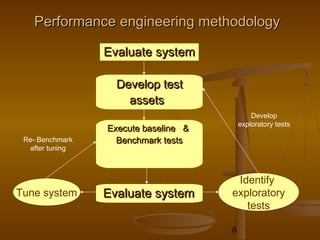
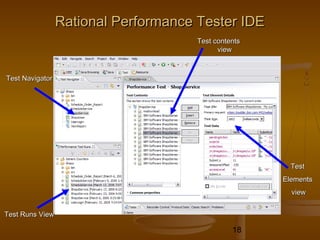
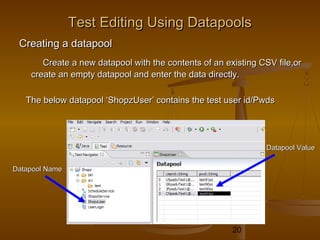
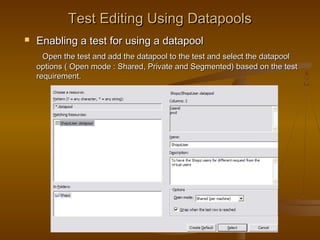
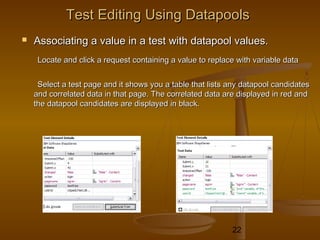
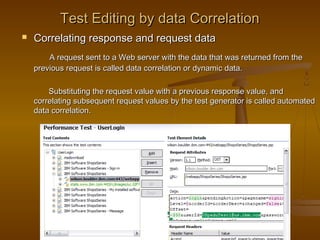
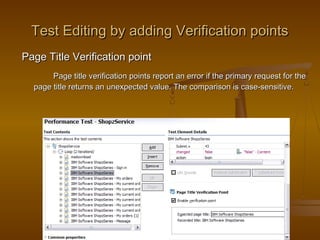
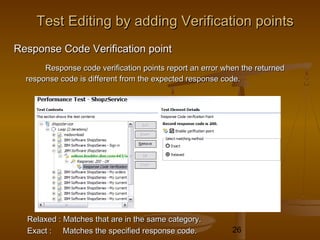
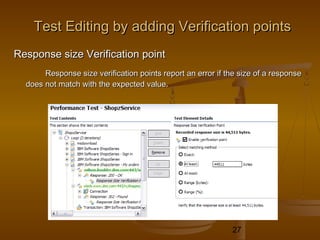
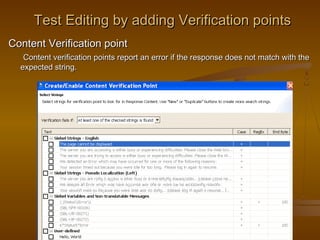
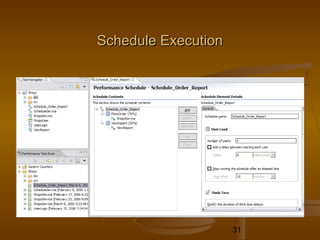
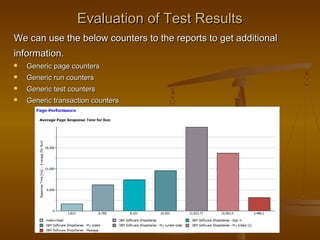
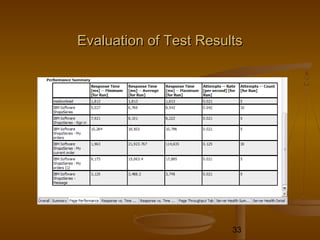
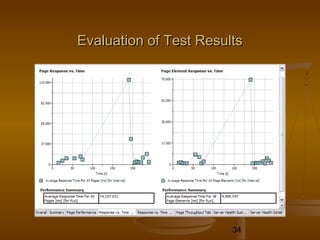
This document provides an overview of performance testing and the Rational Performance Tester tool. It discusses why performance testing is important, different types of performance testing, performance engineering methodology, performance objectives and metrics. It also provides an overview of the Rational Performance Tester tool, describing its test creation, editing, workload scheduling, execution and results evaluation capabilities.