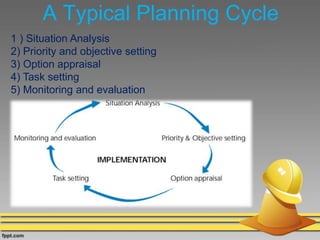
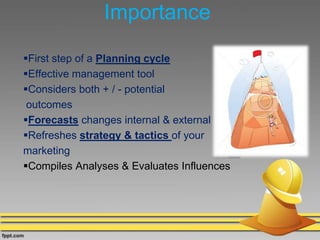
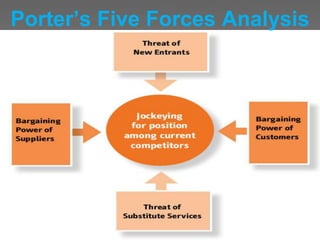
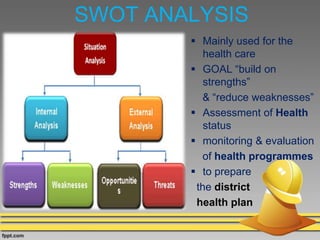
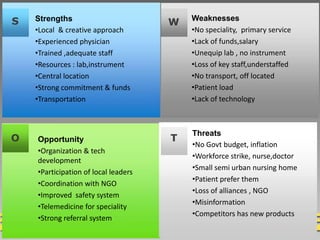
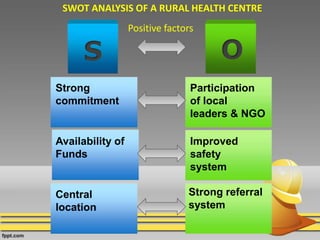
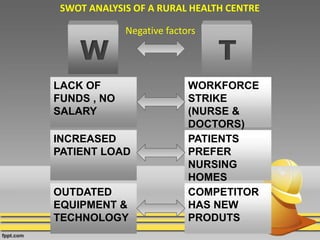
The document discusses various techniques for conducting situational analysis in healthcare. It defines situational analysis as the systematic collection and study of past and present data to identify trends and conditions that can influence business performance and strategy choices. For healthcare, situational analysis describes and analyzes the health status and services in an area to assess how well services address needs. It also prioritizes problems to inform planning. Common techniques include 5C analysis, PEST analysis, Porter's Five Forces, and SWOT analysis. The summary provides an overview of how each technique is applied to understand strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats to better plan healthcare services.