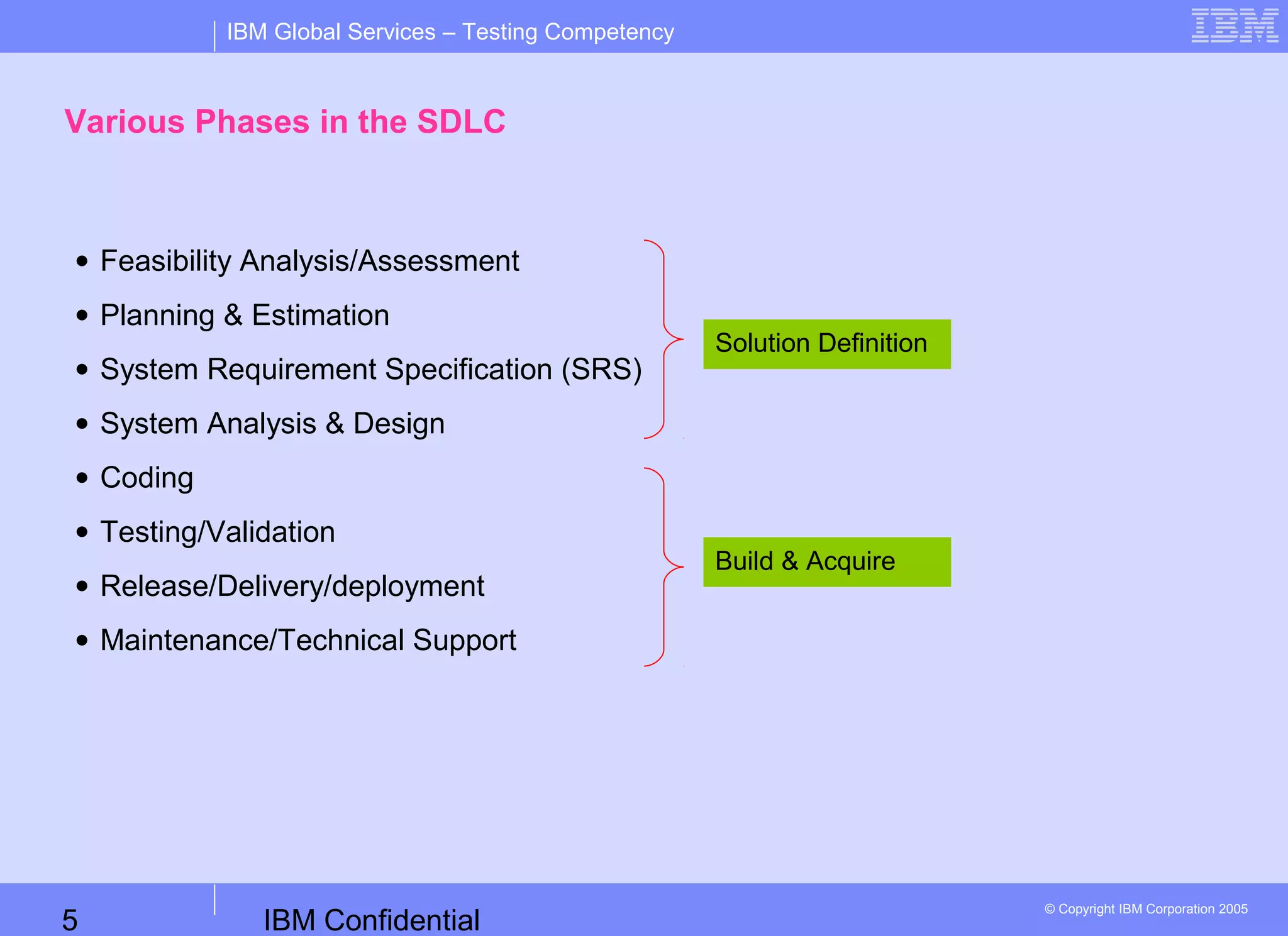
This document provides an overview of the software development life cycle (SDLC) or project life cycle (PLC). It describes the typical phases of the SDLC, including feasibility analysis, planning, requirements specification, design, coding, testing, deployment, and maintenance. For each phase, it outlines the key activities, deliverables, and responsible roles. The overall SDLC is presented as a structured process to develop software, from initial requirements through maintenance of the completed system.