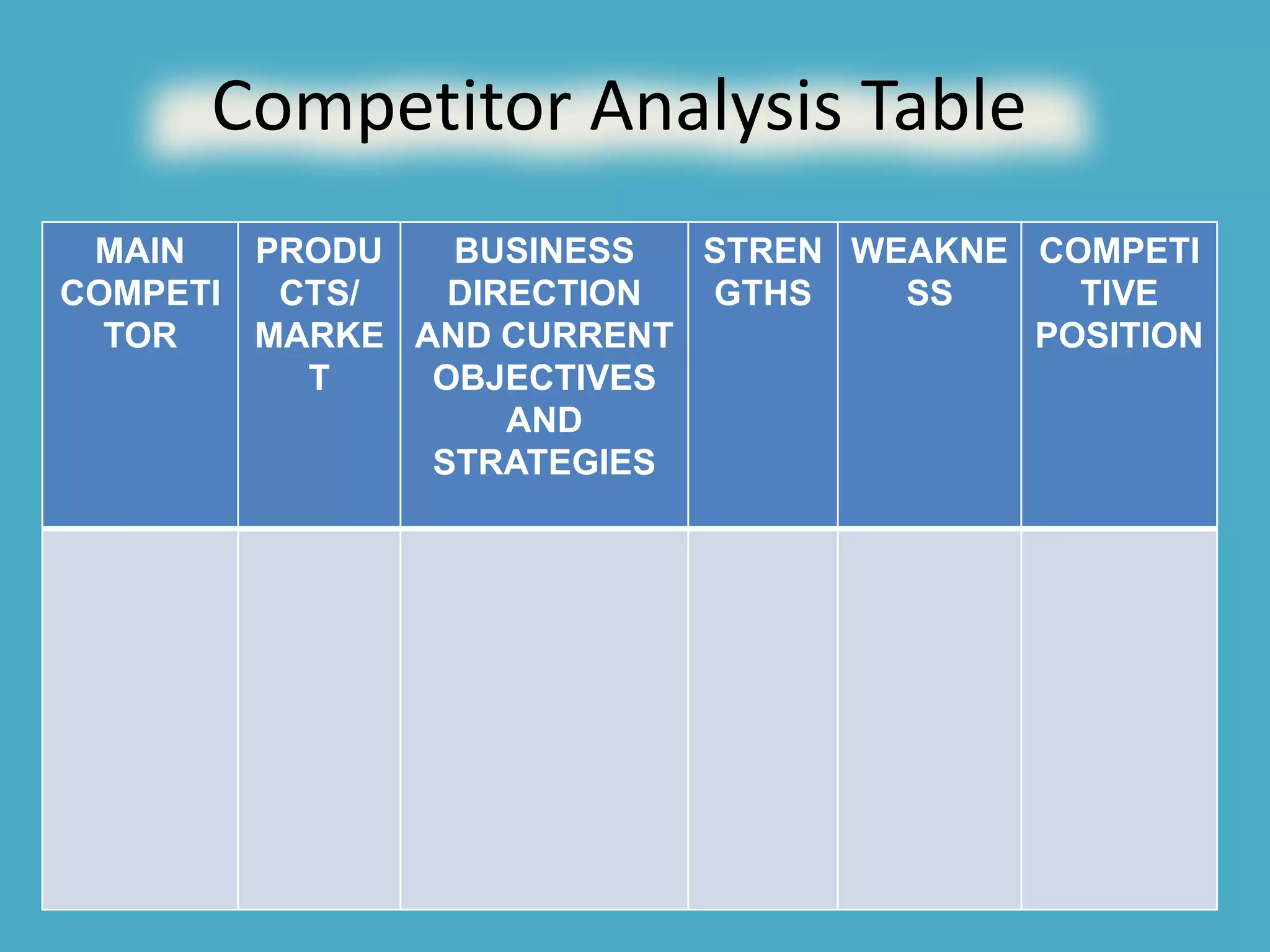
Situation analysis and market audits are essentially the same thing - a means for companies to understand how they relate to their external environment. A situation/market analysis typically includes examining the actual and potential market size, trends, customers, customer segments, and distribution channels. It also involves a SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats) analysis. SWOT draws together the key internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats identified through audits. It is a tool commonly used in auditing and strategic planning.