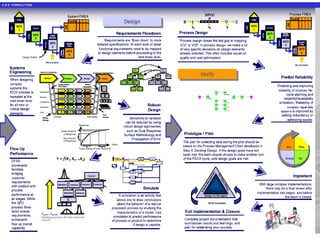
Six Sigma is a data-driven approach to process improvement that aims to reduce defects. It was introduced by Motorola in 1987 and involves defining, measuring, analyzing, improving, and controlling processes to minimize errors. The goal of Six Sigma is to operate processes with as close to zero defects as possible by reducing process variation. A Six Sigma process is one that produces only 3.4 defects per million opportunities. Key aspects include using statistical tools and methodologies, defining customer requirements, and establishing roles like Champions, Black Belts and Green Belts to lead improvement projects.